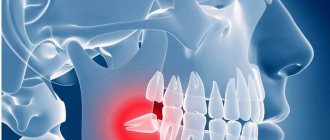
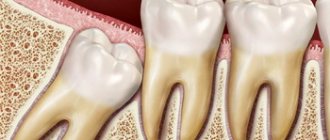
A wisdom tooth is the 8th tooth in a row (figure eight) or 3rd molar, its eruption period is 17-25 years. This is a large molar, often with a complex root system. The peculiarities of its development and growth in most cases become the cause of various dental problems. Although the structure of the figure eight is characterized as an ordinary molar, its chewing function is practically absent. If a wisdom tooth hurts, it is rarely preserved. The figure eight is destroyed early, often erupts with a carious lesion, grows at an angle or in a horizontal position.
How can you tell if your wisdom tooth hurts?
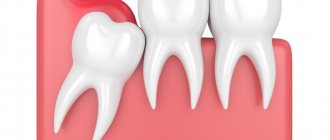
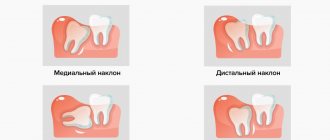
Eights erupt much later than all the other teeth in the row, when the dentofacial apparatus is fully formed, and there is simply not enough space for a beginner. Due to the density of the gums and bone tissue, eruption is quite painful, accompanied by inflammation of the gums and damage to neighboring units. Pain during wisdom tooth growth is quite specific:
- Spreads along the jaw, extends to the temple, neck, head, ear, throat;
- around the figure eight there is swelling and redness of the gum tissue;
- due to pain and sore throat, swallowing is difficult;
- numbness of the jaw and severe pain indicate that the 3rd molar is growing crookedly, injuring the jaw nerve;
- it is difficult to open your mouth, especially if the wisdom tooth grows in the opposite direction from the jaw.
Each similar symptom indicates the presence of problems with the 3rd molar. You can temporarily relieve pain when wisdom teeth erupt with an analgesic. If the figure eights grow crookedly, the bite is disturbed, the cheek or gums are injured, they form in the bone tissue without erupting to the surface or appear only partially - they must be removed.
Help with home remedies -
As we said above, only with minor discomfort and inflammation can you cope with the situation with home remedies. It is better to use analgesics from the NSAID group (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) as an anesthetic. These drugs (for example, based on ibuprofen) have not only analgesic, but also a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. If there are symptoms of inflammation of the hood above the wisdom tooth, it is necessary to use antiseptic rinses and anti-inflammatory gel applications.
- Chlorhexidine solution 0.5% - rinse 2-3 times a day for 1 minute, the solution is sold at the pharmacy ready to use. Immediately after rinsing, blot the gum above the wisdom tooth with a dry gauze swab and apply anti-inflammatory gel (it adheres better to dry mucous membranes).
- Applications of Cholisal gel are carried out 2-3 times a day, immediately after antiseptic rinsing. The gel is applied with light massaging movements to the hood area, then apply another portion of the gel to the hood without rubbing it. After application, it is not advisable to eat or rinse your mouth for 2-3 hours (you can drink). By the way, this gel not only relieves inflammation, but also has an analgesic effect.
However, keep in mind that if you have swelling of the cheek, difficulty opening your mouth, painful swallowing, suppuration from under the hood, swelling and pain in the submandibular area, you cannot self-medicate and should urgently consult a doctor. We hope that our article on the topic: How wisdom teeth are cut was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Higher prof. the author's education in surgical dentistry, 2. Based on personal experience as a dental surgeon, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Pathology of wisdom teeth eruption” (Rudenko A.), 5. “Qualified removal of third molars” ( Asanami S.).
Why can a wisdom tooth hurt?
- Non-standard eruption
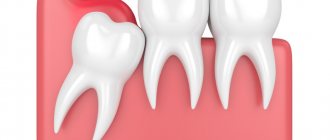
- impacted teeth formed in the jawbone, not erupted completely or partially, can be positioned horizontally or vertically. When the figure eight is placed on the side, it puts strong pressure on neighboring units, causing acute pain. - Gum hood
– dense gums can prevent teething; a “hood” of mucous tissue forms over the wisdom tooth. Bacteria and food particles begin to accumulate under it, which cannot be removed when brushing your teeth. This area is constantly injured, inflamed, and painful. An acute inflammatory process often develops into a purulent one. - The molar is rotated
around its axis - the more pronounced the rotation, the stronger the impact on the dental nerve, which causes pain in the molar itself, the adjacent unit or the entire jaw. - The cheek hurts
due to a wisdom tooth if it grows in its direction. The pain intensifies when chewing, the mucous membrane of the cheek is constantly injured and inflamed. - Caries
- the localization of the 3rd molar makes it difficult to care for it; often it is cut already with carious lesions of hard tissues, which causes pain. The sensitivity of the tooth increases, it reacts painfully to temperature and chemical stimuli. - Cyst
- due to systematic injury to the gum tissue, the molar itself, a cystic formation may form at the neck. A wisdom tooth cyst is often accompanied by serious complications - inflammation of the periodontal tissues, pericoronitis, abscess, and destruction of bone tissue.
