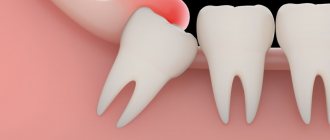
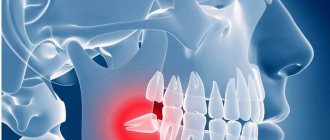
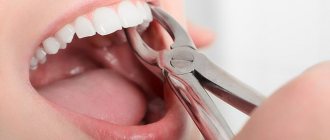
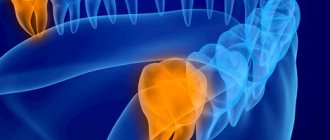
The jaw of modern man is smaller than that of his ancient ancestor. This difference is 10-12 mm. The reason for the reduction of the jaw is a change in the nutritional pattern of living people. Food has become softer, carefully processed chemically or thermally. Therefore, the need for a large and powerful jaw disappeared. Wisdom teeth, which are located outermost in the dentition, have thus lost their practical use and become rudiments. Eights usually grow up later than others - between 14 and 25 years of age or later. Hence the wisdom-related name for the third molars, as dentists call them.
Every person has two rudiments of “eights” on the upper and lower jaw, but often there is not enough space for all the rudimentary teeth, and they cause a lot of problems. Wisdom teeth often fully erupt and not all become aligned. The figure eight may remain impacted, that is, hidden under the gum or bone, or may only partially erupt. The formation of third molars takes a long time. The growth of wisdom teeth can take years. Periods of growth usually alternate with phases of rest and development.
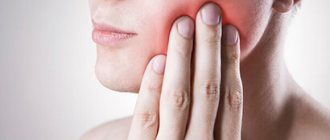
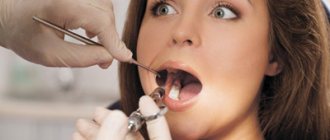
Unlike other teeth, eights do not have milk predecessors. In addition, it is very inconvenient to fully clean them due to their extremely difficult to reach position. All this leads to the development of pathological processes and difficulties during periods of their growth. Removing wisdom teeth is also considered a complex procedure with a high degree of trauma. The most common complaints that patients come to dentists with are swelling, inflammation and soreness of the gums near the “eight”. The causes of these uncomfortable phenomena are caries, pericoronitis, difficulties in the germination and eruption of wisdom teeth, as well as deep infectious and inflammatory processes in the root area and nearby tissues.
Painful eruption and incorrect position during germination
Periods of active wisdom teeth eruption often cause discomfort. Many people experience pain during this process, swelling and inflammation of the gum tissue. The reason for this manifestation is the absence of the previous milk tooth in the place where the figure eight grew. Third molars are forced to find a path of growth and break through dense bone tissue, which, given the large size of these teeth, becomes the cause of discomfort. Often, the lack of space for the normal position of the figure eight leads to its complicated germination.
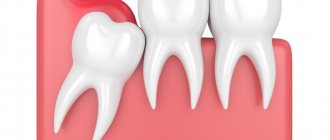
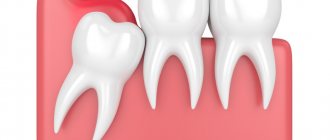
In particularly difficult cases, the tooth takes on a dystopic position. It grows in an atypical direction, not upward, but at an angle. It causes injury to neighboring teeth and displacement of the entire dentition, up to bite deformation. A wisdom tooth growing horizontally can injure the cheek, tongue and roots of its “neighbors”.
Features of wisdom tooth eruption
Wisdom teeth or third molars, also known as figure eights, are the outermost teeth in a row, located at the edges of each jaw. There are four of them in total, but often not all of them erupt, and sometimes they may not grow at all.
This will not affect the chewing functions of the jaw, and if you do not have a single eight, there is no need to sound the alarm.
The eruption of third molars is possible at any age, even after 30 years; the patient’s age does not affect the course of the process. But the direction of growth, the presence of free space in a row, the structural features of the jaw can significantly influence the process - will it be painful or will it go unnoticed, will there be a health hazard and will the growth provoke the development of inflammation.
How does pericoronitis occur?
