From this article you will learn:
- symptoms of wisdom tooth growth,
- what to do if your wisdom tooth is cutting out and your gums are swollen or you have a fever.
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
The wisdom tooth is located at the very end of the dentition, and therefore it is often called the “figure eight” (the serial numbers of the teeth are assigned starting from the central incisors). Thus, a person has only 4 wisdom teeth - one on each side of the upper and lower jaw. No other teeth cause us so much discomfort and pain when they begin to erupt. It most often occurs between the ages of 18 and 21, but can occur at 14 or 40 years of age.
It is interesting that the incidence of difficult wisdom teeth eruption increases with each generation. This is due to the chewing load, and the fact that people are increasingly eating too soft, overly processed food. As a result, the chewing load that the teeth transmit to the bone tissue of the jaws turns out to be insufficient, which leads to a gradual decrease in the mass and volume of the bone, including a decrease in the length of the lower jaw. As a result, with the same number of teeth, we have less and less space for their eruption.
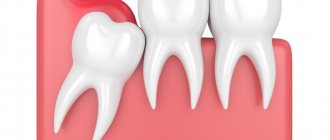
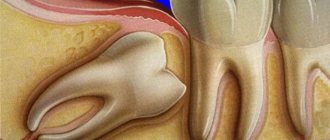
How a wisdom tooth is cut: photo, x-ray
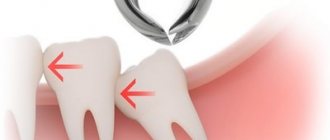
As a result, competition arises between teeth for a place in the dentition, and those teeth that erupt last are in the most disadvantageous position. Most people are familiar with the fact that when a wisdom tooth is cut, the symptoms of eruption and associated inflammation can cause a lot of inconvenience. And this is not only pain, suppuration or just felt discomfort. If there is not enough space in the dentition, the erupting wisdom teeth put pressure on the teeth in front, moving them to the center of the dentition. It is for this reason that many patients experience crowding of their front teeth over time.
A few facts about wisdom teeth –
Wisdom teeth are the only teeth in which the formation of germs does not occur during intrauterine development, but already in a born child at the age of 4-5 years.
In this case, the crown part of the wisdom tooth completes its formation at the age of 12 years, and the end of the formation of the roots usually occurs no earlier than 24 years. On the x-ray you can see a wisdom tooth whose roots have not yet completed formation (compare with the roots of the 7th tooth in front). Well, the last feature that we talked about above is that the eruption of all other teeth in the permanent dentition occurs in the period from 6 to 13 years, and only the eighth teeth usually begin to erupt no earlier than 18-21 years.
Eruption of wisdom teeth: symptoms
The duration of symptoms of the eruption of a wisdom tooth will depend on the availability of sufficient space in the dentition for its eruption, as well as on the position of the tooth in the jaw. If there is not enough space for eruption, it can only partially erupt (for example, by one or several cusps of the crown part of the tooth). The tooth can remain in this state for many years and decades - until it moves the tooth in front and makes room for itself.
All this time, you may feel periodic discomfort, especially pronounced during periods of colds. Also, the cause of difficult eruption may be the incorrect orientation of the tooth in the jaw, for example, it may begin to erupt at a strong angle to the 7th tooth in front (resting against it with the cusps of the crown part). Unfortunately, this process will be accompanied not only by negative symptoms of teething, but will also lead to the gradual destruction of the crown of the 7th tooth.
Destruction of the crown of the 7th tooth during the eruption of a wisdom tooth –
Eighth teeth that have difficulty erupting (due to horizontal position or lack of space in the dentition) are usually called impacted. Dentists most often recommend removing such teeth to prevent displacement and crowding of the front teeth, or damage to the teeth in front. You can read more about the indications for deletion/saving at the link below.
→ Indications for wisdom teeth removal
How to avoid inflammation
Preventing a disease is always easier than treating it later. To prevent the figure eight from causing discomfort, you must:
- Maintain good oral hygiene. Getting to the last molar is very difficult, often impossible. You need to use special dental brushes, an irrigator, rinses, and floss.
- Do not take hormonal medications without a doctor's prescription. If long-term treatment with hormones is planned, you need to periodically take blood tests to monitor your health.