Also, the reason that the wisdom tooth began to hurt are various dental pathologies - pulpitis, periodontitis (acute, chronic), periodontal disease. Removing the figure eight is not always justified; the doctor decides this issue individually, depending on the clinical picture. First, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out, the doctor determines the location of the roots, assesses the condition of the jaw bone, gums around the figure eight, and the entire dentofacial apparatus.
In what cases is it better to remove a tooth?
Old school dentists insist that at the first discomfort of the patient, wisdom teeth should be removed without regret. Modern dentistry is more humane and is convinced of the need for strict indications for the procedure, rightly noting that in due time “eights” may become the only possible support for dentures.
Indications for removal are:
- eruption of the third molar outside the dentition;
- threat of displacement of adjacent teeth;
- abnormal position of the crown and pressure on the second molar;
- impossibility of therapeutic treatment of the tooth.
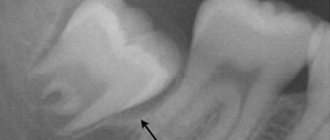
Today, at the first visit with complaints of pain caused by the “eight”, the dentist first takes an x-ray to examine the position of the roots, the shape of the tooth and its condition. And only then evaluates all the risks. With this approach, a wait-and-see tactic is increasingly being chosen: the doctor selects painkillers that will help survive the pain that is natural to the teething process. If necessary, incises the gum and cuts off the hood. And then for several months he observes how the wisdom tooth will behave.
Dentists of the Israeli school even fight for impacted wisdom teeth, pulling them out and putting them in the right place with the help of orthodontic instruments. The main thing is that there is enough space in the patient's jaw.
Is it painful to have a wisdom tooth removed?
26% of operations to remove “eights” are no different from the removal of other molars. The wisdom tooth is simply pulled out using hand forceps after local anesthesia is administered. In this case, the patient, as a rule, does not even have time to get scared, the whole procedure goes so quickly.
Another thing is difficult removal. This operation can last up to 40 minutes, during which the surgeon saws the tooth with a drill and takes it out in parts. Unfortunately, this is the only way to remove a tooth that lies horizontally, or has frozen in its development, and has not erupted, but due to its location causes constant pain.
And even in this case, modern anesthesia can completely relieve pain. The same applies to the recovery period. First, in most cases, the surgeon will stitch up the resulting wound, speeding up the healing process. Secondly, he will prescribe painkillers for the coming days. Therefore, you should not be afraid of removal - it will cause much less pain than regular exacerbations.
Indications for removal
- Pathological eruption of the figure eight (partial or complete retention, dystopia), accompanied by pain, chronic inflammation of the gums, destruction of adjacent molars, malocclusion, damage to the jaw joint and other problems;
- 3 molar has erupted outside the dentition, leading to crowding;
- inability to carry out treatment or prosthetics due to limited access to the dental unit;
- the presence of complications - cysts, granulomas, periostitis, periodontitis;
- orthodontic treatment - figure eights must be removed if they interfere with the installation of a corrective apparatus or prevent the teeth from taking the correct position when correcting the bite.
Impacted third molars
- Lack of space leads to abnormal placement of the tooth in the jaw arch. Impacted teeth can grow towards the cheek and constantly injure its mucous membrane.
- In the absence of an antagonist in the opposite jaw, they cause serious malocclusion, ultimately leading to imbalance of the masticatory muscles, pinched nerve endings, dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint and even neurological disorder.
- A tooth that does not come out of the bone often provokes the formation of a follicular cyst, which does not manifest itself for a long time. This is explained by the presence of remnants of a follicle around it, the cells of which, for as yet unknown reasons, begin to multiply. The roots of the adjacent molar often get into the lumen of the cyst. This leads to necrosis of their pulp and necessitates the treatment of pulpitis and depulpation of the tooth.
- The third molar can put pressure on the roots of the second, causing headaches, soreness in the ear or throat.
When do you need a doctor's help?
