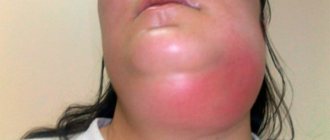
Photo: phlegmon of the submandibular region
Phlegmon of the submandibular region is a diffuse purulent-inflammatory lesion of the subcutaneous tissue and muscles in the area of the lower jaw. This disease is characterized by the intensive spread of the pathological process, which from the very beginning has a diffuse course.
In dental practice, it is customary to distinguish between several types of phlegmon. These can be odontological, adenophlegmon and osteophlegmon. According to statistics, the ratio of abscesses and phlegmons in the maxillofacial area is 4:1.
Causes and pathogenesis of abscesses and phlegmons
Most purulent lesions of the maxillofacial area are odontogenic in nature. This means that the disease is formed due to the spread of infection from the inflamed root or periodontium. In such cases, streptococci and staphylococci from the primary lesion penetrate through the lymphatic vessels into the deep layers of the soft tissues of the face.
The state of immunity is of great importance in the development of the purulent process. A decrease in the body's protective abilities is a powerful predisposing factor for tissue suppuration.
Types of dental abscess
- Osteomyelitis
- Phlegmon
- Tooth loss
Osteomyelitis
When pus remains in the soft tissues, complications arise. Dense formations with pus form in the bone tissues, and swelling of the lymph nodes also occurs.
Phlegmon
A life-threatening complication occurs when the infection spreads into the soft tissues of the gums. The growth of pus leads to chronic pathologies.
Tooth loss
If the infected fluid spreads to the base of the tooth, painful swelling appears, which may lead to tooth extraction.
Clinical picture of the disease
In the initial stages, abscesses and phlegmons adjacent to the lower jaw are manifested by compaction and progressive swelling of the soft tissues of the face. The skin over the purulent focus is often hyperemic. The key symptom of suppuration is fluctuation - the feeling of fluid in a confined space.
The course of phlegmon is accompanied by general intoxication, in which the patient presents the following complaints:
malaise and feeling of chronic fatigue; increase in body temperature; fatigue and joint pain.
Abscesses, as a rule, do not cause such symptoms due to the limited nature of the pathological process.
Abscess, phlegmon of the maxillofacial area in children is characterized by an acute and severe course of the disease. Diffuse purulent lesions of soft tissues are formed as a result of the imperfection of the children's immune system.
What is a gum abscess, definition of the disease
Let us consider in more detail what an abscess on the gum is and the mechanism of its occurrence. A purulent focus occurs as a result of long-term untreated inflammation of periodontal tissues. The pathogenesis of the disease is associated with the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms (mainly Bacteroides forsythus and Porphyromonas gingivalis) into the periodontal tissues. Possible routes of penetration of microbes:
- from the outside: through a carious cavity, chips, cracks on the surface of the segment;
- from the inside (hematogenously, lymphogenously): in the presence of other septic foci in the body.
During their life, bacteria produce toxic substances that lyse tissue cells, resulting in the formation of a cavity filled with pus. The abscess under the tooth is surrounded by a connective tissue capsule, which separates it from the intact periodontal tissues.
Microbial metabolic products have a neurotoxic effect on nerve receptors located in the pulp of the segment, which causes pain. In addition, they increase the permeability of the capillary walls, resulting in swelling of the surrounding tissues.
Diagnosis of the disease
Establishing a diagnosis for acute odontogenic infections includes the following measures:
Collection of medical history. The doctor finds out the patient’s complaints and the general condition of the patient. External examination of the maxillofacial area and palpation of regional lymph nodes. Most inflammatory and purulent processes cause enlargement and pain of the lymph nodes. Instrumental examination of the oral cavity, during which the doctor detects chronic foci of odontogenic infection. X-ray in frontal and lateral projection. Laboratory blood test, in which there is an increase in SOE, leukocytes and a decrease in the concentration of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
General principles of treatment of the disease
The doctor who treats phlegmon of the maxillofacial area is an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Each doctor, when starting to treat an odontogenic process in the maxillofacial area, is guided in his actions by the following principles:
The tooth that caused the development of phlegmon is removed. Timely diagnosis is very important due to the characteristics of this area, from where the infection can spread, causing severe consequences (in particular, mediastinitis). It is necessary to eliminate the spread of the infection, that is, promptly open the lesion and eliminate the inflammatory exudate, relieve tissue tension. The rate of subsidence of inflammation depends on the quality of evacuation of all decay products from the wound, that is, careful postoperative treatment of the wound is necessary. Comprehensive treatment of pathology using all means and methods available in this medical institution. Friendly management of the patient with colleagues from other areas, timely appointment of consultations with all specialists for combined lesions. Visible external changes often occur, which are not always pleasant for the patient, which is especially painful in the face area. Therefore, there is an urgent need to organize work with patients by a medical psychologist in the early stages after surgery, especially if there is a significant visible defect. Correct stage-by-stage treatment, organization of medical rehabilitation, referral to the appropriate department with complete information about the patient. Fully informing relatives and the patient about the violation of significant functions of the maxillofacial area, if any. Upon leaving the hospital, the patient should have clear further recommendations, especially if it is necessary to continue treatment on an outpatient basis.
