- Therapeutic properties of lysobact
- Indications for use of lysobact
- How to take lysobact?
- Contraindications for use
- Use during pregnancy
- Taking during lactation
- For sore throat
- For stomatitis
- Drug interactions
- Overdose and side effects
Lyzobact is a drug with the active ingredients lysozyme and pyridoxine hydrochloride.
Lysozyme is a natural enzyme found in human saliva. It fights pathogenic microorganisms that cause pain and inflammation, destroys viruses, bacteria and fungi, thus providing protection against inflammation and strengthening the immune system. Against the background of hypothermia and stress, the enzyme becomes insufficient to contain pathogens. Then the body needs additional help.
The active substances of lysobact act directly in the mucous membrane and destroy pathogens, affecting the membrane of bacteria and viruses and destroying it.
The topical drug is available in tablet form. Lysobact also contains lactose monohydrate and vanillin to improve taste.
Pharmacodynamics
A combined drug whose effect is determined by its constituent components.
Lysozyme is a protein enzyme, used as an antiseptic due to its direct effect on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, as well as fungi and viruses; takes part in the regulation of local nonspecific immunity.
Pyridoxine has a protective effect on the oral mucosa (has an anti-aphthous effect). Does not affect the pharmacodynamic properties of lysozyme.
Can a nursing mother take Lizobact?
Acting locally, the drug destroys pathogenic flora, regardless of its etiology: it can be bacteria, fungus or a viral infection. Once in the gastrointestinal tract, the drug is quickly absorbed, its components can accumulate in tissues and muscles. Lysozyme and pyridoxine are excreted by the kidneys - in the urine.
Despite the fact that lysozyme easily passes into breast milk, treatment of a nursing mother does not become dangerous for the baby. This is explained by the fact that lysozyme is a natural component that is part of the saliva of a healthy person. The child has his own lysozyme, secreted by the salivary glands. Increasing its content does not have negative consequences.
Pyridoxine is vitamin B6, which accelerates the healing process of damaged oral tissue, which also does not pose a risk to the child’s health.
Taking during lactation
Upon penetration into the gastrointestinal tract, the components of lysobact are quickly absorbed and accumulate in muscles and tissues. Excretion is carried out through the kidneys with urine.
Lysozyme and pyridoxine pass into breast milk, but do not have a negative effect on the baby's health. This is explained by the presence of lysozyme in human saliva; it is a natural component that does not pose a threat to the child. An increased content of lysozyme cannot lead to dangerous consequences. Pyridoxine belongs to the B6 vitamins and is also not dangerous for the baby.
How to take lysobact?
Lizobact is a local antiseptic drug. The tablets should be dissolved slowly in the mouth without swallowing. It is advisable to keep it in your mouth longer until completely dissolved.
The dosage of the drug depends on the age of the patients.
For children 6-7 years old it is 1 tablet three times a day, up to 12 years old - 1 tablet 4 times a day, over 12 years old and adults - two tablets 3-4 times a day. Lizobact must be taken for five days.
Important! The antiseptic effect of the drug is possible only if the rules of administration are followed. The tablet needs to be dissolved for a long time, after which you should not eat for 30-40 minutes. This is due to the fact that, together with food particles, the components will immediately penetrate into the stomach, without providing the proper effect. Such treatment will not bring results. It also makes no sense to take the tablets with water; they are intended solely for resorption.
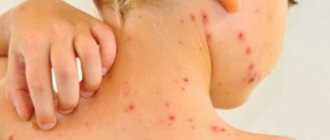
For sore throat
Sore throat affects the upper respiratory tract and occurs as a result of exposure to streptococcus. Affects the upper respiratory tract.
Lizobakt has an antiseptic effect and helps fight pathogens at the local level. However, it is not the mainstay in the treatment of the disease. When a diagnosis is made, the patient is prescribed antibacterial drugs; Lysobact acts as an additional drug for healing damaged areas.
As an adjuvant, the drug is prescribed:
- children over three years of age – one tablet at intervals of at least 4 hours;
- over 17 years of age and adult patients - two tablets with an interval of at least 4 hours.
Lizobakt during pregnancy
The use of the medicine is permitted throughout the entire period of pregnancy: from the first trimester until childbirth. It is especially important for pregnant women to know which drug can safely protect against the spread of infection in case of upper respiratory tract disease. Your own saliva, which contains lysozyme, may be produced in insufficient quantities, because many expectant mothers are prohibited from drinking a lot of liquid due to edema.
In addition, altered hormonal levels during pregnancy can have an inhibitory effect on the functioning of the salivary glands. Lyzobact will easily compensate for the lack of natural lysozyme, which effectively copes with its antiseptic properties without harming the unborn child.
Lizobakt and Laripront: is there a difference?
Laripront, like Lyzobact, contains lysozyme, a natural component that is safe for pregnant women and children. However, Laripront contains another active component - Dequalinium chloride, which is a synthetic antiseptic, active against a large number of pathogenic bacteria, as well as fungi.
The direction of action of both drugs is identical - they are intended for resorption in the oral cavity, disinfecting the mucous membranes of the pharynx. However, the patient may have pronounced allergic reactions to Laripront, which is less common in patients taking Lysobact.
Immunocorrective therapy for infectious lesions of the oral cavity
Results of clinical use of imudon
In recent years, one of the promising areas in increasing the effectiveness of therapy and preventing many diseases is the use of immunocorrective agents and methods. Currently, among the main groups of immunocorrective drugs, immunomodulators of microbial origin are of interest, among which there are three main groups - purified bacterial lysates, immunostimulating membrane fractions and bacterial ribosomes in combination with membrane fractions. New generation immunomodulators that can activate the formation of antibodies and stimulate defenses in the oral mucosa deserve special attention. Among them, Imudon should be mentioned first of all.
