Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
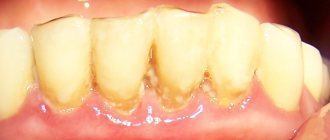
Inflammation of the gums, or periodontitis, is one of the most common dental diseases. This pathology of the oral cavity can occur due to both chronic diseases and local traumatic injuries.
The main symptom of periodontitis is an acute inflammatory process of gum tissue. Lack of treatment can lead to the development of severe forms of the disease, characterized by tooth loss and displacement.
Prevention and treatment of periodontitis at home
The most effective method of treating almost any disease, including periodontitis, is its prevention. There are simple prevention methods that can be used at home. Their use will prevent the occurrence of periodontitis symptoms and avoid the need for drug and surgical treatment.
The main thing that needs to be done to prevent any pathologies of the oral cavity is to strictly follow the principles of dental hygiene:
- brush your teeth twice a day with therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste using a medium-hard brush;
- After a meal, remove leftover food using dental floss.
- a rinse with an antibacterial effect, for example, Asepta based on lemon balm, calendula or St. John's wort extract, has a soothing effect on the gums;
- it is necessary to regularly consume solid and plant foods, ensuring sufficient chewing load on the teeth;
- one of the reasons for the development of periodontitis is a lack of vitamins A, C and B vitamins in the diet. To prevent the disease, it is recommended to take a vitamin complex containing a sufficient amount of these vitamins;
- You should visit your dentist twice a year for preventive teeth cleaning. Timely removal of plaque and tartar will help avoid gum inflammation and further development of pathology.
Recommendations after the procedure
Recommendations after curettage in dentistry are always individual. In some cases, for the first time you just need to give up solid food and brush your teeth with a hard brush. In others, you have to comply with more stringent requirements, see a dentist and remove stitches after the damage has healed. It is important to listen carefully to the doctor’s advice and try to follow all instructions as accurately as possible - then the curettage procedure will bring maximum benefit and periodontitis will not bother you for a long time.
Gums are bleeding - contact a periodontist
If you notice the slightest symptoms of periodontitis, immediately go to the doctor. The first sign is regular bleeding of the gums after mechanical impact.
If there is a single bleeding, there is no reason for serious concern: to strengthen the gums, you can change the toothpaste to a special product for the treatment and prevention of periodontitis, or use a strengthening gel or balm. But if bleeding becomes regular, you need to see a specialist.
If the disease progresses, some teeth may need to be removed. Therefore, the earlier the diagnosis is made and treatment is started, the greater the chances of completely getting rid of periodontitis without negative consequences.
Why is curettage of periodontal pockets necessary?
There is a practice when, to get rid of periodontitis, they do not go through surgery, but limit themselves to taking antibiotics, removing dental plaque, using a laser or local anti-inflammatory therapy. But such steps are more likely an attempt to cure the disease than a truly effective remedy for periodontitis. For what reasons may such therapy not work?
- If the periodontal pocket is very deep, then it is impossible to completely clean it of deposits with ultrasound. The procedure is carried out blindly: the dentist “feels” with the attachment under the gum, but does not see what is happening there. Therefore, even after the highest quality cleaning, there remains a possibility that some amount of subgingival stone remains in its place.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy and cleaning of subgingival deposits cannot guarantee that periodontitis will stop, since a favorable “climate” for the development of infection still remains.
This is why most doctors strongly advise patients to undergo surgery. Only surgical intervention can get rid of all the problems associated with periodontitis, namely:
- remove granulations;
- remove gum pockets;
- remove deposits from under the gums.
Among the most popular surgical methods for treating periodontal diseases is curettage of periodontal pockets. If necessary, it can also be used for periodontal disease and gingivitis.
Acute and chronic periodontitis: symptoms and treatment
As mentioned, the treatment plan will depend on the severity of the inflammation and how widely it has spread. Periodontitis affecting a few teeth is localized; periodontitis affecting most (or all) teeth is generalized.
Acute periodontitis, which has pronounced symptoms, occurs less frequently than chronic periodontitis and usually affects one or two teeth. It is often caused by trauma to the tooth or periodontal tissue, or improper installation of a crown or filling. This type of disease often occurs aggressively, causing rapid destruction of bone and muscle tissue.