Symptoms of gum abscess
Gingival abscess manifests itself in two types of symptoms: local and general clinical. Local symptoms are caused by reactive manifestations in the area of inflammation. The appearance of general symptoms is associated with intoxication of the body. The main symptomatic manifestations of the disease:
| Local inflammatory reaction | Symptoms of intoxication |
| pain when pressing on the affected unit; hyperemia of the gums over the area of inflammation; swelling of the tissue around the abscess; smell of rot from the mouth; violation of facial configuration; formation of a tubercle with purulent contents near the tooth; increased mobility of the diseased unit; darkening of tooth enamel; enlargement of nearby lymph nodes. | hyperthermia; dyspnea; cranialgia; violation of orientation in space; tachycardia; aching joints; lethargy; drowsiness; irritability. |
The leading symptom of an abscess is pain. It can be fixed only at the point of inflammation, but more often the discomfort radiates to the head, auricle, eye socket, neck, and neighboring segments. Soreness has different intensity, character (sharp, shooting, dull), occurs periodically in response to stress factors, or is constantly present.
Complications of abscesses and phlegmon
Purulent lesions of the maxillofacial area can be complicated by the following pathologies:
Sepsis is a serious condition of the body that is caused by the penetration of a bacterial infection into the circulatory system. Treatment of such a complication is difficult due to the development of body resistance to antibiotic therapy. Sepsis is often the cause of death. Mediastenitis in the form of purulent inflammation of the tissue of the mediastinum, where the heart, lungs and bronchi are located. Meningitis . Inflammatory damage to the meninges develops as a result of the spread of purulent infection through the lymphatic and blood vessels of the head.
Types of dental abscess
- Desnevoy
- Periodontal
- Periapical
- Pericoronal
- Combined (periodontal-endodontic)
Desnevoy
A superficial formation on the soft tissues in the area of the gingival papillae between the teeth. Inflammation is associated with the ingress of food, foreign objects, or trauma to the gums with a toothbrush or floss. A gum abscess is relatively easy to correct, but if not treated early, complications can arise.
Periodontal
This is an internal inflammation of the soft tissues of the gums, often caused by periodontitis. In this case, the infection is localized between the outer wall of the alveolar ridge and the gum when the dental pulp is healthy. A purulent exudate forms in the affected gum, which forms a lump in the periodontal pocket. There is no place in the gum for fluid with infection to escape, so the soft and bone tissues near the site of suppuration are gradually affected.
Periapical
The most common type of abscess, the cause of which is complicated caries or untreated periodontitis. The infection affects the root system of the tooth, resulting in pus accumulating at the apex of the root. When the immune defense is weakened, the inflammatory process affects the periosteum of the tooth, spreads to the soft tissue of the mucosa and leads to the formation of a fistulous tract and a purulent lump on the gum.
Pericoronal
Inflammation occurs in the soft tissues above the erupting tooth when food debris and bacteria get there. Pericoronitis can cause swelling of the neck, jaw, and also lead to angina pectoris (impaired respiratory function).
Combined (periodontal-endodontic)
Damage to the gums in the pulp and soft tissues, which causes periodontitis on adjacent teeth.
Consultation, image and treatment plan free of charge
Enter your phone number, we will call you back and select a convenient appointment time for you. Or call us yourself - +7
Already received your application
We will contact you from 9 to 10 am and advise you on all your questions.
Forecast and prevention of the disease
The prognosis of odontogenic abscesses and phlegmons is usually favorable. A positive treatment result is observed with timely indication of full surgical care. In such cases, the patient must be hospitalized in a specialized medical hospital.
Lethal outcomes from purulent lesions of the soft tissues of the maxillofacial area are associated with late presentation of the patient and systemic suppression of his immunity.
Prevention of the disease is achieved in the following ways:
sanitation of the oral cavity, during which the dentist treats all carious, pulpitic and periodontitis teeth; strict adherence by patients to the rules of personal hygiene and regular brushing of teeth; undergoing regular preventive examinations at the dentist, at least twice a year; timely consultation with a doctor if symptoms of dental diseases are detected. Every person should remember that the cost of prevention is much lower than the cost of treatment. And in some cases, sanitation of the oral cavity can prevent the development of severe complications, which are accompanied by high mortality in patients.
Causes of dental inflammation
The main causes of tooth gum abscess and pulp infection:
- Advanced caries affecting the root apex. Suppuration develops against the background of periodontitis.
- Untreated gingivitis and periodontitis (gum disease). They often develop as post-traumatic complications: pathogenic microflora accumulates in periodontal pockets.
- Weakening of the immune system after illness (flu, sore throat, etc.).
- Iatrogenic factors - bacteria entered after the use of unsterile instruments during treatment, injections, or incorrect tooth extraction.
The development of the inflammatory process may be preceded by damage to the oral mucosa and the formation of boils.