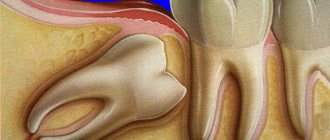
The intestine is an organ that performs an important function in the body and is involved in the process of digestion, hematopoiesis, and the production of immune cells. It is divided into two sections:
- thin;
- thick.
There are a number of provoking factors that cause inflammatory processes in this organ of an infectious and non-infectious nature. In this case, the death of epithelial cells of the intestinal mucosa occurs, a rush of blood to the foci of inflammation, a pain syndrome appears and intestinal function is disrupted, which is manifested by characteristic symptoms. What to do if the intestines are inflamed?
Symptoms of ovarian inflammation
Symptoms of this disease include:
- aching, nagging pain in the lower abdomen that occurs when the body is overcooled, as well as during menstruation;
- pain during sex.
Later, when the disease develops, the above symptoms are also added such as:
- chills;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- a sharp increase in body temperature to 38-39 ° C;
- intense pain radiating to the lower back;
- copious vaginal discharge that appears clear.
In particularly severe cases, nausea and vomiting may also occur. Chronic inflammation of the appendages contributes to increased pain sensations, as well as their range. Therefore, symptoms of adnexitis (inflammation of the ovaries) may include pain in the lower abdomen, groin, sacrum and vagina.
Chronic inflammation can be accompanied by sexual dysfunction, menstrual disorders, miscarriages and the development of ectopic pregnancy.
Causes of this disease
The infection can enter the body through sexual intercourse (during sexual intercourse from an infected partner). In this case, microorganisms enter the appendages, after which they cause an inflammatory process. This could be chlamydia, gonococci, mycoplasma or trichomonas. Those women who are promiscuous, as well as those who continue sexual activity immediately after childbirth or abortion, are susceptible to such inflammation.
Also, this disease causes the activity of microflora located in the woman’s body or entered into it through non-sexual means (activation of autoinfection). Streptococci, staphylococci, E. coli penetrate the appendages, after which they cause inflammation. As a rule, they cause other types of inflammation, but for some reasons (for example, a general decrease in immunity, the presence of other diseases in the body: dysbacteriosis, sinusitis and even ordinary caries) this microflora can become aggressive.
Why is this disease dangerous?
Inflammatory processes in the appendages can disrupt the integrity of the epithelium of the fallopian tubes, resulting in adhesions that make the fallopian tubes impassable. And this, in turn, leads to infertility.
Factors that can cause inflammation
These include:
- promiscuous sex life, lack of contraception, frequent change of partners;
- stress, poor and irregular nutrition, overwork;
- hypothermia: in no case should you neglect a hat in severe frost; you should not wear nylon stockings and tights in the cold season;
- using a heating pad when pain occurs: this will only provoke further development of inflammation;
- advanced diseases: sore throat, gastritis, untreated caries, dysbacteriosis.
What to do if symptoms appear? It should be remembered that treatment should only be carried out by an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
STIs are a fairly large group of microorganisms that are mostly conditionally dangerous. In relatively small quantities, they create a certain “ecology” in the vagina, being part of its microflora. This flora also includes microorganisms that act as orderlies. They prevent the reproduction of the above-mentioned opportunistic flora. But in case of decreased immunity, the balance is disturbed and vaginal dysbiosis subsequently develops.
A decrease in immunity occurs in the following cases: during exacerbations of chronic diseases; for acute infectious diseases (for example, influenza, ARVI); after emotional stress or against the background of chronic stress that develops over a long period of time. In addition, a decrease in immunity can occur against the background of a sharp climate change or pregnancy.
All sexually transmitted diseases are characterized by their own distinctive features, but all of them are characterized by a chronic course, as well as minor symptoms. In most cases, women do not notice the disease, and only against the background of a common cold do they notice discomfort in the genital area, increased vaginal discharge, vague periodic nagging pain in the lower abdomen and itching.
Chlamydia
What are chlamydia? These are microorganisms that parasitize the epithelial cells of the patient, destroying them.
Infection occurs during sexual contact, not necessarily genital, but also oral or anal. The incubation period averages 7 – 14 days.
