Have questions?
Herpetic or herpes stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa caused by the herpes simplex virus. The disease manifests itself as ulcers in the mouth, headache and even fever.
This type of stomatitis accounts for about 80% of all infectious lesions of the oral cavity. The infection mainly develops in children's bodies, and children under three years of age are most susceptible to it. HIV carriers, diabetics, patients with chronic pathologies and people with weakened immune systems are also at risk.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of herpetic stomatitis vary depending on the form and stage of progression of the disease. Common signs of a viral infection include:
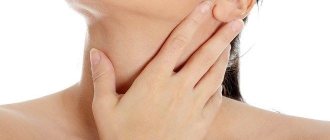
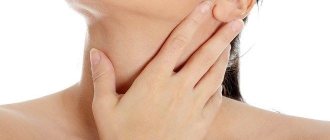
- swelling of the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes;
- jump in body temperature;
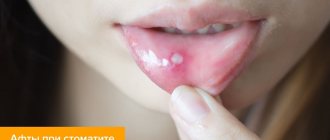
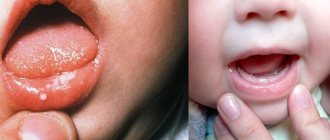
- blisters on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, tongue, palate, which are damaged and turn into bleeding ulcers and erosive formations;
- discomfort, pain, burning, itching in the mouth;
- weakness, migraine.
In adults, viral herpetic stomatitis is more complicated. At the same time, a severe form of the disease often develops in people who had an acute stage of the disease in childhood, and at the moment their body is weakened due to severe hypothermia, blood disease, cancer, etc.
What can cause stomatitis?
Many factors can lead to inflammation of the mucous membrane: from banal mechanical damage to disruptions in the body that are not related to the dentist’s field of work.
The following causes lead to stomatitis :
- neglect of oral hygiene recommendations;
- injury to the mucous membrane from sharp edges of teeth or fillings, dentures or other objects;
- dental diseases - caries, tartar, etc.;
- allergies - not only to food, but also to hygiene products and even dental materials;
- various diseases - from viral to endocrine, such as diabetes;
- poorly made prostheses;
- expired prostheses;
- metabolic or immune disorders;
- problems with microflora in the body;
- direct contact with the mucous membrane of pathogenic microorganisms;
- bad habits - smoking, drinking strong alcohol;
- reaction to certain medications.
The mucous membrane is much easier to damage than the skin. Especially in the mouth, where it is always exposed to temperature changes, touched by teeth, dentures, braces and solid food particles.
The cause of dental disease is mainly pathogenic bacteria (for example, caries is caused by streptococcus), which also harm the gums. And tartar is a hardened plaque that contains not only microbes, but also other unfavorable components. In addition, if the stone is subgingival, then the mucous membrane suffers first.
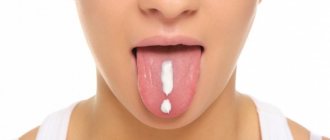
In many cases, allergies are discovered suddenly. The patient may not be aware of its presence, since he calmly eats any food. However, chemicals in toothpaste or mouthwash can cause a reaction. Studies have shown a negative effect on the mucous membranes of sodium lauryl sulfate, contained in some toothpastes. If the problem began soon after the restoration or treatment of the tooth, then you should consider the possibility of the body's response to the filling or crown material.
Decreased immunity can also cause deterioration of gums. And metabolic disorders affect not only the supply of microelements to the body’s tissues (including the mucous membrane), but also the composition of saliva, a decrease in the protective properties of which makes the oral cavity vulnerable to bacteria. Approximately the same can be said about the beneficial microflora: if it is in order, it helps to suppress the work of harmful microorganisms; if it is disrupted, the microbes attack vulnerable areas.
The cause of stomatitis in adults and children can be obvious - direct entry into the mouth of a large number of pathogenic bacteria. They can get from contaminated surfaces. Simply put, if a child constantly puts various objects into his mouth, stomatitis may occur. If an adult has carried through the years the bad habit of biting nails or pens, this can also contribute to the appearance of inflammation.