Imudon (produced by an international pharmaceutical company) belongs to the group of purified bacterial lysates. The drug is made from a mixture of lysates of strains of the most common bacterial and fungal pathogens of pathological processes in the oral cavity. Among them are Lactobacillus acidophilus, Streptococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Corinebacterium pseudodiphtericum, Candida albicans and others.
Imudon is intended for specific antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory immunotherapy of oral diseases. The drug is a polyvalent complex of antigens that can cause the formation of antibodies. The therapeutic effect of imudon is explained by its influence on the immune system, which is expressed in an increase in phagocytic activity due to a qualitative improvement in phagocytosis, an increase in the content of lysozyme in saliva, stimulation and an increase in the number of immunocompetent cells responsible for the production of antibodies, and an increase in the content of local antibodies (JgA ).
The antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activity of the drug determines its use both for the treatment of corresponding diseases of the oral cavity and for the prevention of relapses.
Imudon is available in white tablets for resorption in the oral cavity.
Imudon was prescribed to 88 patients with various diseases of the oral cavity (see table). Among the patients there were 45 men and 43 women aged from 18 to 72 years.
All patients received etiotropic and pathogenetic general therapy in accordance with the existing disease. The main clinical indications for the use of imudon were chronic, relapsing course, as well as the presence of an inflammatory process in the oral cavity.
Imudon was prescribed eight tablets per day with an average treatment duration of 10 days. For chronic conditions - six tablets per day for 20 days or more. It was recommended to keep the tablet in the mouth until it is completely dissolved.
In patients with chronic recurrent processes, imudon was prescribed two to three courses of treatment per year.
Clinical effectiveness of the drug Imudon - 95%
| Clinical recovery | 25 people (28%) |
| Significant improvement | 44 people (50%) |
| Improvement | 15 people (17%) |
| No effect | 5 people (5%) |
The effectiveness of Imudon is generally 95% (see figure). No deterioration from the therapy was noted. Treatment was well tolerated in all patients; no side effects were observed.
The clinical effect of therapy with imudon manifested itself quite quickly - on the third or fourth day of taking the medication - and was expressed in a decrease in acute inflammatory phenomena and pain in areas of lesions of the oral mucosa.
The effectiveness of imudon largely depended on the clinical form of the disease. The most impressive results were obtained in patients with various stomatitis; the use of the drug led to rapid epithelization of aphthae and cure. At the same time, chronic tonsillitis and pharyngolaryngitis required repeated courses of Imudon (two or three per year) to obtain an anti-relapse effect. A significant improvement and reduction in relapses was noted when imudon was prescribed to patients with recurrent oropharyngeal candidiasis and gingivitis of various etiologies.
Thus, this drug can be recommended for the treatment of acute and chronic diseases of the oral mucosa. The method is characterized by good efficiency, tolerability, short duration of use and is especially convenient in outpatient practice. Long-term results of treatment are characterized by a decrease in the number of relapses, as well as an extension of remission periods.
How to take Lizobact for sore throat
Sore throat is an infectious (contagious) disease of the upper respiratory tract that occurs when the throat is infected by the bacterium streptococcus. Lizobakt, having an antiseptic effect, helps the body fight the pathogen. However, the drug should not be used as the main therapy for angina. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the attending physician will prescribe treatment with antibiotics, which the patient will take orally. Lysobact will help accelerate the healing of damaged tissue.
For angina, Lizobact can be taken as an adjuvant therapy in the following dosages:
Children over 3 years old – dissolve 1 tablet every 4 hours.
Adults and children over 17 years old - dissolve 2 tablets every 3-4 hours.
Therapeutic properties of lysobact
Lysobact is used to treat inflammation and infections affecting the mucous membranes of the mouth, larynx, and gums. The antiseptic effect is ensured by the content of the following components:
- Lysozyme. An enzyme responsible for regulating local immunity. It tends to accumulate in the body in summer, a decrease is observed in autumn, and the content is lowest in spring. Affects pathogens, provides an antiseptic effect and immunomodulatory effect. Under the influence of lysozyme, the cell walls of microorganisms dissolve, in addition, it provides a secondary immunomodulatory effect. Due to the above properties, lysozyme is used to treat various infections, including SARS-CoV-2.
- Pyridoxine. Protects the oral mucosa without interfering with the activity of lysozyme. The inflammatory process is accompanied by the destruction of mucosal cells. A component with anti-aphthous action prevents cell damage and accelerates regeneration processes. Promotes the acceleration of amino acid metabolism and the formation of antioxidant protection.
A decrease in the level of natural lysozyme is possible due to exposure to pathogens; a deficiency can also be observed in children. Lysobact is prescribed to patients of different age groups. According to research results, the combined effect of lysozyme and pyridoxine promotes an increase in IgA in saliva.
Use during pregnancy
Lysobact is prescribed for the treatment of pregnant women in any trimester. It provides safe protection against viruses and the spread of infection during inflammation of the upper respiratory tract. During pregnancy, the enzyme content in saliva may be insufficient, which prevents effective protection against viruses and bacteria. Hormonal changes provoke slow functioning of the salivary glands. Taking the drug helps to compensate for the deficiency of the enzyme. Provides an antiseptic effect without harm to the child.