There are no problems with the treatment of chlamydia. Correct selection of an antibacterial drug, its dosage, correctly calculated duration of treatment, as well as the patient’s strict compliance with all doctor’s prescriptions (which is very important) will lead to successful treatment. In most European countries, the USA and Russia, the cost of treatment for chlamydia and other hidden infections is much lower than the cost of diagnosis.
Hidden infections are chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma and trichomonas. They are always subject to mandatory treatment, and for both partners, even if only one of them gets sick.
How to treat intestinal inflammation
The method of treatment depends entirely on the etiology of the disease:
- intestinal infections are treated with antibacterial or antiprotozoal drugs, the course of treatment and dosage should be determined by a doctor;
- inflammatory processes are treated with anti-inflammatory drugs (corticosteroids, aminosalicitals);
- drugs are used in parallel to strengthen the immune system;
- if the intestinal microflora is disturbed, drugs containing beneficial bacteria or promoting their production are used.
How to relieve pain, drug treatment
No-spa will help relieve cramps in the intestines
To eliminate or reduce pain, symptomatic medications are used:
- antispasmodics – No-spa, relaxes smooth muscles, relieves pain, significantly improves the patient’s condition;
- defoamers - Espumisan, used for bloating, reduce gas formation, help reduce bubbles, facilitate their release;
- probiotics and prebiotics - used to restore microflora and improve intestinal motility, which also helps eliminate pain.
Suppositories for intestinal inflammation
Suppositories are used mainly for colitis (inflammation of the large intestine), they quickly stop the inflammatory process and relieve swelling of the intestinal walls. A suppository is inserted into the anus twice a day - morning and evening. The use of candles has a number of advantages:
- does not cause a gag reflex, as with treatment with some oral medications;
- does not have a negative effect on the gastric mucosa;
- facilitate the act of defecation;
- eliminate rectal bleeding.
Natalsid - suppositories that will relieve intestinal inflammation and relieve pain
The most common and effective suppositories for intestinal inflammation:
- Natalsid;
- Methyluracil;
- Salofalk;
- With propolis;
- Ultraproct;
- Indomethacin.
All suppositories have a healing, anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect. Before use, you must study the instructions and pay attention to contraindications.
How to relieve inflammation at home, folk remedies
A medicinal decoction of chamomile will act as an anti-inflammatory agent
Intestinal inflammation caused by poor diet, helminths or microflora disorders can be treated at home using traditional medicine recipes:
- Chamomile decoction. Has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and soothing effects. For cooking you need 1 tbsp. l. dry chamomile brew 1 tbsp. boiling water and leave for 15 minutes. Drink as tea 2 times a day.
- Mint tea. Has an antispasmodic, sedative effect, eliminates flatulence. 1 tbsp is enough. l. Brew the raw material with a glass of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. Drink without sugar twice a day.
- Tea with thyme. It has an anti-inflammatory effect, removes toxins from the body, and relieves pain. Drink during the day without sugar, after cooling until warm.
- Sage. Used for diarrhea, vomiting and nausea. A decoction of sage promotes the healing of ulcers and contains tannins. The decoction is prepared from 1 tbsp. l. sage and 3 tbsp. boiling water, infuse for 20-30 minutes and drink three times a day.
- Castor oil. The most common way to get rid of constipation. Stimulates intestinal motility, relieves inflammation. Can be purchased at the pharmacy in capsules.
- Senna grass also has a laxative effect and helps cleanse the intestines of waste and toxins. Should be used sparingly.
Complications
In men, chlamydia causes inflammation of the epididymis (epididymitis), and in women it causes cervical disease, inflammation of the epididymis, and tubal infertility. During pregnancy, chlamydia can cause serious pathology of the fetus. It also leads to Reiter's disease (severe damage to the eyes and joints).
Monitoring the results of treatment for chlamydia, as well as other hidden STIs, should be carried out no earlier than 3 weeks after stopping medication. Symptoms may persist for several weeks or even months after successful treatment. As for resuming sexual activity, this is possible only after a follow-up examination of two partners.
Ureaplasmosis
Ureaplasmas are very small microorganisms that do not have and do not need their own cell membrane. This feature allows them to penetrate the cells of the host body, so very often they are not visible to the protective cells of the immune system. Consequently, ureaplasma can exist in the human body for more than 10 years. Note that ureaplasmosis is more common among women than among men.