Medicines can have different effects on the body, in particular, they can affect the immune system, microflora and saliva production. Dry mouth is promoted by antihistamines and antihypertensive drugs, anticoagulants, antipsychotics, antispasmodics, etc. And a low level of saliva production provokes the growth of bacteria. Antibiotics and anti-asthma medications can lead to Candida infections in the mouth. There can be many options, including the influence of the sugar contained in the medicine. stomatitis often appears in adults as a result of treatment for a completely different pathology.
Classification of the disease
Before starting treatment for herpes stomatitis, it is necessary to determine the form and degree of its progression. At the same time, acute herpetic stomatitis in children is diagnosed already when the virus first enters the body.
The severity of the disease is divided into:
- Light. Small blisters form on the oral mucosa - they quickly disappear after they rupture;
- Average. The rashes are more extensive, body temperature rises (up to 38º);
- Heavy. The patient has an abundance of ulcers in his mouth, and after they disappear, new ones appear. Symptoms are supplemented by fever, headache and chills, sometimes the patient feels sick and has diarrhea.
In the absence of proper treatment, chronic recurrent herpetic stomatitis develops. This form of the disease is already characterized by group rashes (on the inside of the cheeks, tongue and palate). The formations combine and form painful erosions. In the recurrent stage, except for rashes, no other symptoms of the disease are noted. The disease may return 2-6 months after treatment.
Stomatitis
Cold
HIV
Fungus
Scarlet fever
Gastritis
12052 24 September
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Stomatitis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Stomatitis is a collective name for diseases of the oral mucosa, manifested by its redness, swelling with the formation of areas of erosion, ulcers or blistering rashes. Stomatitis affects approximately 20% of the population, most often children. Stomatitis can be either an independent disease or a complication or manifestation of other diseases (for example, scarlet fever, influenza, measles, etc.).
Causes of stomatitis
There is no single factor that is the sole cause of oral inflammation. With stomatitis, bacteria or viruses are detected, especially in ulcers on the mucous membrane. However, a diverse microflora is always present in the oral cavity, but stomatitis makes itself felt only when there is a strong additional impact on this microflora.
These impacts include:
- trauma to the mucous membrane caused by overzealous brushing of teeth, rough food, etc.;
- decreased immunity due to colds, vitamin deficiencies, chronic diseases, stress, poor nutrition, as well as more serious diseases (anemia, cancer and autoimmune diseases, HIV);
- entry of a large number of pathogenic microorganisms into the oral cavity through dirty hands, unwashed foods, etc.;
- conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microflora due to the presence of caries, tartar and plaque, lack of proper teeth cleaning, etc.;
- uncontrolled use of drugs that affect the quantity and quality of saliva and reduce its antimicrobial potential;
- inhibition of normal microflora by antibiotics;
- dehydration of the body with a decrease in the amount of saliva;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, pancreatitis, etc.).
Classification of the disease
Due to its occurrence:
- traumatic stomatitis
occurs as a result of the influence of physical (wound, burn from hot food, etc.) or chemical (burn of the oral mucosa with caustic substances, etc.) factors on the mucous membrane; - infectious stomatitis
occurs as a result of a viral, bacterial or fungal infection; - specific stomatitis
occurs as a result of a specific infection (tuberculosis, syphilis); this group includes radiation, drug, and stomatitis due to occupational diseases; - symptomatic stomatitis
develops against the background of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular, nervous, endocrine systems, and blood diseases; - allergic stomatitis
develops upon contact with allergens.
According to the clinical picture:
- catarrhal stomatitis;
- ulcerative stomatitis;
- aphthous stomatitis.
With the flow:
- spicy;
- chronic.
There are stomatitis associated with dental problems - for example, denture stomatitis occurs due to damage to the mucous membrane by dental structures, due to poor care of removable dentures, and the patient’s failure to comply with oral hygiene.