- Eat right, eat plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables. Once or twice a year, it is advisable to take a course of vitamins and minerals selected by a therapist. Ascorbic acid is very beneficial for gums. It does not allow increased bleeding to develop.
- Stop smoking and drinking alcohol. Because of these bad habits, the condition of the oral mucosa worsens, local blood circulation is impaired, and wounds heal more slowly.
- Massage your gums every day. You can do it yourself. First you need to wash your hands, and then use your fingertips to gently massage all areas of the mouth one by one.
- Buy a new brush every three months. Give preference to high-quality and proven pastes.
It is very useful to rinse with plain warm water after each meal. This will allow you to remove food debris in a timely manner.
If the gum tissue becomes inflamed at the base of the wisdom tooth, you should immediately make an appointment with the dentist. Self-medication can be dangerous.
The main symptoms of teething are:
Traditionally, we will start with the most unpleasant symptoms that patients have to face. They arise as a result of the development of inflammation of the gums over a partially erupted wisdom tooth. Depending on the severity of the inflammation, only swelling and redness of the gums may be observed, or they may also be accompanied by suppuration and swelling of the soft tissues of the face (24stoma.ru).
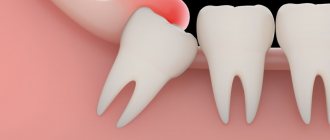
- Swelling of the gum or cheek near the wisdom tooth – swelling of the gums around a wisdom tooth usually occurs as a result of the formation of a “hood” over it. The latter is a section of the gum mucosa that hangs over the crown of the wisdom tooth (Fig. 2). Such a hood is formed when a tooth partially erupts, and dentists call its inflammation the term “pericoronitis.” Inflammation occurs because food debris and plaque accumulate between the hood and the chewing surface of the tooth, i.e. good conditions are created for the growth of bacteria.
If you have an inflammation of the hood - 1) it is necessary to determine the feasibility of saving the tooth, 2) if there are no indications for removal, the hood must be excised, as well as anti-inflammatory treatment prescribed (see below), 3) but if there is not enough space in the dentition, excision of the hood will not solve the problem completely, because After some period of time, the gums will again partially cover the crown of the wisdom tooth, and new inflammation will develop.Important : if your gums are swollen, your wisdom tooth needs to be shown to the dentist urgently. Although with minor inflammation (only swelling and redness of the hood, without suppuration), in some cases you can cope with home remedies, which we wrote about at the end of the article. If you see that pus is oozing from under the hood, or it appears when you press the hood, you need to urgently run to a dental surgeon. In some cases, suppuration of the hood of a wisdom tooth ends with the development of phlegmon of the floor of the mouth or submandibular space.
The same applies to the situation when a wisdom tooth is cut - the cheek is swollen, and not just the gums. This also indicates the development of purulent inflammation and its spread towards the soft tissues of the cheek. In all of the above situations, you cannot self-medicate, postponing a visit to a dental surgeon, because In most cases, no antiseptic rinses or antibiotics help.
- Difficulty opening the mouth is an unfavorable symptom that indicates the progression of purulent inflammation and its transition from the hood above the wisdom tooth to the masticatory muscle. If you don’t immediately consult a dentist, your mouth will open less and less (until it closes completely). As soon as this happens, it will be possible to help the patient only in a hospital setting.
- Painful swallowing is also an extremely unfavorable symptom, which indicates the spread of purulent inflammation towards the pharynx and floor of the mouth. This is a very dangerous place for localization of inflammation, because all this can result in abscesses and phlegmon of the peripharyngeal space, as well as the area of the floor of the mouth. If this happens, you will remember the experiences you receive in the hospital for the rest of your life.
- Temperature during the eruption of wisdom teeth - if a wisdom tooth is being cut - a temperature of up to 37.5 may periodically appear even without suppuration of the hood. In general, the temperature will directly depend on the severity of inflammation, and if suppuration does occur, the temperature may be higher. A slight fever and slight discomfort in the area of the erupting wisdom tooth often appear during periods of decreased immunity, hypothermia, and against the background of colds.
- Painful sensations –
pain is characteristic of any inflammatory process, including inflammation of the hood.
