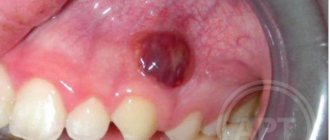
If the dental crown breaks almost at the very root, there is a risk of it becoming overgrown with gum tissue. A tooth can break for various reasons - mechanical damage, trauma, for example, a strong blow, carious process, etc. Small fragments gradually come out on their own, but the root remains inside the gum. Gum tissue grows, gradually covering the rest of the tooth.
An overgrown root may not bother the patient for a long time. As the pathological process develops, painful sensations appear, the gums become inflamed and swollen. Patients often complain of pain when chewing.
An overgrown root must be removed, as overgrowth is quite dangerous and can cause serious problems:
- Dental disorder.
- Damage to adjacent teeth.
- Inflammation of the gums.
If a crown breaks off, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. The specialist will assess the complexity of the problem and select a treatment program.
If the tooth is overgrown and the pathological process has spread to the surrounding tissues, the patient will face a rather complicated operation with a long recovery period. The wound may take a long time to heal. A timely visit to the clinic will help avoid this.
Hyperplasia as the main cause of pathology development
Why does this phenomenon occur when gums grow on a tooth? Most often this is due to the proliferation and enlargement of its cells. Scientifically, this process is called hypertrophy or hyperplasia (i.e. proliferation and increase in volume of tissue). The problem in most cases occurs against the background of an inflammatory process occurring in the oral cavity or metabolic disorders and hormonal imbalances in the body.
On a note! Hyperplasia or hypertrophy is a pathology in which soft tissue cells begin to grow uncontrollably, and the gums themselves can become inflamed and increase in size, they can begin to “crawl” onto the crown, partially or even completely (in the most advanced situations) block it.
Classification
Depending on the prevalence of the pathological process, local (affects a small area of the dentition) and generalized (involves the entire dentition) form of the disease is distinguished.
The degree of tissue deviation from the normal position makes it possible to distinguish between mild, moderate and severe degrees of the disease. Some dentists also distinguish between physiological (associated with natural processes in the body or the anatomical features of its structure) and symptomatic forms of pathology. In the second case, it is a consequence of other dental diseases, for example, gingivitis, periodontitis, and malocclusion.
Prerequisites for the development of hyperplasia
Various reasons can serve as prerequisites for accelerated and enhanced cell division:
- excessive accumulation of hard tartar and bacterial plaque above and below the gums,
- malocclusion: in such a situation, some teeth and, accordingly, the soft tissues and mucous membrane that surrounds them are subject to increased stress and pressure, they are constantly injured. The nutrition and blood circulation of tissues is disrupted, as a result of which their cells can begin to grow rapidly,
- endocrine diseases,
- genetic predisposition and heredity,
- long-term use of steroid hormonal drugs, antidepressants, anticonvulsants,
- hormonal imbalance during pregnancy, after childbirth, during menopause in women, changes in hormonal status in adolescents during puberty1,
- acute vitamin deficiency: hyperplasia often occurs due to a lack of vitamin C,
- traumatic damage to the mucous membrane due to incorrectly installed fillings, artificial crowns or braces,
- teething,
- leukemia
Main diseases characterized by tissue hyperplasia
Fibrous or hypertrophic gingivitis
Between the teeth there are gingival papillae, which during the development of fibrous gingivitis begin to gradually increase in size, they become denser and grow. In this case, the mucous membrane remains painless for a long time, and there is no bleeding.
Read more about all types and symptoms of gingivitis in a separate article on the website.
The disease develops against the background of poor oral hygiene and the accumulation of a large amount of plaque; it can appear due to poor-quality prosthetics and constant trauma to the mucous membrane. People who have hormonal imbalances or gastrointestinal diseases also encounter fibrous gingivitis. The disease often occurs in both adults and children.
Important! A growth over a tooth is not always associated with hyperplasia; it can be nothing more than a gumboil, abscess, fistula or cyst, indicating advanced dental diseases. Most often, such manifestations are very painful, they are white in color, because... pus accumulates in them.