Symptoms of stomatitis
In children, the disease is more severe than in adults: body temperature may rise significantly and intoxication may be present.
In adults, oral stomatitis, as a rule, is not accompanied by fever, except in cases of deep damage to the mucous membranes in the ulcerative form of the disease.
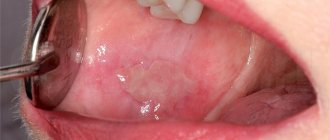
The most common is catarrhal stomatitis, which is characterized by inflammation of the oral mucosa without the formation of deep defects (ulcers). For those around you, catarrhal stomatitis manifests itself as “stale breath”, for the patient himself – pain, swelling and redness of the mucous membrane. Gingival papillae are easily injured and bleed.
In persons with pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as with inadequate treatment, catarrhal stomatitis tends to progress to the next stage - ulcerative with the formation of defects throughout the entire depth of the mucous membrane. It is accompanied by an unpleasant odor from the mouth, even putrefactive, the ulcers are covered with a gray coating, and eating any food leads to increased pain. Ulcerative stomatitis is more severe than catarrhal stomatitis and can cause a slight increase in temperature and enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
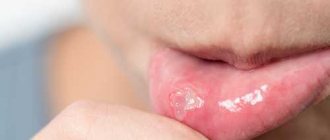
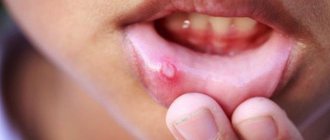
Aphthous stomatitis manifests itself in the form of small (3-5 mm) single or multiple defects of the mucous membrane of an oval or round shape, surrounded by a thin bright red border and covered with a yellow-gray fibrin coating. Aphthae do not form simultaneously, so you can see different stages of their development. Healing of aphthae begins after the fibrin plaque peels off on its own and ends with the complete disappearance of the defect.
Allergic stomatitis in the mouth occurs against the background of an exacerbation of the underlying disease - allergies. Increased sensitivity of the body can occur to food, medications, pollen, animal hair, cosmetics and care products, and even clothing. Most often, stomatitis is provoked by toothpastes that contain flavorings and chemical components.
Among viral stomatitis, the most common is herpetic stomatitis, which worsens against the background of ARVI. The disease begins with general malaise and lasts 7-10 days.
The oral mucosa becomes red and swollen, and regional lymph nodes become enlarged. After a few days, a blistering rash appears on the tongue and inner surface of the cheeks, and inside the rash there is a translucent liquid. After the bubbles open, small erosions appear, which are covered with a yellowish film.
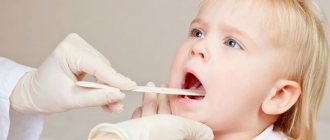
Diagnosis of the disease
Adequate treatment of stomatitis can be prescribed by determining what caused it - bacteria, fungi or viruses.
If a fungal infection is suspected and to assess the effectiveness of therapy,
Candida albicans
in an oropharyngeal scraping and culture is performed for yeast-like fungi of the genus
Candida
and
Cryptococcus to determine sensitivity to antifungal drugs.
How to treat herpetic stomatitis?
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis in children and adults can be general or local. The therapeutic treatment strategy is determined by the form and severity of the disease. In this case, the patient is usually shown:
- high-calorie diet, drinking plenty of fluids, bed rest;
- antiviral drugs (orally, intravenously or intramuscularly);
- restorative therapy (taking vitamins);
- symptomatic treatment (use of antipyretics, painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs);
- local therapy (rinses, applications, etc.).
When choosing tactics for treating acute or chronic herpetic stomatitis in adults and children, it is important to correctly determine the form and stage of the disease. That is why experts urge patients not to self-medicate, but to immediately consult a doctor if signs of damage appear.
Therapy under the supervision of a specialist will allow you to recover quickly and without consequences for the body. With the right approach, herpes stomatitis in a child or adult can be cured in 10-14 days.
