– substances of natural or semi-synthetic origin that inhibit the growth of microorganisms or cause their death.
Antibiotics only affect microorganisms. Their effect does not apply to viruses or fungi. Therefore, it is advisable to use antibiotics for diseases caused by microbes. In case of viral diseases (hepatitis, influenza, etc.), their use makes no sense and can even cause harm due to side effects.
Depending on the chemical structure, antibiotics are divided into groups , for example, fluoroquinolones, penicillins, tetracyclines, macrolides, cephalosporins, etc.
Each group may contain antibiotics of different generations (for example, in the fluoroquinolone group, ciprofloxacin belongs to the first generation, levofloxacin to the second, and moxifloxacin to the third).
Basic principles of antibacterial therapy
There are certain requirements for prescribing antibiotics.
The antibiotic prescribed by the doctor must penetrate well into the tissues where there is a purulent-inflammatory process. For example, lincomycin penetrates well into bone tissue and is used for osteomyelitis, amoxiclav - into soft tissues, and can be used in the treatment of boils and erysipelas.
The antibiotic must have an inhibitory effect on the microorganism that caused the inflammation. For example, it makes no sense to use Tsifran for anaerobic infections (caused by anaerobic microorganisms), because Tsifran has no effect on them. In such a situation, Avelox is indicated - an antibiotic that acts incl. and anaerobic microorganisms.
To determine the sensitivity of the microorganism to antibiotics, a culture is taken from the wound. The difficulty is that the doctor usually receives the culture result in about 5–8 days, and an antibiotic must be prescribed immediately upon detection of microbial inflammation. In such a situation, empirical antibiotic therapy is used, the meaning of which is to prescribe an antibiotic that suppresses the most likely causative agent of the infection. For example, for a boil or carbuncle, antibiotics are prescribed that suppress Staphylococcus aureus, because It is this microorganism that most often causes suppuration in boils and carbuncles. Then, when the culture result comes, you can change the antibiotic to the one to which the microbe is sensitive in this particular case (if this is still necessary).
Antibiotics should be used to minimize the risk of side effects and complications in a given patient. For example, fluoroquinolones should not be prescribed to patients with epilepsy; aminoglycosides are not suitable for patients with hearing loss.
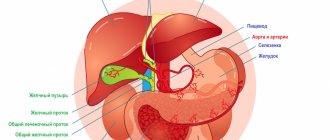
Common Causes of Stomach Problems
To choose an effective and efficient drug for the stomach, you need to determine the origin of the problem. It can be:
- chronic pathologies;
- acute conditions that cannot be managed without medical care;
- minor temporary disturbances.
Taking a more detailed look at the problem, five main reasons can be identified.
Poor nutrition
Eating products of questionable quality, fast food and an unbalanced diet can provoke periodic spasms. When you overeat, internal pressure builds up, causing heartburn. Regular consumption of legumes leads to gas formation. Foods high in toxins (melons, fruits) can cause poisoning of the body of varying severity.
Impact of stress
Stress factors can provoke acute and unexpected cramps in the stomach. The cause is extreme situations, not chronic and prolonged depression. In such situations, it is recommended to take herbal soothing tea, an antispasmodic.
Antibiotic therapy
Any medications taken for a long period of time have a positive and at the same time negative effect on a person. Even if therapy is not carried out in relation to the gastrointestinal tract, it is he who primarily suffers from side effects. Oral antibiotics enter the stomach, where they are divided into individual components that are distributed according to their intended purpose.
As a result, the microflora of the digestive system is disrupted, which causes unpleasant sensations. The most pronounced side effects are with cephalosporin and tetracycline. Even with a shortened course of treatment they:
- destroy beneficial microflora;
- provoke pH imbalance.
Probiotics can help in such cases. You can also normalize stomach acidity by regularly consuming fermented milk products.
Peptic ulcer
An intestinal or stomach ulcer occurs for reasons such as:
- chronic stress;
- bacterial infection;
- entry into the gastrointestinal tract of aggressive chemical components.
In a chronic condition, pain is almost imperceptible. It progresses during periods of exacerbation after consuming sour or spicy foods, alcohol, and various spices. In critical cases, acute pain may be accompanied by internal bleeding.
Gastritis
This is an inflammatory process that affects the gastric mucosa. The disease can be chronic with regular pain or acute with sudden attacks that quickly appear and disappear. Treatment of gastritis is recommended to begin at the earliest stages.
Routes of administration of antibiotics
- oral (by mouth), intramuscular and intravenous - should also be taken into account in outpatient practice. Thus, for patients receiving treatment at home, it is not advisable to prescribe antibiotics that require three intramuscular injections (for example, cefazolin), because such a patient will have to go to the treatment room three times a day.
