Symptoms Causes Degrees of mobility Diagnostics Treatment methods Splinting Treatment at home Prevention
Normally, healthy teeth have little mobility due to the elasticity of the ligamentous apparatus and the need to absorb the chewing load. Physiological mobility is 0.06 - 0.15 mm, completely invisible to humans. Excessive mobility, noticeable when pressing on the tooth, is an anomaly that requires the intervention of a dentist. Even if a mobile tooth looks normal and does not hurt, loosening indicates a violation of the dentogingival connection, which is fraught with loss of a dental unit.
Pathological tooth mobility occurs due to various dental problems or injuries. What to do if a tooth is loose? Go to the dentist. Timely diagnosis and treatment will preserve the integrity of the dentition, restoring the functioning of the ligamentous apparatus. The treatment method is selected according to the severity of the defect, its location, and the presence of associated factors. After a comprehensive diagnosis, specialists from the RUTT clinic in Moscow will select treatment taking into account the clinical picture and indications for one or another method.
Symptoms
The main symptom is one - when you press on a tooth, it moves left and right or back and forth. Associated symptoms depend on the cause of mobility and may include:
- bad breath;
- redness, bleeding, swelling, soreness of the gums;
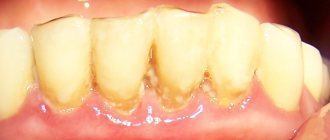
- abundant dental plaque;
- itching, burning gums;
- the tooth is loose and hurts when pressed;
- gum recession (exposure of the neck of the tooth);
- pathological abrasion of enamel;
- muscle hypertonicity;
- symptoms of intoxication - headache, fever, nausea, etc.
All causes are accompanied by corresponding symptoms - the tooth became loose after a characteristic crunch was heard, most likely we are talking about a longitudinal or scaly fracture of the root. A healthy tooth is loose - more often than not, this indicates an occlusal, mechanical injury. Several teeth in a row loosen at once - this is a manifestation of periodontal pathologies (periodontal disease, periodontitis).
Causes of tooth mobility
The roots of the teeth are located in the sockets (alveoli), they are firmly connected by the periodontium - a layer of connective tissue, collagen fibers, nerves and blood vessels. It is the periodontium that provides the necessary shock absorption of the dentition, allowing units to move in different planes, dampening chewing pressure. Periodontium is part of the periodontal tissues, such as gums, ligaments, cement, and bone surrounding the roots. If the connections between the alveolus, periodontium and tooth root are disrupted, the dental units begin to move beyond normal limits. The reasons for these changes are:
- inflammation and destructive changes in the periodontium (periodontitis, periodontal disease, periodontitis);
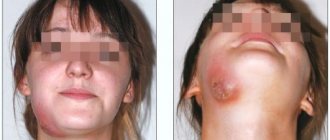
- dental diseases (flux, cyst, etc.);
- chronic systemic diseases (osteoporosis, diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction and other diseases accompanied by metabolic, circulatory, and tissue regeneration disorders);
- malocclusion, uneven pressure on one tooth or group of elements (occlusal trauma);
- bruxism;
- jaw injury (bruise, fracture);
- prosthetics errors (incorrectly installed prostheses, implants);
- damage from solid food;
- large interdental spaces (teeth begin to shift towards the empty space);
- age-related changes (puberty, menopause, pregnancy and lactation, old age);
- bad habits;
- long-term use of certain medications.
Natural mobility associated with age occurs exclusively in children, when baby teeth are replaced by permanent teeth. If a molar tooth in an adult is loose, we are talking about pathology. The cause may be improper redistribution of chewing loads, disease, and not necessarily dental disease. Increased mobility may occur during orthodontic treatment. To eliminate it and stabilize the correction result, after removing braces or aligners, retention devices (retainers) are used.
Strengthening techniques used in dentistry
Experienced dentists use highly concentrated products enriched with minerals when working with “problem” teeth. Additionally, they prescribe fluoride-containing pastes and remineralizing gels to patients, which can be used at home.
This is the name of the most effective dental procedures to strengthen teeth:
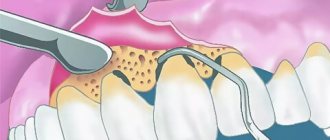
- Remineralization. First, professional hygiene is carried out. Using an ultrasonic scaler, the doctor cleans the crowns of deposits. After this, it covers them with a special remineralizing composition. Prepared enamel absorbs beneficial components like a sponge. Due to this, her condition improves. It becomes dense, very hard and perfectly smooth. In advanced cases, one remineralization session may not be enough. Then it is repeated two to four times at certain intervals.
- Fluoridation. Often this type of treatment is combined with remineralization. This is due to the fact that fluoride is better absorbed after calcium. Fluoridation means the treatment of hard dental tissues with a fluoride-containing preparation. It quickly penetrates into the deep layers of the tooth and saturates its tissues, making them more resistant to negative external factors. It is especially important to undergo fluoridation twice a year for people who live in regions where the water flowing from the taps is low in fluoride compounds.