If the figure eight hurts, you should immediately consult a dentist. Consultation with a specialist is also necessary for pain of unknown etiology - squeezing, spreading over the entire jaw, occurring when chewing or opening the mouth. After examination and diagnosis, the doctor will decide what to do next with the molar. If the growth of a wisdom tooth is accompanied by swelling, redness of the gums, and acute pain, the doctor will prescribe anti-inflammatory therapy.
If eruption is difficult due to the gingival hood, an operation will be performed to excise it and drug therapy will be prescribed.
Prevention of dental diseases
Proper prevention of dental diseases should be carried out from an early age. This will help avoid many problems that lead to constant pain, acute and chronic diseases, as well as tooth loss. Doctors recommend the following methods of prevention:
- daily oral hygiene using toothpaste and rinses;
- removing plaque in the dental office when it appears;
- timely correction of bite and incorrect position of teeth;
- regular dental check-ups.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, you can undergo a comprehensive diagnosis of headaches, as well as receive recommendations for their treatment. Our center has modern equipment that allows you to quickly make an accurate diagnosis and establish the cause of pain. It is important to follow doctors’ instructions and go through all stages of treatment - this will help get rid of dental problems, correct bite and other congenital or acquired pathologies, and also prevent their further development.
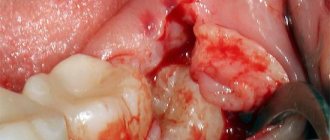
Wisdom teeth removal methods
The intervention tactics depend on the location of the 3rd molar, the degree of exposure to the gum surface, the number of roots, their confusion, and the position of adjacent teeth. Removing figure eights on the upper jaw is easier than on the lower jaw. This is due to the structure of the jaw tissue - the maxillary bone is looser, more airy, the mandibular bone is more massive and dense. Additionally, mandibular eights tend to have more tangled and developed roots.
According to the clinical picture, removal can be simple or complex. A simple extraction is performed like any other extraction - the molar is rocked with forceps and removed from the socket. Complex technology includes:
- gum incision;
- drilling a molar or sawing it into fragments;
- removing each fragment one by one;
- suturing the wound.
Stitches are removed on days 5-7
after the intervention (self-absorbable suture material can be used). The operation is performed under local anesthesia; removal under sedation (during medicinal sleep) is possible.
Treatment of wisdom teeth during pregnancy has its own nuances. Usually, the doctor limits himself to conservative therapy aimed at eliminating pain and inflammation. If possible, removal is performed after childbirth. The operation is carried out according to strict indications, if the inflammation has become purulent and threatens the health of the mother and child. For anesthesia, special drugs are used that are safe for the fetus.
At the RUTT clinic, the removal of a wisdom tooth with a complex root system and location is performed by experienced maxillofacial surgeons. This eliminates surgical complications - extensive trauma to the bone structures of the jaw, perforations, wandering root remains, postoperative fistulas, osteomyelitis, etc. Only maxillofacial surgeons have enough skills and experience to perform such interventions without complications.
Treat or remove?
Although the eruption of the extreme molars causes a lot of discomfort, these units have their significance. They can become supporting teeth for prosthetics. After losing adjacent units, figure eights retain the volume of the jawbone. If your wisdom tooth hurts, treatment is selected after diagnostic measures.
The decision to keep or remove the figure eight is made by the dentist after studying the position of the tooth, the degree of tissue destruction, the severity of symptoms, etc. If, after diagnosis, the doctor recommends removing a molar, you must follow the advice. A diseased wisdom tooth not only threatens the health of the jaw (especially the lower one) and the entire row, it is a constant source of infection in the body. Therapeutic treatment is carried out in the absence of carious complications.
Recovery after surgery
The removal of the figure eight itself is painless, since it is performed under anesthesia. But due to injury to the gums and bone socket, after the anesthetic wears off, the figure eight, or rather the periodontal tissues, hurt for several days. Painful sensations after a simple removal usually go away within 2-3 days, after a complex one they can persist for about a week. On days 2-3, swelling increases, which subsides after 2 days and the pain subsides. After the intervention, the doctor gives recommendations regarding care, nutrition, lifestyle, and prescribes drug therapy - antibiotics, painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, antihistamines.
How does this happen
The surgeon works in stages:
- Cuts the gum and separates it from the neck of the tooth.
- Using a bur or ultrasonic scalpel, the bone tissue located above the tooth is removed.
- Extracts the tooth.
- Treats the hole with an antiseptic solution.
- Places stitches on the gum.
Despite the certain complexity of the procedure, thanks to effective modern anesthesia it is almost painless. If you are worried and afraid, your doctor will suggest sedation.