If the pathology is chronic, then phases of exacerbation are replaced by phases of remission. At the same time, chronic periodontitis slowly and steadily progresses from the initial stage to the severe one. This form of pathology can be caused by both local factors (for example, trauma to the oral cavity) and general ones.
Flaws
Gum curettage is a simple dental operation with good results. However, it is not without its drawbacks:
- Traumaticity. Like any surgical intervention, curettage injures soft tissue.
- The need for anesthesia. Normally, the operation is performed under local anesthesia. Sedation or general anesthesia is used in extreme cases or when the patient is in panic.
- Rehabilitation. The gums heal quickly, but at this time it is necessary to follow the recommendations and take care of the oral cavity. Infection of the wound can lead to complications.
Professional hygiene for effective treatment of periodontitis
In the vast majority of cases, the development of this disease is associated with insufficient oral hygiene. The periodontal tissues become inflamed due to extensive dental plaque, so the first thing to do to treat periodontitis is a professional cleaning.
This procedure includes the following steps:
- removal of dental plaque
- polishing the tooth surface
- treating the tooth with protective varnish.
Modern cleaning methods are gentle on the enamel and cause minimal discomfort. Also, at the stage of removing tartar and plaque, preparations should begin for the treatment of caries and the removal of hopelessly affected teeth.
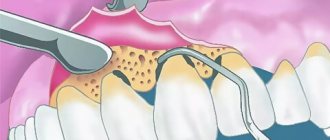
Closed curettage of periodontal pockets: how to do it
The operation is effective when the depth of the gum pockets is 3-5 mm.
Conventionally, the following stages of the procedure are distinguished:
- Examination of the gums, introduction of the patient into local anesthesia.
- Cleaning pockets without cutting the gums.
- Polishing of tooth roots.
At the same time, the operation can be performed in the area of 2-3 teeth. Within a week, the main wounds heal, but the process of forming connective tissue and attaching the gum to the tooth takes about a month. A significant disadvantage of closed curettage is that during the intervention the doctor does not see whether all pathological formations have been removed.
If the depth of periodontal pockets is more than 5 mm, such an operation can only temporarily stop the development of periodontitis. Partial removal of granulations and clearing of deposits allows for temporary respite, but in almost 100% of cases the disease begins to progress again.
Drug treatment of periodontitis
The next stage of treatment is to relieve inflammation and eliminate bleeding gums to prevent further development of the disease. This goal is achieved through drug therapy.
Medicines for the treatment of periodontitis are divided into local and general:
- local remedies are used to treat the affected areas. This includes rinses, antiseptic solutions, anti-inflammatory gels and balms. Local treatments also include therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes, which can be used as an addition to the main therapy;
- general drugs, which are combinations of antibiotics in the form of tablets or intramuscular injections.
Non-invasive treatment for periodontitis may also include physical therapy. Auxiliary procedures using laser or electrophoresis will help eliminate inflammation faster.
Transplantation of a flap from the palate
Recession flaps are usually taken from the hard palate. In this case, the graft can consist only of connective tissue, or be epithelialized. The thickness of the flap depends on the tasks and the result that needs to be achieved. Direct closure of gingival recessions requires thick flaps, while restoration of visible gingival areas is carried out using thin and epithelialized fragments.
The graft is usually taken from the area of the hard palate, which borders the canines and premolars. In this case, it is necessary to retreat 2 mm from the edge of the gum. These rules allow you to avoid crossing the palatine artery and the development of bleeding. The thickness of the mucous membrane from the donor area should not be less than three millimeters, so probing is carried out first. After obtaining a flap, the defect is sutured
Surgical methods
Treating periodontitis surgically is the most radical method. But in the later stages of the disease, it is necessary to eliminate periodontal pockets and remove non-viable teeth. This can only be done surgically.
The degree of intervention depends on the severity of the pathology. In some cases, a positive result can be achieved by simply depulping the tooth to remove pathogenic bacteria. The procedure for splinting teeth (connecting mobile teeth with adjacent teeth to ensure immobility) and other methods is also used.
A separate stage of surgical treatment is prosthetics. This is done to restore the functionality of the dentition, distribute the chewing load evenly, and prevent displacement and further loss of teeth. In some cases, a temporary prosthesis can be used to quickly unload the chewing surfaces and eliminate mobility during the recovery phase.