Degrees of mobility
- I
– the tooth deviates back and forth from neighboring units
by no more than 1 mm
, there are no symptoms from the periodontium or gums; - II
– amplitude of swing back and forth and sideways
by 1 mm or more
, tartar and plaques are visible on the enamel, redness, swelling, bleeding and soreness of the gums are possible; - III
– the teeth swing strongly in any direction with slight pressure with the tongue or chewing, the amplitude of the displacements
significantly exceeds 1 mm
; - IV
– the tooth shifts in all planes, rotates around its axis, and
barely stays
in the gum tissue.
Pathological mobility of any degree requires complex treatment. If the tooth is located in the gum, the periodontium and socket are intact, the process is reversible. Dental units begin to become very loose when periodontitis or periodontal disease is advanced. With deep periodontal damage, weakening and destruction of the ligamentous apparatus, bone atrophy, tooth extraction may be required, followed by implantation and prosthetics.
Signs in the presence of which you need to think about strengthening
You should ask a qualified dentist how to strengthen your teeth if:
- the enamel has acquired an unsightly yellow or gray tint, which is why the smile begins to look less aesthetically pleasing than before;
- when eating sour, sweet, or spicy foods, sharp dental pain periodically appears;
- the coronal part has become transparent in the area of the cutting edge;
- pain occurs when biting and chewing hard foods;
- chips and cracks appeared;
- rapidly progressing caries developed.
In all these cases, you need to make an appointment with a dentist as soon as possible. The doctor will conduct a simple diagnosis and determine what caused the problem, and select medications that will improve the condition of the enamel.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis begins with collecting anamnesis. The dentist finds out when the tooth began to become very loose, whether this happened before, and what chronic diseases the patient has. Next, a dental examination of the oral cavity is carried out, the general condition of the dentition and periodontium is assessed. The degree of unsteadiness is assessed according to the subjective sensations of the patient and the dentist. The doctor checks the direction and magnitude of the deviation using tweezers:
- the instrument is applied to the upper part of the dental crown and moved in different directions;
- to identify vertical or circular displacement, the crown is clamped, carefully lifted up, and rotated.
Additionally, X-ray diagnostics are performed: orthopantomogram, CT scan, targeted X-ray to identify periodontal pathologies, injuries, and assess the depth of tissue damage. Based on the results obtained, effective treatment is selected. If mobility is due to a chronic disease, a specialized specialist (endocrinologist, therapist, rheumatologist, etc.) is involved in treatment. Why the lower teeth are loose, what is causing the mobility of the upper incisor - the doctor will be able to accurately answer these questions after a comprehensive dental examination.
Rinse
By rinsing, we remove food debris, pathogenic bacteria, and treat gums locally. You can rinse your mouth with a solution of soda, decoctions and diluted herbal tinctures (chamomile, St. John's wort, nettle, sage, oak bark) or special dental rinses. Read the instructions for use carefully! In folk medicine, hydrogen peroxide, carrot juice, and sauerkraut are used (it must be chewed periodically). Please note that rinsing for many diseases is only an additional, concomitant method of treatment.
Treatment methods
The treatment regimen and the scope of medical manipulations are selected according to the patient’s somatic status. The inflammatory process is eliminated, professional oral hygiene is performed, and antimicrobial therapy is prescribed. Treatment of mobility is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause that led to the weakening of the ligamentous apparatus. If it is periodontal disease, then infection and inflammation are treated; in case of malocclusion, orthodontic treatment is carried out; in case of injury, a temporary splint is applied.
Treatment includes various methods, including grinding crowns, normalizing occlusion, splinting, and prosthetics.
- Thanks to bite correction, the load on the periodontium is normalized, the teeth occupy a more stable position in the sockets.
- Wearing a special mouthguard that prevents clenching or grinding of the teeth will help strengthen loose teeth in the gums during bruxism or clenching.
- In case of physiological changes, hormonal levels and nutrition are corrected, vitamin therapy is carried out, and the immune system is strengthened.
- In case of injury, a special device is installed on the dentition - a splint, which helps to fix loose units and correctly distribute the load between healthy and injured teeth.
In some cases, it is impossible to save a loose tooth. Direct indication for extraction
is mobility of 3-4 degrees with loss of bone tissue by 70%, atrophy of the jaw bone by more than 50% with damage to the dental pulp. In such situations, it is advisable to remove the loose tooth, preserving the bone tissue for subsequent implantation.
Splinting teeth
The method is aimed at strengthening the teeth in the gums and preventing their further loosening. The essence of the manipulation is to combine mobile units into one block with healthy ones using a special fixing structure. Splinting can be temporary ( up to 1-3 months
), long-term (
up to 1 year
), permanent. Tires are divided into:
- removable
– mouthguards, clasp dentures; - non-removable
- tape, fiberglass or aramid thread, crowns, pin inlays (intradental splints), cap splints.
An effective option is fiberglass splinting
, aesthetic nanomaterials or ceramics. A strong, translucent white tape or thread is fixed to the inner surface of the teeth using a light-curing composite. The material is biocompatible with the human body, does not absorb saliva, does not enter into chemical reactions, firmly adheres to the enamel, and reliably holds the units in the desired position.