Only a doctor should prescribe an antibiotic , because the use of antibiotics without indications or when there are contraindications can cause side effects and complications, and ultimately cause harm rather than benefit.
Effective broad-spectrum antibiotics
Modern antimicrobial drugs are potent, effective agents. They have a wide spectrum of action against various types of pathogenic microorganisms. If the infectious disease is severe, there is often no time to carry out bacteriological culture, in particular, this applies to coronavirus. Therefore, the doctor can decide to take antibiotics based on the available indications.
Ceftriaxone
This medication is a 3rd generation antibiotic. The drug is characterized by a strong effect on pathogenic microorganisms. When taken, the active substance quickly spreads through the systemic bloodstream, which allows you to destroy all bacteria. This minimizes the risks of developing chronic diseases.
Since the active substance can penetrate the placenta, it is not treated during pregnancy. Also a contraindication is individual intolerance to the active substance. The product has a minimal number of side effects. The main ones:
- Dyspeptic disorders.
- Fungal infection.
- Kidney inflammation.
- Allergic rash.
Amoxiclav
The effectiveness of the complex drug is guaranteed by the content of two active substances:
- Amoxicillin, which fights viral infection.
- Clavulanic acid, which inhibits bacterial synthesis.
The antibiotic is often prescribed to treat bronchitis and pneumonia. When an infection enters the bloodstream, the drug helps prevent sepsis. Side effects are observed only if the dosage is violated, these can be:
- Dyspeptic disorders.
- Inflammatory processes in the kidneys.
- Allergic reactions.
Contraindications are individual intolerance to active substances. Also, the drug is not prescribed for infectious mononucleosis and phenylketonuria. During pregnancy and lactation, it is permissible to treat with an antibiotic, but with caution: for control, you will need to conduct blood and urine tests more often.
results
- According to the data obtained, after one year the difference in the sum of the RMDQ scores between the amoxicillin group and the placebo group was −1.6 (95% CI −3.1-0.0, P = 0.04).
- Subgroup analysis also did not reveal clinically significant differences. For patients with Modic 1 changes, the difference was −2.3 (95% CI −4.2 to −0.4, P=0.02), for patients with Modic 1 changes −0.1 (95% CI −2.7-2.6, P=0.95).
- Fifty patients (56%) in the amoxicillin group had at least one adverse event, compared with 31 patients (34%) in the placebo group.
Interactions of antibiotics with other drugs
Tetracyclines cannot be combined with therapy with medications containing the following substances:
- calcium
- magnesium
- iron
- zinc
- other metal ions
The action of tetracycline drugs is negatively affected by concurrent therapy with barbiturates and carbamazepine. It should be taken into account that antibiotics from this series reduce the effectiveness of oral contraceptive pills. Treatment with macrolides and aminoglycosides should not be combined. Tetracyclines and chloramphenicol or lincomycin are not prescribed together. There are a number of other features of the interaction of antibiotics and other drugs that the attending physician should talk about, taking into account the patient’s medical history and his current diseases, in addition to inflammation of the appendages.
Treatment of antibiotic-associated diarrhea
Diarrhea that develops while taking antibiotics requires adjustment of the treatment regimen. You should not stop taking medications on your own; you should consult your doctor. Typically, the course of antibacterial therapy is interrupted or the drug is replaced with an antibiotic of a different group.
Normalization of digestive processes, intestinal motility and stool consistency are tasks that require an integrated approach. There are three general principles that are important for all people suffering from diarrhea after taking antibiotics:
- Nutrition correction: it is important to follow a diet. The diet should include crackers and rice water. It is important to reduce the amount of carbohydrates consumed as much as possible, and also give up milk, dairy products, baked goods, fresh vegetables, berries and fruits; legumes, pasta.
- Compliance with the drinking regime: it is necessary to drink at least 2 liters of water per day to replenish fluid loss during watery stools.
- Symptomatic therapy: the pathological process can be stopped with the help of medications.
Due to the fact that many sources of natural probiotics and prebiotics are prohibited for diarrhea, one of the key principles of treatment is the prescription of medications containing these components. Strict dietary restrictions require the use of probiotics and prebiotics for antibiotic-associated diarrhea: it is important to restore normal intestinal microflora to prevent the proliferation of opportunistic microorganisms.
In most cases, medication correction is indispensable. Remember that only a doctor can prescribe medications.
There are several groups of drugs that can be recommended for antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
Sorbents
Infectious and inflammatory diseases are accompanied by intoxication of the body, and in the process of antibacterial therapy, decay products of pathogenic microflora accumulate. Therefore, the doctor may prescribe enterosorbents - products that literally absorb toxins and harmful substances and remove them from the body.