Ureaplasmas received this name because of their ability to break down urea - ureolysis. That is why ureaplasmosis is a urinary infection; without urea, ureaplasma cannot survive. Very often, ureaplasmosis is associated with diseases of the urinary system, chronic cystitis, urethritis and pyelonephritis.
Ureaplasma is usually transmitted sexually, but it is also possible for a child to become infected during childbirth. The incubation period is approximately 1 month. The further development of the disease depends on the body’s immunity, the presence or absence of other vaginal diseases, etc.
In most cases there are no symptoms. Sometimes patients may complain of more abundant discharge than usual, a burning sensation when urinating, discomfort in the genital area and intermittent nagging pain in the lower back and lower abdomen.
Ureaplasma and pregnancy
Ureaplasma can lead to a destructive process in the appendages and uterus, thereby contributing to the development of complications that can lead to pathologies during pregnancy. That is why during this period it is imperative to get tested for this infection, and if it is confirmed, then undergo treatment.
Ureaplasma does not cause malformations in the fetus. In most cases, infection of the baby occurs during childbirth during the passage of the fetus through the infected birth canal. In addition, ureaplasmosis can cause miscarriage, premature birth, threatened miscarriage and endometritis (one of the postpartum complications).
Treatment during pregnancy is most often carried out at 18-20 weeks.
Treatment of ureaplasmosis
Treatment of this disease must be comprehensive and long-term. First of all, antibacterial drugs are prescribed, but taking antibiotics alone is not enough, since ureaplasma can easily adapt to the effects of antibiotics during treatment. Also used in treatment are drugs that increase general and local immunity; antifungal drugs, since antibiotics can cause thrush. The drug complex also includes drugs that can protect the intestines from the effects of antibiotics.
As for the need to treat a partner if he does not have an infection, this is a controversial opinion. This issue must be resolved by the attending physician and the partners themselves.
During pregnancy, the choice of drugs is limited. Only those drugs that are approved during this period can be used. Antibiotics include Vilprafen, Rovamycin, and Erythromycin.
Gardnerellosis
The disease is not an STD. It is caused by gardnerella vaginalis, and, in fact, gardnerella is a manifestation of vaginal dysbiosis. That is, this is not inflammation in the vagina. That is why this disease is also called bacterial vaginosis.
Unlike other infections, with gardnerellosis the symptoms are pronounced and specific. Symptoms include heavy, thin vaginal discharge that is white or yellowish in color and has a very unpleasant odor, similar to rotten fish. This odor may become stronger during and after menstruation, as well as after sexual intercourse. This disease causes discomfort and burning in the external genital area.
During a gynecological examination, an experienced doctor will be able to immediately make a diagnosis, since the discharge has a slightly foamy characteristic appearance. In some cases, there may be no symptoms, so gardnerella can only be detected during an examination.
Gardnerella is located directly in the vagina. This infection most often does not penetrate further, therefore there are no symptoms such as, for example, pain in the lower abdomen.
Gardnerella and pregnancy
Gardnerella can cause a lot of trouble during pregnancy. It is possible, although very rare, that intrauterine infection may occur. Gardnerella can also cause inflammation of the uterus after childbirth or abortion. That is why bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy must be treated immediately when it is detected.
Gardnerella usually appears in a simple smear on the flora. The PCR diagnostic method is also used to identify them.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out in 2 stages. First, the infection is destroyed, and then the microflora in the vagina is restored.
At the 1st stage, drugs such as flagyl, fasigin, clindamycin, trichopolum are used.
The 2nd stage is longer, it can last 1 month or even more. Here you need to be patient, because... If the microflora is not restored, the disease will return again. Sexual activity during the treatment period is possible, but only if the partners use a condom.
In men, gardnerella “takes root” and does not develop, so treatment of sexual partners is not required.
Intestinal inflammation during pregnancy
Espumisan will reduce bloating
Most often, intestinal inflammation during pregnancy develops against the background of changes in hormonal balance. Fermentation may be disrupted, food is not processed in the required volume and causes flatulence, colic, and bowel dysfunction.
In this case, a pregnant woman should consult a doctor, but at home you can use:
- Pancreatin is a pancreatic enzyme preparation that improves digestion;
- Espumisan is an antifoam agent that reduces gas formation and bloating;
- Probiotics – for microflora disturbances during pregnancy.