If a wisdom tooth grows for a very long time or grows atypically, then partial gum loss above the surface of the tooth may occur. This creates a gum hood over the figure eight. This formed hood contains food debris that is very difficult to remove. They cause the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, which ultimately leads to pericoronitis. In addition, if there is an upper double figure eight, then the gingival hood is constantly injured when biting, which becomes the cause of a non-infectious inflammatory process in the gum tissue. Pericoronitis can be acute (purulent or catarrhal) or chronic. Signs of pericoronitis:
- acute pain radiating to the neck or ear;
- soreness of the gum tissue during palpation and chewing;
- inability to open your mouth;
- purulent discharge;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- specific odor from the mouth;
- temperature increase;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
If the disease has taken a chronic form, then you will not have to wait long for noticeable painful manifestations. Pericoronitis regularly recurs with all the symptoms of an acute purulent form. Complications of untreated pericoronitis can be periostitis, abscess, osteomyelitis of the jaw or phlegmon. Therefore, if signs of pericoronitis are detected, urgent dental care is needed. The specialist, taking into account the phase and form of the disease, will select the appropriate treatment. Medication or surgery may be needed.
Clinical manifestations
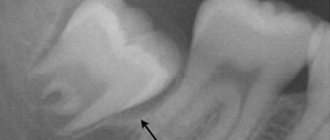
After cutting the gum, a growing molar is visible - the cause of pain and swelling
Symptoms indicate what processes are occurring and how serious the pathology is.
Problems with the germination of wisdom teeth may be the following:
- weak, aching pain indicates that the sharp edge of the tooth is pressing or cutting the gum;
- hot tissue in the area of the third molar is a sign of an inflammatory process, which is possible with a hematoma, pericoronitis or abscess;
- severe pain with sharp spasms or tingling;
- the appearance of bad breath in the presence of the above symptoms may mean the spread of alveolitis;
- swelling can be very pronounced, spreading to the cheek and even the neck, which will create certain difficulties when swallowing; a similar picture is typical for an abscess, which can result in a phlegmatic complication;
- purulent processes can contribute to the formation of a cyst - a small ball with a purulent mass on the gum.
Complications if you consult a doctor in a timely manner are unlikely, however, if you ignore the initial symptoms and go to the dentist for severe pain, then in most cases pathological processes can already develop in this situation.
A high temperature rises, the person has a fever, purulent processes form in the gums, etc. Therefore, it is advisable not to take things to extremes and visit the clinic at the first negative signs.
Infectious and inflammatory processes, caries
The hygiene of wisdom teeth is complicated by their inaccessibility, so they are prone to various dental diseases. Due to incomplete eruption, specific structure and prolonged germination, eights are predisposed to various painful conditions:
- Caries is a common disease that also occurs in impacted eights. Very often, wisdom teeth erupt with signs of crown destruction, even if they have been under the gum tissue for a long time.
- Complications of caries - periodontal cyst, pulpitis, periodontitis.
- Acute purulent-inflammatory processes - fistula, flux and abscess.
Read also
The gum under the tooth hurts
Gum inflammation
Inflamed and bleeding gums
If the pain suddenly overtakes a person, and he does not have the opportunity to visit the dentist at the moment, you can reduce the pain by following these recommendations:
- To avoid aggravating gum inflammation, do not apply warm compresses to it;
- to relieve the pain caused by a wisdom tooth, take 1-2 tablets of analgin, paracetamol or tempalgin;
- It is recommended to rinse your mouth with a weak solution of soda at room temperature;
- do not take anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics without a doctor’s recommendation;
- At the first symptoms of pericoronoritis, contact your dentist immediately.
It should be noted that all of the above methods only temporarily reduce gum inflammation caused by an erupting wisdom tooth, and in order to completely eliminate the causes of pain, the help of a professional dentist is necessary.
First aid
Before going to the dentist, you can relieve pain at home using certain pharmaceutical products.
- Drink a painkiller drug - Nimid, Nice, Analgin, Ketanov, Paracetamol, Tempalgin.
- Place the turunda on the swollen area with a special ointment or gel - Kamistad, Dentinox, Metrogyl-Denta, Cholisal.
- Rinse the mouth with antiseptic solutions - Miramistin, Chlorhexidine and Furacilin.
You can use home help methods for three days. Next, the supervision of a professional doctor is necessary. If the pain does not go away and the swelling does not go away, then you should immediately visit a dentist to find out and eliminate the cause of the painful condition. Inflammation during pericoronaritis is relieved by washing the gingival hood with pharmaceutical antiseptic solutions: Iodopharm, Potassium permanganate, Furacilin.