As inflammation develops, pain increases. However, in some cases, a sudden cessation of pain may not be due to the cessation of inflammation, but to the fact that the pus has come out of the confined space, but not out, but into the surrounding tissues. Also, pain during the eruption of wisdom teeth may be associated with a lack of space for eruption. In this case, the erupting wisdom tooth begins to make room for itself in the dentition due to the displacement of the remaining teeth. Those. it puts pressure on the seventh tooth in front, which in turn presses on the sixth molar, etc. That is, teeth shift (almost like during orthodontic intervention). Such tooth movements can also be accompanied by pain.
Pericoronitis and laser excision of the hood: video 1-2
Danger of condition
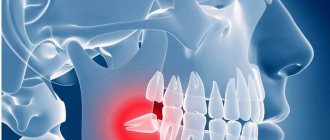
Incorrectly erupting figure eights pose a threat not only to the oral cavity, but also to the body as a whole. Untimely assistance from specialists leads to blood infection. The infiltrate that has been in the oral cavity for a long time does not find a way out and breaks out. The tissues of the neck and jaw have a loose structure, which contributes to the rapid spread of pathogenic flora from the head down. In advanced cases, the situation is life-threatening.
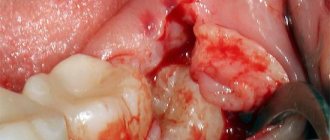
The photo shows dental phlegmon - a common complication of untimely professional dental care.
Another danger posed by an erupting wisdom tooth is malocclusion. Due to an incorrectly positioned unit, other elements in the oral cavity are also displaced. Malocclusion leads to inadequate chewing of food, distortion of diction and aesthetic defects. Insufficient grinding of food products leads to dysfunction of the digestive organs. Aesthetic defects cause prolonged depression and neurological problems in the patient.
If the figure eight grows into the cheek, then injury to the mucous membranes of the mouth is possible. Chronic non-healing ulcers appear on their surface. Microdamages cause pain to a person with every meal and conversation.
To prevent the development of consequences, you should consult a doctor 1-2 days after the onset of dangerous symptoms. The doctor will decide the future fate of the wisdom tooth after examining the oral cavity, analyzing the patient’s complaints and studying the x-ray.
If a wisdom tooth grows for a long time and hurts, then intoxication of the body is possible, manifested by nausea and increased body temperature. The patient's condition worsens and it becomes difficult for him to cope with daily activities.
Help with home remedies -
As we said above, only with minor discomfort and inflammation can you cope with the situation with home remedies. It is better to use analgesics from the NSAID group (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) as an anesthetic. These drugs (for example, based on ibuprofen) have not only analgesic, but also a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. If there are symptoms of inflammation of the hood above the wisdom tooth, it is necessary to use antiseptic rinses and anti-inflammatory gel applications.
- Chlorhexidine solution 0.5% - rinse 2-3 times a day for 1 minute, the solution is sold at the pharmacy ready to use. Immediately after rinsing, blot the gum above the wisdom tooth with a dry gauze swab and apply anti-inflammatory gel (it adheres better to dry mucous membranes).
- Applications of Cholisal gel are carried out 2-3 times a day, immediately after antiseptic rinsing. The gel is applied with light massaging movements to the hood area, then apply another portion of the gel to the hood without rubbing it. After application, it is not advisable to eat or rinse your mouth for 2-3 hours (you can drink). By the way, this gel not only relieves inflammation, but also has an analgesic effect.
However, keep in mind that if you have swelling of the cheek, difficulty opening your mouth, painful swallowing, suppuration from under the hood, swelling and pain in the submandibular area, you cannot self-medicate and should urgently consult a doctor. We hope that our article on the topic: How wisdom teeth are cut was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Higher prof. the author's education in surgical dentistry, 2. Based on personal experience as a dental surgeon, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Pathology of wisdom teeth eruption” (Rudenko A.), 5. “Qualified removal of third molars” ( Asanami S.).
Signs of inflammation
Inflammatory reactions at the base of the third molar manifest themselves as follows:
- aching or sharp pain;
- an increase in the volume of soft tissues (they seem to increase in size, become taller);
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- swelling of the cheek;
- unit mobility;
- discomfort when pressing;
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes;
- bleeding, bad breath;
- pulsation and burning in the mouth on the affected side;
- the formation of fistulas through which pus and bloody exudate come out;
- hyperthermia of the inflamed area.
Often there are no accompanying symptoms. Then the patient complains only of discomfort at the base of the figure eight.