Bone grafting
In severe periodontitis, there is a loss of bone tissue, which contributes to the loosening of teeth. In order to stop this process, bone grafting is used. The patient's own tissue, as well as artificial substitutes, can be used as a graft. In the first case, a section of bone can be taken from the chin, upper palate, or lower jaw. Since the patient’s own tissues are absolutely biocompatible, this method is the most effective, but requires two operations: tissue collection and transplantation.
Special bone substitutes do not have this disadvantage, so bone grafting in such cases is carried out in one stage. However, this method is characterized by a lower tissue survival rate, so it is not always possible to achieve the desired result with its help.
Treatment and prevention of periodontitis at home
After successful treatment of periodontitis, it is necessary to pay increased attention to oral hygiene. To do this you should:
- Visit your dentist regularly to remove plaque and tartar;
- eliminate caries and fill dental canals at the slightest manifestation of pathological processes;
- use hygiene products designed to prevent gum disease;
- After each meal, use dental floss and mouthwash with an antiseptic;
- follow other rules for the prevention of periodontitis.
Rehabilitation after surgery
After gum curettage, special rehabilitation is not always required. Closed curettage procedures, especially those performed using ultrasound or laser methods, require virtually no special restrictions. Only in the first hours it is necessary to refuse to eat, and in the next 2-3 days - limit yourself to only soft (or semi-liquid) non-hot and not cold food. At first, teeth may react to hot and cold, but this sensitivity disappears later. After open curettage, it is necessary to carefully follow the doctor’s recommendations to prevent complications.
Asepta Parodontal - specialized products for the treatment of periodontitis
has developed a whole range of drugs for the treatment and prevention of gum disease. It includes:
- Asepta therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste, which helps eliminate inflammation and bleeding of the gums. Contains a unique complex of medicinal extracts and active ingredients;
- Asepta Sensitive toothpaste for sensitive teeth. Provides gentle care for sensitive enamel and gums prone to inflammatory processes. Thermal mud in the paste helps heal damaged tissue and relieve irritation;
- Asepta mouthwash is intended to relieve symptoms of gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis and toothache caused by infection. The antimicrobial components of the drug help relieve inflammation and pain, and also have an antiseptic effect;
- Asepta Fresh mouthwash eliminates inflammation and bleeding of gums, prevents the formation of dental plaque, and also gets rid of pathogenic bacteria that cause bad breath;
- Asepta gel with propolis has an intense anti-inflammatory effect, reducing the sensitivity of enamel and promoting the healing of trophic ulcers. Effectively strengthens periodontal tissues and is suitable for patients of all ages.
- The adhesive balm in this series eliminates the causes and symptoms of inflammatory diseases of the mouth. The sticky base ensures a longer and more effective effect of the drug, allowing it to remain on the gums for a long time;
- Asepta vitamin and mineral complex contains all the necessary substances and active components for healthy teeth and gums.
Take care of your health with professional hygiene products!
Periodontal pocket: what is it?
Due to the inflammatory process, bone tissue is destroyed and gradually replaced by granulation tissue. The latter mainly consists of osteoclasts and microbial cells, which, gradually expanding their “habitat” zone, lead to even more active bone atrophy. Against the background of such “events”, a violation of the ligament between the tooth and gum occurs.
As a result, a periodontal or periodontal pocket is formed. It is a space equal in size to the area of destroyed bone and filled with granulation tissue, purulent masses, and food debris. Such a pocket is diagnosed in one of the following ways:
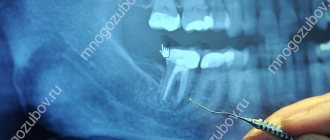
- using x-rays. Bone atrophy is determined by the presence of darkening in the image;
- periodontal probe. Normally, the probe penetrates under the gums by 1-2 mm; exceeding this indicator indicates a gum pocket.
Lack of treatment leads to further deepening of periodontal pockets, as a result of which the teeth sooner or later take a “fan” position. It should be noted that folk remedies not agreed with the doctor in this case are not considered treatment.