Acute herpetic stomatitis in children and adults: treatment
When herpetic stomatitis is detected in adults and children, it is possible to determine how and how to treat this disease only after differential diagnosis: the herpetic and aphthous types are very similar in symptoms, but the drugs used for therapy are completely different. Therefore, first of all, you need to do tests and make sure that the cause of the disease was the herpes virus.
When treating the disease, antiviral drugs, immunomodulators (to stimulate the immune system), local antiseptic treatments, and vitamin complexes are used to maintain the body's defenses. Additionally, symptomatic medications are used: painkillers, antipyretics for high body temperature in children (above 38.5 degrees).
The doctor prescribes all medications and treatment regimens individually, taking into account the patient’s age, the general condition of his body, the severity of the disease and its form (acute or chronic). In addition, proper dental care is also important - both during and after treatment. The doctor will give all the necessary recommendations for care and help you choose hygiene products individually.
Herpetic stomatitis during pregnancy requires a special approach. In addition to local treatment with antiseptics, it also requires antiviral therapy, but the doctor selects the drugs very carefully, taking into account the possible risks for the pregnant woman and the fetus. Treating yourself in this situation is extremely risky; self-medication can cause serious complications in the body of the mother and her unborn child.
“32 Dent” clinics provide all types of dental services, including gum treatment. Dentists are equipped with the latest equipment, and doctors have extensive experience working with a variety of, even the most complex, clinical cases. By contacting us, you receive high-quality treatment and lasting results at an affordable price.
Sources:
- Personal experience as a dentist;
- Danilevsky N.F., Leontyev V.K., Nesin A.F., Rakhniy Zh.I. Diseases of the oral mucosa. - M.: OJSC "Dentistry", 2001;
- Ivanova E.N. and others. Diseases of the oral mucosa. - Rostov n/d.: Phoenix, 2007;
- Ed. prof. A.L. Mashkilleyson, prof. E.V. Borovsky. Diseases of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and lips. - M.: MEDpress, 2001;
- Kolesov A.A. Pediatric dentistry. M.: Medicine, 1991;
- Vinogradova T.F., Maksimova O.P., Melnichenko E.M. Periodontal disease and oral mucosa in children. M.: Medicine, 1983;
- Whitley RJ, Roizman B. Herpes Simplex virus Infection // The Lancet. 2001.
What happens if stomatitis is not treated?
To avoid the question “To treat or not to treat?”, you should remember two facts about inflammatory processes:
- Neglected inflammation eventually progresses to the chronic stage. This means that problems with the mucous membrane will continue in the future. Chronic inflammation not only causes constant discomfort, but can also develop into a more serious problem.
- Inflammation of one area of the mucous membrane can spread to others. Thus, inflammation of the gums and inner surface of the lips can spread to the respiratory tract and further.
Here are some of the possible complications:
- chronic stomatitis,
- respiratory diseases (for example, laryngitis),
- periodontitis,
- loosening of teeth (after periodontitis),
- scars on the mucous membrane after healing of numerous ulcers,
- gastrointestinal diseases
- vision problems (with a herpetic infection, inflammation can rise there too).
General symptoms of stomatitis
The main manifestation of stomatitis is inflammation of the mucous membrane, however, depending on the form of the disease, additional different symptoms may occur.
There are 3 main features:
- Hyperemia and redness. Swelling and an unhealthy red color indicate the beginning of a pathological process. immediate treatment at this stage of stomatitis , then small round ulcers may appear in the future. They are usually gray or white, with a red border and film.
- Severe pain and ulcers. At this stage, the surface of the mucous membrane is covered with small ulcers. They can be on the inside of the lips and cheeks and even under the tongue. The patient experiences pain at this time and finds it difficult to eat.
- Fever and headache. The rise in temperature may vary depending on the degree of inflammation. With profuse ulcers, it becomes high, and the headache becomes more pronounced.
Stomatitis should be treated as recommended by your dentist. It is best to consult a specialist at the stage of swelling and redness to prevent further development of inflammation and the appearance of ulcers. However, not everyone pays attention to the first symptoms stomatitis .