How long does swelling last?
The duration is directly related to the complexity of the surgical intervention. On average, after tooth extraction, swelling lasts for 3 days. Moreover, on the third day its development can reach its maximum. Then the swelling begins to gradually subside, at which time a hematoma may appear. The most important thing is to provide timely assistance to the body in treating the tumor and monitor whether the swollen area is amenable to simple therapeutic measures. However, if the healing period is prolonged, you should immediately consult your dentist.
Traditional medicine methods
Folk remedies can be auxiliary methods for eliminating inflammation in the early stages. At the initial stages they are able to give excellent results. There are herbs, decoctions and infusions of which can have anti-inflammatory, disinfectant, wound healing and antimicrobial effects. To get such a decoction, you need to pour a teaspoon of beneficial herbs with a glass of boiling water and let it brew. Next, the resulting substance is filtered and the inflamed area is rinsed 4-6 times a day. Healing plants in this situation are chamomile, lemon balm, oak bark, calendula, sage and St. John's wort. A weak soda-salt solution can also have an anti-inflammatory effect. You need to rinse your mouth with it three to five times a day.
Specialist help
In case of inflammation of the gingival tissues around the eights, the best solution is to immediately visit a dentist. The specialist will conduct an x-ray and a visual examination of the condition of the tooth and the surrounding area. Based on the examination results, competent treatment will be prescribed:
- Medication - by prescribing antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, special ointments and gels, antiseptic baths.
- Surgical - cutting the gum or gingival hood, removing the figure eight that caused the problem.
If inflammation is accompanied by unbearable acute pain and severe swelling of the gums, a specialist performs a novocaine blockade. Sometimes laser therapy is prescribed, which has an anti-inflammatory effect on the affected area.
Causes of inflammation
Inflammation of the gums near the eighth tooth is accompanied by pain and discomfort. To diagnose the disease, it is necessary to take an X-ray of the tooth and take a blood test. Based on the results of the studies, the doctor makes a decision:
- Remove the tooth.
- Prescribe therapeutic treatment.
- Or cut the gum.
The gums can become inflamed and painful, most often due to the incorrect position of the tooth, which has difficulty erupting and grows in the wrong direction relative to the dental arch. The number eight can take a very long time to erupt, up to several years.
Help with inflammation after removal
Due to their inaccessible location, full or partial impaction, and large tooth sizes, removal of third molars is often painful and traumatic. If after surgery to remove figure eights there is severe swelling, and it is accompanied by increasing pain for more than three days, this may be a sign of a disease called alveolitis. It occurs due to the entry of bone fragments, pathogenic bacteria into the wound formed after extraction, or due to the blood clot being washed out of the hole too quickly.
Signs of alveolitis are sharp pain in the wound area, redness of the gums, swelling of the extraction site, absence of a blood clot in the first week after the removal procedure, purulent discharge, fever, enlarged submandibular lymph nodes, general weakness.
It is very important to treat alveolitis immediately. This condition, without proper help, can cause tissue necrosis, abscess, phlegmon and osteomyelitis. In addition, alveolitis can lead to blood poisoning. If there are any signs of this problem, an urgent visit to the dentist is indicated.
Swelling of the gum tissue around the wisdom tooth is the first signal about the development of complex and dangerous dental diseases. Therefore, it is important not to rely on self-medication, but to consult a specialist in time.
Treatment
The treatment regimen depends on the degree of inflammation and the severity of the disease. It includes the use of:
- solutions and gels for applications;
- antiseptic compositions for rinsing;
- antibiotics;
- vasodilators.
If it’s all about the hormonal background, then it must be put in order. This process is long. Therefore, in parallel, to relieve painful symptoms, the patient can use local anti-inflammatory gels.
If caries is to blame, then urgent treatment at the dentist’s office is indicated. Often, a carious cavity in the crown of the figure eight is regarded as an indication for its removal. This is due to the difficult-to-reach location of the unit and the inability to carry out full treatment.
For pericoronitis, therapy is simple if a person consults a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease. Then antibiotics are prescribed to neutralize inflammation. If pus begins to accumulate in the tissues, the patient suffers from symptoms of general intoxication, and a simple dental operation is performed. The dental surgeon cuts the gum under local anesthesia, rinses the cavity from pus and exudate and installs a drainage tube to drain the accumulated masses. The hood covering the molar is excised so that nothing prevents the unit from erupting completely.