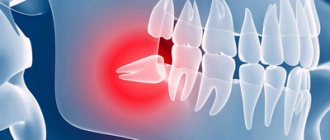
Wisdom teeth (third molars, “eights”) are rightfully considered the most problematic teeth. For a rare lucky person, their eruption proceeds safely. After all, even if the number eight has enough space in the dentition - which is rather an exception in modern realities - while passing through the gums, this large multi-tubercular tooth causes a lot of suffering to its owner. That is why in America, for example, wisdom teeth are removed prophylactically, before eruption - even during their formation.
What problems can arise from wisdom teeth?
Reasons for the formation of pus in the gums
There are several reasons for the formation of pus:
- The inflammatory process causes a disease such as periodontal disease (gingivitis).
- Periodontal disease.
- Mechanical damage to the gums.
- Chemical or thermal burn.
- Unprofessional removal of tartar, which affected the gums.
- Extensive caries causes pulpitis.
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards when performing dental procedures.
- Unsanitary oral cavity.
- Types 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Summing up the causes of purulent inflammation of the gums, we can highlight the main factor that causes this disease – the vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms.
Tooth abscess - symptoms and treatment
A tooth abscess does not go away without treatment. If you open it yourself, the pain may decrease significantly, but this does not eliminate the need for dental treatment. If the abscess is not drained, the infection can spread to the jaw tissue and other areas of the head and neck, which can lead to various complications.
Phlebitis and thrombophlebitis
When the veins are located close to the source of infection, a serious complication such as thrombophlebitis develops - inflammation of the vein with subsequent formation of a blood clot. First, the inflammatory process affects the walls of blood vessels (phlebitis), then spreads to the tissue surrounding the vein (periphlebitis) and finally covers the entire wall of the vein. Due to damage to the vessel, blood flow becomes slower, the composition of the blood changes, and clotting increases. All this contributes to the formation of a blood clot. In some cases, blood clots form in the venous sinuses of the brain.
Mediastinitis
Mediastinitis is an inflammation of the mediastinum (a complex of organs located in the chest cavity between the left and right mediastinal pleura, the posterior surface of the sternum and the thoracic spine and rib necks). Can be fatal.
The infection can penetrate into the mediastinum by contact, through the blood or lymph flow. The purulent exudate is so active that it can melt the intermuscular septa and walls of large arteries. In this regard, the infectious process spreads quickly and creates the risk of severe bleeding.
The source of the spread of infection leading to mediastinitis is usually inflammation in the area of the apex of the tooth root (sometimes in combination with infection of the tonsils or damage to the oral mucosa).
Acute or chronic sepsis
Sepsis is the most severe complication of a tooth abscess, which occurs when the immune system fails. The body cannot resist the infection, and it spreads throughout the body. Depending on the speed of onset of symptoms, sepsis can be fulminant (1-2 days), acute (5-7 days), subacute (1-2 weeks) and chronic. First of all, the functioning of the lungs is disrupted, and then other organs: liver, kidneys, etc. Subsequently, septic shock develops: blood circulation in the organ tissues slows down, and failure of several organ systems develops - multiple organ failure syndrome. When this syndrome occurs, most patients die within 2-3 days [8].
Meningeal diseases
Meningeal complications of a tooth abscess (meningitis, brain abscess, etc.) are not so common, but their mortality rate is quite high: it reaches 40-90%. Most often, these diseases arise due to the spread of infection from primary foci, the temporal region, pterygopalatine or infratemporal fossa.
Signs of pus and purulent inflammation
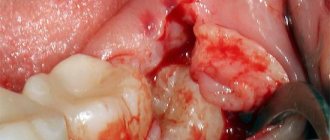
- severe pain in the area of the wisdom tooth; when you press on the gum, pus is released;
- redness of the gums and swelling;
- a large carious cavity is filled with softened soft tissue;
- colored plaque on the tooth and tartar;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- change in facial contour. It becomes asymmetrical.
What problems can arise from wisdom teeth?
- Due to the fact that the tooth is located far in the dentition, it is difficult to properly clean it of plaque and food debris. As a result, caries occurs, and then quickly becomes complicated into pulpitis. Anyone who knows pulp pain will not confuse it with anything.
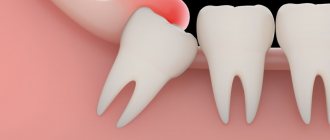
- Wisdom teeth often do not have enough space in the jaw, causing them to grow sideways or even towards the second molar (seven), permanently damaging it.
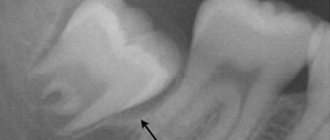
- Another complication is the formation of a cyst in the area of the erupting wisdom tooth. This cyst grows quite rapidly, which leads to rapid destruction of bone tissue. Its presence on an x-ray is an absolute indication for wisdom tooth removal.
- In the absence of space for eruption, the “figure eight” crowds and shifts adjacent teeth, causing them to become crowded and crooked in position. For this reason, the eruption of wisdom teeth can lead to treatment with braces or aligners even for a person with previously completely straight teeth.