Fibromatosis
This is a hereditary disease and therefore often manifests itself in childhood. It is characterized by the growth of individual areas of the gums and proceeds very slowly. The color of the affected tissues is usually no different from healthy ones; they are painless.
The disease occurs mainly in the frontal area of the smile, and soft tissues can grow so much that they cover the crowns by more than 2/3. If fibromatosis is not treated, it is fraught with destruction of interdental septa, osteoporosis, and a severe violation of the aesthetics of the smile.
Fibropapilloma
If the gums have grown onto the crown, then a disease such as fibropapilloma may be to blame. This is a benign tumor. The tumor is hard to the touch, but painless. Its appearance in childhood is more dangerous, because can lead to disruption of the formation, growth and eruption of permanent elements.
Epulis
Epulis, like fibropapilloma, is a benign formation. It has a mushroom shape, because the tumor grows on a stalk. Appears as a result of chronic irritation and tissue injury. The most common location is the area of the incisors or canines. If the tumor is not removed, it can lead to pathological mobility and tooth loss.
Associated symptoms
The tooth consists of three parts:
- Crown.
- Neck.
- Root.
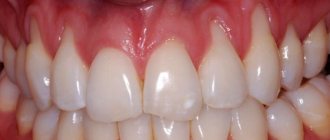
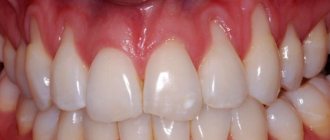
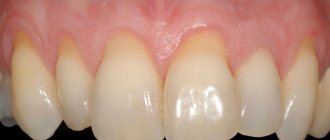
In a healthy state, only the crown should be visible, the neck should be covered by the gum, and the root should be located in the alveolus (a special recess for the root). When the process of recession begins, the neck of the tooth is exposed, but that’s not all; along with this problem, the following symptoms usually appear:
- High tooth sensitivity when in contact with extremely cold, hot, sweet, salty and sour foods, because the tooth exposed the sensitive part of the neck, on which there is almost no protective enamel.
- Noticeable darkening of the enamel spoils the appearance; the situation is also aggravated when the neck of the tooth, which is yellow, is exposed.
- Visually, the tooth appears longer.
- Feeling of discomfort in the gums. When you try to press on it with your tongue, it does not fit tightly to the tooth, but moves away from it.
- When brushing your teeth, your gums become very swollen, painful and red.
- Wide interdental gaps appear at the base of the tooth.
It should be noted that any of the above symptoms are more acutely felt in adolescence and middle age, while older people may not notice or feel that anything is wrong. Therein lies a great danger, because adult patients most often come when the situation has reached a critical point and it is almost impossible to save the tooth.
Why does the problem appear in children and when should you see a doctor?
The situation when gums grow on a child’s tooth most often occurs during the period of teething, as well as the change from a primary bite to a permanent one. During eruption, the mucous membrane swells and increases slightly in size, because it is irritated, blood circulation increases in it, but in this case we are not talking about hyperplasia. However, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the child’s oral cavity over time.
You should consult a doctor in the following situations:
- if 2-3 months after the crown “hatched”, it did not come out completely, and most of it remains under the gum or soft tissue hangs over it, partially covering it,
- the baby tooth did not fall out during the change of bite, but gums are growing on it: perhaps a permanent element is “hiding” under the formed tubercle, which did not have enough space, and it began to make its way in a different direction or into the second row,
- the growth is filled with white contents, and the child has a bad smell from the mouth: perhaps we are talking about the presence of advanced dental diseases, which are complicated by a fistula, abscess or cyst.
Surgery to close gum recession
The gum itself, as you understand, will not rise, it will not “bounce into place”, it needs to be put back in its original place, and this is called closing the gum recession.
But I repeat once again: there are also indications and contraindications for the operation, in accordance with certain classes of gum recession according to Miller.