All other reasons require a thorough examination by a doctor. Infectious diseases are treated with antibiotics, and during pregnancy, antibacterial therapy should be carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor.
Human papillomavirus
Recently, this infection has received the attention of most researchers, as well as practitioners. This is due to the fact that the ability of this infection to cause cancer of the genital organs in both women and men has been proven.
Human papillomavirus infection, like many other STDs, very often occurs without symptoms, thereby contributing to its even greater spread in the human body. Not all cases of HPV cause cancer, but almost every case of cancer is caused by HPV.
Currently, more than 120 types of HPV have been identified, 34 of which affect the genitals, as well as the perineal area. Moreover, each virus is responsible only for its own “area”.
How does a person become infected with this virus?
HPV can be transmitted during direct contact of mucous membranes and skin when:
- traditional sexual intercourse (the main route of transmission of infection);
- non-traditional sexual intercourse (anal or homosexual sex). It is also believed that HPV transmission is possible through oral-genital contact;
- during childbirth during the passage of the fetus through the infected genital tract of the mother;
- The household route of transmission is also possible: through hands, bath accessories, dirty clothes.
Factors that provoke the development of HPV
These factors include:
- promiscuity, early sexual activity, a large number of partners;
- repeated abortions;
- the presence of other STDs (chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma);
- smoking;
- chronic diseases of the genital organs (inflammation of the uterus, appendages, vagina);
- anal sex;
- aggravated medical history (cervical cancer in close relatives).
The incubation period ranges from 1 to 8 months. People aged 17-26 years are most often susceptible to HPV infection, which is associated with increased sexual activity at this age. But this does not mean that older people cannot be infected.
Sometimes there are cases that the virus leaves the body on its own, without treatment. This happens most often in young people over 30 years old. If the virus enters the body after 35 years, then the likelihood that it will leave the body on its own is, unfortunately, small.
Forms of infection
This infection can occur in 3 forms:
- Latent form. It is asymptomatic. In this case, there are no changes or abnormalities, but the infected partner can transmit the infection through sexual contact.
- Subclinical form. Patients may have the following symptoms: vaginal discharge, a feeling of discomfort and dryness in the external genital area, which intensifies after sexual intercourse, itching, burning. At the same time, an ordinary gynecological examination will not reveal changes in the genital area. They can only be detected through a detailed examination (for example, colposcopy).
- Clinical form. Finally, the most common symptom of HPV is condylomas. This is a type of wart that is located on the mucous membrane of the genital organs, namely: at the entrance to the vagina, in the area of the clitoris, anus, urethra, and on the walls of the vagina. Occasionally they can be found on the skin of the perineum and labia.
Condylomas are skin growths that resemble a cockscomb in appearance. They can be on a stem or on a base. The color of condylomas is no different from the color of the surrounding tissues.
HPV is detected using the PCR diagnostic method.
Treatment
Condylomas are removed chemically (using various medications), using a laser, and also by cryodestruction. Then treatment is carried out aimed at increasing the body's immunity. In this case, vaginal and rectal suppositories are prescribed for local immunity and various drugs that stimulate general immunity - tablets or intramuscular injection.
It is also necessary to screen your partner for this disease. Sexual intercourse during treatment is possible only with the use of a condom.
Treatment for inflammation of the sciatic nerve
At the first painful sensation, you should immediately contact a neurologist. Otherwise, the pain will only intensify and lead to complications. In the hospital, the specialist first stops the inflammation with painkillers. Afterwards, the doctor will begin to eliminate the cause of the disease. To diagnose the disease, a specialist will examine the damaged area of the body. Afterwards, the patient is sent for physiotherapeutic procedures - magnetic therapy, electrophoresis or UHF.
If the inflammation was caused by infectious pathogens, the patient is indicated for antibacterial and antiviral treatment of the affected area. For sciatica caused by a hernia, doctors resort to surgery using microdiscectomy.
Also, to eliminate the cause of inflammation, a neurologist may send you to other specialists, for example, a gynecologist, oncologist or urologist. It all depends on the cause of the disease, including the recovery period. However, in all cases, the patient is shown complete rest until the acute pain disappears.