Probiotics and prebiotics
It is important to address the root cause of diarrhea and restore normal intestinal microflora after taking antibiotics. For this, probiotics are used - bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, as well as prebiotics - a nutrient substrate to stimulate the growth of one's own beneficial microflora. Synbiotics include both probiotics and prebiotics and are widely used in gastroenterological practice.
If there is a pronounced shift in the microbial balance, the doctor may recommend intestinal antiseptics or bacteriophages - they are designed to prevent the growth of opportunistic microflora and help restore the number of beneficial microorganisms.
Enzymes
Enzyme replacement therapy is not the mainstay of treatment for antibiotic poisoning. However, preparations based on digestive (pancreatic, gastric, intestinal) enzymes stimulate the digestion of food, normalize intestinal motility and peristalsis and participate in the restoration of normal microflora of the large intestine.
Symptomatic therapy
Diarrhea is often accompanied by painful symptoms: flatulence, nausea, cramping and abdominal pain. You can quickly alleviate the condition with the help of medications. They are unable to cope with the main problem, but will bring temporary relief. Report your symptoms to your doctor, and he will select one or more remedies to improve your well-being:
- for increased gas formation - defoamers (drugs based on simethicone) or herbal carminatives;
- analgesics or antispasmodics for pain;
- Oral rehydration solutions are products designed to replenish normal fluid volume and prevent dehydration.
If diarrhea is accompanied by elevated body temperature, the doctor will select an antipyretic drug.
General strengthening agents
Weakened by an infectious or inflammatory disease, as well as subsequent use of antibiotics, the body may require complex recovery. A specialist can prescribe immunomodulators, vitamin-mineral complexes and restorative drugs.
Restrictions in food during diarrhea can also cause hypovitaminosis and lack of minerals. During long-term antibiotic therapy, it is necessary to discuss preventive measures with your doctor in advance.
Antidiarrheal drugs
If you cannot cope with diarrhea, your doctor may prescribe drugs from the following groups:
- eubiotics - live bacteria that are designed to restore the balance of intestinal microflora and restore normal digestive function;
- synthetic drugs based on loperamide: bind to opioid receptors of the intestinal wall and inhibit the release of mediators that stimulate intestinal motility;
- herbal preparations based on tannins.
Sorbents also have an antidiarrheal effect. They are natural and synthetic. Enterosorbents, entering the intestines, absorb toxins and harmful substances, contribute to the formation of stools and their reduction. It is important to remember that at least two hours should pass between taking sorbents and other drugs.
For severe antibiotic-associated diarrhea, antibacterial agents targeting Clostridium difficile or another infectious agent may be appropriate.
The drug “Fitomucil Sorbent Forte” can be used as an adjunct to relieve diarrhea syndrome. It contains inulin, a prebiotic that promotes the growth of normal microflora, as well as 5 types of probiotic bacteria. In addition, the drug contains psyllium, a natural component that helps reduce diarrhea and relieve intoxication, since it turns into a gel and absorbs toxins. The triple effect (enterosorbing, detoxifying and restorative) distinguishes Fitomucil Sorbent Forte from other sorbents prescribed for AAD. Live bacteria populate the intestines and not only help relieve diarrhea, but also improve the condition of the microflora that has been damaged by taking antibiotics.
However, to restore microflora it is not enough to take one drug.
Only a doctor prescribes specific therapy. It is necessary to stop taking uncontrolled medications and agree with a specialist on medications for symptomatic therapy.
Why does diarrhea occur after taking antibiotics?
The development of complications during antibacterial therapy in the form of diarrhea is associated with a decrease in beneficial microflora, which is involved in a complex of digestive processes:
- breakdown and absorption of nutrients from food;
- evacuation of the contents of the stomach and intestines;
- residual digestion of food;
- removal of toxins and metabolic products;
- secretion and absorption of water in the intestine;
- formation of feces, regulation of their excretion.
Even with standard antibacterial therapy, leading to a slight imbalance, side effects may occur in the form of disruption of intestinal function.
In addition, bacterial infections themselves can contribute to diarrhea, which is the basis for taking antibiotics. The waste products of pathogenic bacteria have a toxic effect, and stool liquefaction may be associated with an increase in body temperature. Antibiotics fight the underlying agent and root cause of the disease, and in many cases they are truly necessary. However, this group of medications can worsen the digestive system.
Contraindications to the use of antibiotics
Contraindications to the use of tetracyclines are:
- renal failure
- hypersensitivity to this medicine
- diagnosis of leukopenia
- if the patient is less than 8 years old
- while breastfeeding
- when carrying a child
Contraindications for treatment with macrolides:
- pregnancy (only some drugs)
- breastfeeding (clarithromycin and others)
Contraindications for fluoroquinolone therapy:
- gestation
- lactation
- lack of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- the appearance of allergic manifestations in response to taking the drug
- cannot be given to children