If this is a class one recession, then one forecast. If this is class II gum recession, the prognosis is different. There are many contributing factors to both successful gum recession and failure. That is, at the very beginning of the treatment path, the doctor must determine all the factors for successful closure of gum recession.
Gum growth on wisdom teeth
There are situations when gums have grown on a wisdom tooth. And this is not related to the phenomenon of hyperplasia. If the third molar has only recently begun to erupt outward, one of its cutting edges has already appeared, and suddenly you feel pain, bad breath appears, and upon examination, inflammation, swelling of the soft tissues and their overhang over the tooth are discovered, then you probably have pericoronitis began.
Pericoronitis is an inflammation of the gingival hood over the third molar. The disease develops due to the fact that small pieces of food begin to get into the gap between the gum and the “eight” that has not fully penetrated, which rot because they are difficult to remove.
For more information about what pericoronitis is and how it is treated, read the feature article on the website.
High fever and pain due to inflammation of the hood
The eruption of the figure eight may be accompanied by general symptoms such as high fever, weakness, nausea, and lack of appetite. Such signs are associated with infection, so you need to consult a doctor, since treating intoxication at home is unsafe. First aid will be to drink plenty of fluids and take diuretics. A high temperature during the eruption of the figure eight can last for several days, so the doctor will individually prescribe antipyretics and tell you how to relieve pain and treat inflammation in the gum area in order to avoid unpleasant symptoms in the future. It is easy to remove inflammation and relieve pain at home, but this will only mask a serious disruption in the process of teething, so it is important to know the dangerous symptoms that require immediate consultation with a dentist.
When should you see a dentist if your figure eight is teething and your hood is inflamed?
- It is not possible to treat inflammation at home, and the symptoms only get worse;
- The gums near the figure eight are swollen, there is throbbing pain;
- It hurts to chew and swallow, the symptoms make it difficult to sleep at night;
- It is not possible to relieve pain in the gum area with analgesics;
- The gums around the figure eight swell, purulent exudate accumulates;
- The figure eight erupts incorrectly and puts pressure on the adjacent tooth.
What such phenomena can lead to without treatment, you will be told at the Leaderstom clinic, where consultation is not only free, but also saves the health of the eight and the entire dentition.
If a broken tooth is healed
Situations where a tooth broken at the very root is overgrown with gums are not uncommon. It can break due to injury or collapse due to advanced dental disease. After this, many people are in no hurry to remove the root, and in some cases it gradually grows over from above (this process can last several years), and then does not bother or hurt for a long time. However, sooner or later, unpleasant sensations still appear: it becomes painful to chew, overgrown tissues swell and are constantly injured.
“My gums have grown on my back tooth, which broke off three years ago. I completely forgot about him, because... It didn’t give me any trouble, only sometimes after cleaning it would scavenge, but I didn’t attach any importance to it. All this was revealed during an examination at the dentist, when I went there with a completely different problem. In principle, the doctor decided everything quickly: he opened this growth and removed the root, then put stitches, but then it healed for a very long time and painfully. It was also very disappointing to hear that if I had contacted him immediately after the tooth was chipped, it could have been restored, but I immediately decided for myself that it was lost. That’s it!”
Varvara, review from 32top.ru
Remember that if a tooth is broken, then either its timely removal or restoration and prosthetics is necessary, because a serious inflammatory process can begin under the overgrown tissues or at the root, which can spread to the jaw, cheek, can develop deep into the body, lead to periostitis and osteomyelitis.
How is an overgrown tooth removed?
Root extraction is a fairly common dental operation. It is performed under local anesthesia and, as a rule, does not cause complications. An overgrown root cannot be removed using traditional methods, since it is completely covered with gum tissue and there is no access to it. Treatment is carried out in several stages:
- Examination by a dentist, x-ray examination. X-ray allows the doctor to see the size, position, and depth of the root. The dentist assesses the risk of damage to adjacent teeth during surgery.
- The operation is performed under anesthesia. First, the doctor makes an incision in the gum, providing himself with access to the root. After this, the root is removed and sutures are applied.
- During the rehabilitation period, the doctor selects anti-inflammatory drugs and agents that accelerate wound healing.