With temporary splinting, the structure is fixed for several months. This option is used for mild forms of periodontitis, periodontitis, to consolidate the result of orthodontic correction or mobility caused by injury. A permanent splint is installed in the treatment of moderate periodontitis, the presence of voids in the row (removed or fallen units). The fixing structure is replaced with a new one every 4-5 years
, sometimes more often (according to indications).
Splinting clasp prosthesis
Clasp prosthesis
– metal base (arch) with plastic gum and artificial crowns. Since the design has an attachment for each dental unit, the prosthesis can replace several lost teeth while simultaneously splinting loose elements. This method is used in the treatment of pathologies of moderate severity, when in addition to movable units there are healthy ones that serve as support for the prosthesis.
Splinting with crowns
The teeth are depulped, the root canals are filled, ground, and crowns made of durable material (metal-ceramics, ceramics, etc.) “soldered” to each other are fixed on them. This method is characterized by high reliability and long service life. The elements under the crowns are firmly locked together and completely motionless.
Products that can help improve the situation
In the human body, a lot depends on nutrition. It is impossible to have a healthy smile if you consume a huge amount of junk food every day. If a person wants to make his enamel resistant to the negative influences of external irritants, he should eat a lot of fresh fruits and vegetables. Also useful:
- Seafood. They are a quality source of phosphorus.
- Fermented milk and dairy products containing calcium.
- Kiwi. This fruit is a real storehouse of ascorbic acid. At the same time, unlike oranges, tangerines and lemons rich in this vitamin, it does not irritate the enamel.
- Greenery. Source of a huge amount of vitamins and microelements. You definitely need to eat it. If a person does not like greens, they should treat them as natural medicine and still use them in their cooking on a regular basis.
- Honey. Beekeepers call it a natural antiseptic. It perfectly relieves inflammation and promotes rapid healing of gum disease.
To strengthen your teeth, it is very important to stop drinking any sweet carbonated drinks, smoking, and alcohol. It is also not recommended to frequently chew nuts and seeds or smoke.
Adjuvant therapy
The main treatment involves auxiliary therapy aimed at preventing further loosening of the teeth. It includes:
- prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins, biostimulants;
- ointments, gels to strengthen gums;
- antibiotic therapy;
- systematic professional teeth cleaning;
- physiotherapy (electrophoresis, plasma lifting, etc.);
- gum massage
If the front tooth becomes loose after an impact or several lower units become mobile due to bleeding gums, treatment should begin as quickly as possible. Complex therapy in the early stages around the moving element will help to form healthy tissue, ensuring reliable retention of the tooth in the gum. In complex, advanced cases, with 4 degrees of mobility, removal followed by prosthetics is advisable.
Gels and toothpastes for bleeding
You should choose a toothpaste based on what is causing your gums to bleed. The composition may contain different components: potassium chloride, sodium sulfate, vitamins, medicinal plants, etc.
The most effective and popular means to solve the problem:
- SPLAT Professional Active is a Russian toothpaste, its distinctive feature is its black color. It has several actions at once - antiseptic, hemostatic. The main components included in the composition are skullcap, spirulina extract, and bergenia extract.
- Lacalut Activ is a whole complex that includes a toothbrush, toothpaste and mouthwash. Aluminum cations are used as a basis.
- Parodontax Classic – contains extracts of medicinal herbs. The pasta is produced not in our country, but in the UK.
- Forest balsam is another domestic product that contains many components of plant origin. There is sea buckthorn essential oil, St. John's wort, chamomile and more.
Recommended toothpaste for treatment
Dental gels are no less effective. It is recommended to use Cholisal, Parodium, Solcoseryl, Metrogil Dent, etc.
Interesting!
It is recommended to change toothpastes periodically, this way you can achieve comprehensive care.
Whitening pastes should never be used for bleeding gums. The thing is that they can irritate the gums, thereby further aggravating the situation. In the video in this article you can learn in more detail about which toothpastes and gels are useful for this problem.
Prevention
To prevent tooth mobility, you must maintain careful oral hygiene and use brushes and pastes recommended by your doctor. Don’t forget to floss, irrigate, and rinse your mouth after eating. Regular visits to the dentist (every 6 months) for a preventive examination and professional cleaning will help identify pathology at the initial stage, avoid complications, and maintain a healthy smile.
Author of the article Voznyuk Vladimir Aleksandrovich Maxillofacial surgeon-implantologist of the highest category
Work experience: 28 years.
Stages of the disease
First stage.
There is no tooth mobility, and the periodontal pocket has a relatively small depth (no more than 3.5 mm). The patient experiences virtually no pain.
Second stage.
Periodontal pockets deepen up to 5 mm. The tooth begins to react to cold and hot food and drink. Gradually, the pocket deepens, and the teeth become mobile, and gaps form between them.
Third stage.
With severe disease, the periodontal pocket increases in size. In some cases the pocket may be more than 6mm deep. The mucous membrane of the oral cavity begins to swell. Then the teeth become loosened and displaced, and purulent discharge from the gums is possible. Another symptom of periodontitis is a significant deterioration in the general condition of the patient.
Up to contents