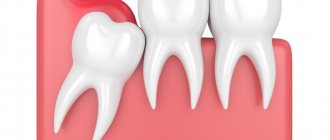
- If the wisdom tooth has not fully erupted, but is partially hidden under the gingival (mucous) hood, pericoronitis (pericoronitis) occurs. This is the name for inflammation of the gums around an under-erupted wisdom tooth.
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed after a visual examination of the oral cavity and determination of the source of pus. Treatment of purulent inflammation can be:
- In a therapeutic way with the help of medicinal drugs.
- Physiotherapeutic.
- Surgery.
If purulent discharge does not stop after a course of therapeutic treatment, the doctor will prescribe surgery. Before the operation, plaque and tartar are cleaned and the mouth is disinfected.
An injection with a local anesthetic is injected into the gum and the gum is cut. The gum mucosa is cleaned of pus. If the fistula through which pus flowed is large, then a drainage is inserted. In the postoperative period, the patient is prescribed therapeutic treatment, which includes taking antibiotics and rinsing the mouth with a 0.05% chlorhexide solution, and is prescribed a complex of vitamins and minerals.
Every day, until complete healing, the patient must come to the dentist, where he is given an antibacterial application on the gum of the wisdom tooth. The patient must strictly follow all the dentist’s recommendations for oral care and consume only liquid foods.
Pericoronitis: treatment
If you have inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth, the treatment most often consists of a dental surgeon removing the hood over the wisdom tooth. However, if severe purulent inflammation is observed, then complete excision of the hood is undesirable immediately, because this can lead to various inflammatory complications.
In case of severe purulent inflammation, the hood is first only dissected to facilitate the outflow of purulent discharge, and anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed. And the doctor will prescribe you for its complete removal after the active inflammation has subsided. Also, in some cases, the doctor may recommend immediately removing the wisdom tooth (24stoma.ru).
Excision of the hood over the wisdom tooth –
Removing the hood of a wisdom tooth involves excision of the overhanging mucous membrane over the erupting eighth tooth. Excision of the hood over the wisdom tooth leads to the elimination of conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. This minor surgical procedure is usually less traumatic, but in some cases a large amount of gum tissue must be excised.
Excision of the hood over the wisdom tooth is performed by a dental surgeon under local anesthesia. The procedure is completely painless if you see a good specialist, if the anesthesia is administered correctly and a good anesthetic is used, and not something like novocaine. Pain will appear only after anesthesia has passed (after 30 minutes), so it is worth taking an analgesic even before the pain appears.
- Hood removal: price for 2021 in an economy class clinic in Moscow, a similar service costs about 2,500 rubles. In the regions, the cost of the procedure may be 2 times lower. By the way, in the clinic at your place of residence (if you have an insurance policy and a passport), you should undergo this intervention completely free of charge.
Stages of excision of the hood –
- Conducting local anesthesia,
- Using a scalpel and surgical scissors (less commonly, a surgical laser), the dental surgeon excises the gum overhanging the tooth.
- Treating the wound with antiseptics.
- An iodoform turunda is usually placed in place of the excised hood.
- The doctor gives recommendations and schedules a re-examination.
Removing a wisdom tooth hood: video
Please note that both hood excision operations are performed with a surgical laser and not with a scalpel. Using a laser avoids bleeding, swelling and severe pain. In Russian dental clinics, lasers are practically not used (due to their absence), and only a few clinics can boast of their presence.
After the intervention, the following are prescribed:
- Antiseptic baths with chlorhexidine solution 0.05% (3-4 times a day);
- Antibiotics are not prescribed in every case;
- for pain - good tablet analgesics.
Usually this is enough for you to completely forget what wisdom tooth pericoronitis is after 4-5 days.
However, if the doctor performed the operation traumatically, the pain may last for 7-10 days. If you want to remove inflammation as quickly as possible, then after antiseptic rinses, you can additionally apply CholisalGel to the hood 2 times a day in the morning and evening (it has a pronounced analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect). Remember that if you put gauze soaked in iodoform on the wound surface, you need to remove it yourself no later than the next day. Then it itself will become a breeding ground for infection. After you take out this turunda, it may cover a little. Then it is advisable to treat the wound with a gauze swab soaked in 3% hydrogen peroxide.
Important: in some cases, the hood may form again, in which case either a repeat operation may be required, or the issue of tooth extraction will be decided. Often these teeth are in an incorrect position. An experienced doctor can quickly determine the chances of the eighth tooth taking the correct position using an x-ray and external examination of the tooth.
In what cases is it better to immediately remove a tooth with a hood -
If your gums near your wisdom tooth are inflamed, the most radical treatment method will be the removal of the 8th tooth, above which the ill-fated hood appears.
This will solve the problem permanently, but you must be prepared for the fact that the eighth teeth may have curved roots (this can be checked by taking a photo) and then removal may be difficult. Situations where deletion is the best solution to the problem -
- Firstly , when the lower jaw is insufficiently long, which means there is not enough space for the eruption of a wisdom tooth. Removal in this case will prevent the remaining teeth from being displaced by the erupting tooth, and will prevent the development of crowding of teeth in the anterior part of the lower jaw.