The process of removing an overgrown root is individual in each case. The complexity of the operation is influenced by many factors:
- Tooth location. Removal of roots on the upper and lower jaws has its own characteristics and is carried out using various dental instruments.
- The degree of damage to the root and nearby tissues, the presence of fragments. Sometimes, for a successful and as painless removal for the patient as possible, the root is destroyed by a drill into several parts. Separation is required in cases where the tooth has several strong, deep roots. As a rule, after destruction, individual parts are easily removed using ordinary tools.
- The presence of pathology in the surrounding bone tissue, inflammation of the gums.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
If there is no inflammation, the gum is carefully separated from the alveolus and the tooth is removed using suitable dental forceps. The inflammatory process “melts” the surrounding tissue, so for successful removal it is enough to provide access to the root by making an incision in the gum. Application of forceps does not require labor, and there is no need to additionally separate the gingival tissue from the alveoli. In difficult cases, elevators are used.
How long does the gum “grow” and the stages of development of hyperplasia
Pathology can develop slowly if it is caused by fibromatosis, epulis or fibropapilloma. And it can develop more rapidly if it occurs against the background of gingivitis.
As for the stages of development of hyperplasia, doctors identify the following:
- first stage: the gingival papillae thicken and thicken, while there are no other alarming signs,
- second stage: soft tissues grow and can cover up to half of the crown. Due to the volume, tissues are easily injured during oral hygiene and when chewing food, they can begin to bleed,
- third stage: the most rare stage. The tissues grow so much that they can even cover the cutting area of the crown. Granulations appear on the affected areas.
If you break off a tooth, gum growth may take several years.
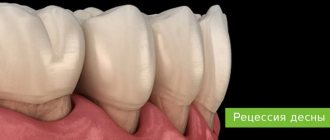
Stages of gum tissue recession
Treatment of the pathology is prescribed based on its stage and form. The following symptoms will help identify them (according to the Miller classification accepted in dentistry):
- tissue loss is hardly noticeable and is visible only at the junction of the dental crown to the gum - the initial stage of subsidence, easily treatable;
- at the point of contact between the gum tissue and the neck of the tooth, the gum level is below normal by 1-2 mm, while the defect does not appear between the teeth;
- receding gums by 3 mm or more, at this stage the necks of the teeth are exposed, soft tissues may bleed, the bone level remains at the same level;
- receding gums by 5 mm or more, accompanied by exposure of tooth roots and mobility of dental units, the most severe stage.
At advanced stages, the gums on the front teeth most often recede - the defect is clearly visible without additional diagnostics.
At the beginning of the disease, it can be determined by the following symptoms:
- the presence of inflammation and bleeding;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- formation of periodontal pockets;
- increased sensitivity of enamel;
- pain when brushing teeth;
- whitish tint of gums.
It is worth adding that the disease can affect both the lower and upper jaws, or both at once. In addition, recession can be localized - within 1-2 dental units, and generalized, when the deformation of the gingival contour spreads to the entire jaw.
Regardless of whether the gums have receded on the lower teeth or on the upper ones, you need to seek help from a specialist.
Signs and symptoms of hyperplasia
Those who have this problem rarely experience pain right away. But almost all patients notice a visual violation of the aesthetics of a smile, because the gums become voluminous and loose, which, as a rule, is the reason for visiting a doctor.
Discomfort and pain appear after the tissues have grown significantly, and they involuntarily have to be constantly injured during hygiene procedures and eating food. Another sign is the appearance of bad breath, which does not go away after careful hygiene or quickly returns again.
Consequences and complications if the pathology is not treated
Many patients see overgrown gums as only one problem – a significant disruption to the aesthetics of their smile. However, this is not so: if the pathology is not eliminated and it is allowed to progress further, then this is fraught with serious complications for the health of the oral cavity and the body as a whole.
If left untreated, the patient may develop degenerative diseases of periodontal tissues, leading to the destruction of the interdental septa and supporting ligaments that hold the teeth in the sockets. You may lose your teeth much earlier than you would like.