Clinical researches
According to the results of the clinical use of the Asepta line of products: the examined patients, already at the first follow-up examination (after 1-2 days) of using the Asepta line of products, showed a decrease in complaints of discomfort in the gums. On examination, hyperemia and bleeding of the gingival papillae are noted. On the 7th day, complaints of gum bleeding persisted in a minority of patients.
Upon examination, a decrease in hyperemia and swelling of the gums was noted, but bleeding persisted upon probing. On day 14, 2 patients continued to complain of bleeding gums when brushing their teeth; upon examination, a significant decrease in hyperemia and swelling of the gums was noted. After the final application of the gel with propolis, normalization of clinical manifestations was revealed, which is manifested by the absence of bleeding during brushing and probing.
Improved dynamics of indicators allows us to recommend the Asepta line of products for the local treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases.
Sources:
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Fuchs Elena Ivanovna Assistant of the Department of Therapeutic and Pediatric Dentistry State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)
- The use of adhesive balm "Asepta®" in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases L.Yu. OREKHOVA*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department V.V. CHPP**, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department S.B. ULITOVSKY*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor A.A. LEONTIEV*, dentist A.A. DOMORAD**, O.M. YAKOVLEV** SPbSMU named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, St. Petersburg - *Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, **Department of Microbiology
- The use of new anti-inflammatory drugs in the complex of therapeutic and preventive measures for periodontal diseases (E.D. Kuchumova, A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, L.Yu. Orekhova, S.B. Ulitovsky) E.D. Kuchumova, Ph.D., Associate Professor, A.A. Leontyev, dentist, O.V. Kalinina, dentist, L.Yu. Orekhova, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of Department, S.B. Ulitovsky, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- Article “Treatment and hygiene features for mild and moderate periodontitis” by S.B. Ulitovsky head Department of PFS, Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences, A.A. Leontyev Associate Professor of the Department of PFS, Ph.D. PSPbSMU named after. I.P. Pavlova
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis of mild and moderate severity using Asepta antibacterial agents (S.I. Gazhva, A.I. Voronina) S.I. Gazhva, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department A.I. Voronina, aspirant, dentist, Department of Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, State Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy"
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
Possible complications
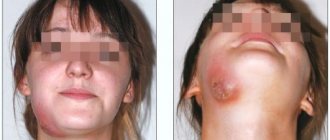
Complications can be caused by the individual characteristics of the body or violation of the doctor’s requirements. Increased tooth sensitivity can last up to two months. In order to speed up its regression, you will need to use special pastes and gels prescribed by your doctor. Swelling and hematoma at the surgical site may persist for up to 14 days. This is not dangerous and goes away on its own. In some cases, tightness and difficulty opening the mouth may occur, but this problem usually disappears within a few days. Teeth can remain mobile for up to 3 weeks. You must wait until the end of this period before returning to solid foods.
Contraindications
Traditionally, there are contraindications to the use of ultrasound in the treatment of periodontal diseases such as a tendency to bleeding, acute processes in the periodontium. The use of Vector has no such restrictions. Treatment with the device cannot be carried out in the following cases:
- Installed pacemaker;
- Individual intolerance to the components of Vector Fluid Polish;
- Malignant tumors in the oral cavity;
- Acute infectious diseases.
The gentle effect of the Vector device and the possibility of using it even in an acute period give the device advantages when choosing a method of treating periodontal diseases. If treatment with the device is started in a timely manner, in many cases it is possible to avoid surgical intervention.
Diagnostics
The presence of at least one of the above symptoms should be a reason to contact the clinic, where a more thorough examination will be carried out. Doctors at our clinic only need a simple examination to make a preliminary diagnosis. A comprehensive diagnosis of periodontitis includes a number of diagnostic procedures that are necessary to clarify the extent of the disease and differentiate it from other diseases. Diagnostic procedures:
- Probing of periodontal pockets.
- Orthopantomogram is necessary to assess the degree of destruction of the jaw bones.
- Calculation of periodontal indices.
- Bacterial culture or PCR of the detachable gingival pocket.
- Schiller-Pisarev test.
To clarify the cause of periodontitis, you may need the results of other examination methods: biochemical and general blood tests, glucose level testing, and others. Gastroenterologists and endocrinologists are often involved as consultants, since without adequate treatment of somatic pathology, the treatment of periodontitis is very difficult.