- Secondly , if the 8th tooth has a strong inclination towards the cheek or the seventh tooth, then it will still have to be removed sooner or later, because it will injure either the buccal mucosa or the root of the 7th tooth, respectively.
For more information about the difficult eruption of wisdom teeth, read the article: → “Features of the growth and eruption of eighth teeth”
What to do at home
If your gums are swollen and painful, and you cannot visit a doctor in the near future, you should try to reduce the inflammation and relieve the pain. For this purpose it is permissible to use:
- pain medication or NSAIDs, which can be found at the pharmacy;
- anti-inflammatory dental gel (it’s good if it contains an antibiotic);
- rinse solution with antiseptic effect.
If the pain is associated with a removable denture, then it is advisable to remove it. It is important to understand that painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs should never be taken every day. Their use should be regarded as a “one-time action” when you can’t bear the pain, and you can only see a doctor tomorrow.
It is unacceptable to use oral antibiotics to “silence” inflammation without medical advice. These are systemic drugs with a large number of side effects. Only a doctor can prescribe them during an in-person examination.
How to help yourself at home
- Painkillers . Analgin, Nimesil, Ketoral will relieve pain for a couple of hours.
- Using gels and ointments to relieve inflammation. Children's gel Kalgel, Kamistad, Cholisal will provide the desired effect.
- Decoctions of medicinal herbs . Traditional ingredients - chamomile, sage, St. John's wort. Prepare the decoction for baths (pour into mouth, do not rinse).
- Antiseptics . An aqueous solution of Chlorhexidine, Furacillin or Miramistin is used for rinsing.
To relieve inflammation, you can prepare an antiseptic solution. Mix 1 tsp. soda and salt in a glass of water, mix, pour in 2-3 drops of iodine. Rinse your mouth with liquid 2-3 times a day.
It is forbidden to apply compresses to the inflamed gums or rinse with warm or hot water. Heating the affected area leads to dangerous complications.
How to relieve wisdom tooth gum inflammation
If there are symptoms of inflammation, treatment at home is impossible. If the pain is acute and causes discomfort, you are allowed to give yourself first aid. Such actions are justified only by the impossibility of urgently visiting the dentist (for example, if the pain is tormented late at night or on a weekend). But at the first opportunity, an examination by a specialist is required, the cause is identified and appropriate therapy is prescribed.
Chlorhexidine
Signs of soft tissue infection
Pus in the gums may appear if, after treatment or tooth extraction, pathogenic microorganisms enter the soft tissues. They destroy healthy cells, which causes suppuration to develop. If treatment is not started at an early stage, pathogenic bacteria will affect deeper and deeper layers of tissue, and can enter other parts of the body through the bloodstream.
Signs of an inflammatory process in the oral cavity are:
- change in the color of the gums - they turn blue, red or dark, swell,
- aching pain when pressing on the affected area of the gum, discharge of pus and blood,
- mobility of one or more teeth - if you do not consult a dentist, they may fall out,
- bad breath.
The patient's health improves slightly when the pus comes out. However, the infectious agents continue to be present in the tissues, so without treatment, a relapse of the inflammatory process or its transition to a chronic form is possible.
Why does a tooth fester?
Let's look at why pus forms in teeth. The causes of the pathology can be:
- mechanical damage to the oral mucosa;
- dental diseases of an infectious nature (caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, periodontitis, gingivitis, etc.);
- hematogenous spread of microbes from other foci of infection in the body (sinusitis, pneumonia, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, adnexitis, etc.);
- maxillofacial injuries accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the segment;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- Iatrogenic causes associated with the introduction of bacteria during dental treatment.
There are risk factors, the presence of which increases the likelihood of pathology: smoking, decreased body defenses, hypothermia, chronic stress. Timely treatment of tooth root periodontitis and other dental diseases reduces the likelihood of an abscess.
Features of professional help
After determining the cause of inflammation, a specific method of intervention is prescribed.
- Taking medications . Antibiotics are indicated for low-grade fever, enlarged lymph nodes, and spread of inflammation to adjacent tissues.
- Operation . It is carried out in case of pericoronaritis, incorrect positioning of the tooth, acute purulent pathologies.
- Dissection of the damaged gum . If the hood above the figure eight is inflamed, it is cut. It is carried out during prolonged tooth eruption.
- Novocaine blockade . Reduced symptoms of radiating pain.
- Physiotherapeutic techniques (laser exposure). Improvement of condition. Often prescribed in combination with other methods.
Symptoms of gum abscess
The main symptom of the disease is pain. It has a different character (aching, pulsating, acute), is constant or occurs periodically under the influence of stress factors (cold, heat, sour, sweet foods). The pain is often worse when chewing. It can be local or spread to neighboring teeth, ears, eyes. In addition, with an abscess there are other clinical manifestations:
- hyperemia of soft tissues around the affected segment;
- swelling of the inflammation zone;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- foul odor;
- mobility and change in the natural color of the segment;
- the presence of an ulcer on the gum with purulent discharge;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- facial deformation due to swelling;
- hyperthermia, lethargy, sleep disturbance.