Hypertrophied tissues are subject to constant trauma, which is why any benign formation can sooner or later become malignant. Another common complication is osteoporosis.
For children, the lack of treatment is fraught with disruption of the formation, as well as the timing of the loss of milk and the eruption of permanent elements.
If a single growth appears on the gum, this may not always indicate hyperplasia or hypertrophy. Some people mistake the growth for a fistula, cyst, or abscess. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner for these pathologies, the purulent contents from these neoplasms can spread throughout the body, causing damage to the cardiovascular and circulatory systems, gastrointestinal diseases, sepsis and even a brain abscess.
Methods of treating pathology in dentistry
The most common method of removing overgrown tissue is surgical excision using a scalpel or laser. Scientifically, this surgical operation is called gingivectomy. The procedure is performed under anesthesia.
About the indications, types and complications after gingivectomy - in the feature article on the website.
If there are few damaged tissues, then doctors may suggest their removal using cryodestruction, when under the influence of low temperatures they die off on their own over time.
If tissue proliferation is accompanied by an inflammatory process, then electrophoresis and darsonvalization may additionally be prescribed.
In addition to excision of excess tissue, treatment should be carried out aimed at eliminating the cause that provoked the development of the pathology. If the cause is a malocclusion, then the patient needs to see an orthodontist, who will prescribe devices to correct the position of the dentition. If there is a fragment of a tooth inside the overgrown gum, then it is necessary to remove it or use prosthetics, if the situation allows. In case of internal diseases of the body, the patient will be referred to specialized specialists - endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist, etc.
Dentists are required to sanitize the oral cavity and remove hard and soft bacterial plaque.
Home care and postoperative period
After treating gum recession, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics, rinses, topical gels, and other topical treatments to prevent complications and speed up the healing process. It is also important to prefer gentle, soft food at a comfortable temperature, and perform regular hygiene according to the recommendations of a specialist.
The dentist will recommend replacing your hard toothbrush with a soft one, and as healing progresses, you will likely need a toothbrush with medium-hard bristles. In addition, the doctor will definitely show the correct cleaning movements and tell you what pressure will be optimal. In many cases, such measures are sufficient to eliminate the causes of exposed tooth necks, as well as maintain treatment results.
Recovery period after surgery
If the gum has grown on the tooth, then now you know what to do - you need to contact a dentist who will prescribe adequate treatment.
Since treatment for hyperplasia involves surgical manipulation, there will be a recovery period after it, taking from 5-7 to 10-14 days. At this time, you need to follow all the doctor’s recommendations: take prescribed anti-inflammatory and wound-healing agents, rinse with antiseptics, and use painkillers as pain occurs.
During the rehabilitation period, it is important to exclude “irritating foods” from the diet: spicy and salty, cold and hot, solid foods. And, on the contrary, you need to diversify your diet with foods rich in vitamins C, E, B, A, calcium and phosphorus.
To care for the oral cavity, you need to use a brush with soft bristles and a non-abrasive toothpaste; you should avoid using an irrigator for a few days.
Preventive measures
To prevent gums from moving away from the tooth, you need to follow simple recommendations:
- brush your teeth twice a day;
- use a properly selected brush and paste;
- visit the dentist in a timely manner;
- prevent tartar from forming;
- no smoking;
- eat more solid foods;
- Healthy food.
At the first sign of a recession, you should see a doctor. Then the disease can be stopped very quickly.
Is it possible to get rid of the problem on my own?
Some people use decoctions of medicinal herbs and plants (chamomile, oak bark, sage and others), as well as solutions to relieve gum inflammation (such as Chlorophyllipt or Stomatophyte) to get rid of the problem. However, you need to understand that hyperplasia cannot be cured by rinsing. This measure will not reduce the volume of overgrown tissue, but will help relieve signs of the inflammatory process and alleviate the condition during teething, and is also well suited as a concomitant therapy after surgical excision of excess gum tissue, which is carried out in a dental office.