Symptoms:
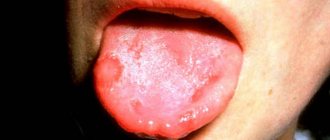
- red, swollen tonsils with white or yellowish coating or streaks;
- a sore throat;
- difficult and/or painful to swallow;
- fever (temperature above 38.0);
- cervical lymph nodes are enlarged;
- hoarse or hoarse voice;
- headache;
- stiff neck muscles;
- abdominal pain (especially in young children).
In infants:
- drooling due to pain in swallowing;
- anxiety;
- refusal to eat
- With chronic tonsillitis, your breath may smell bad.
Treatment of sore throat in children
Mild and moderate forms of tonsillitis are treated on an outpatient basis. If the disease is severe, therapy is ineffective, or a purulent complication is suspected, the patient is hospitalized in the infectious diseases department. During a sore throat, the child is isolated for 3-4 days, bed rest, plenty of fluids, and gentle nutrition are prescribed.
When a bacterial infection is isolated, antibacterial drugs are taken taking into account the resistance of the pathogen - macrolides, penicillins, cephalosporins. The course of treatment is 5–15 days. For viral sore throat, antiviral drugs are indicated.
To alleviate the severity of symptoms and prevent the development of a secondary bacterial infection, local treatment is carried out:
- gargling with antiseptics and herbal decoctions;
- dry heat and warming compresses on regional nodes (unacceptable for fever, body temperature above 37°C);
- irrigation of the pharynx, treatment of the back wall of the pharynx and tonsils with antimicrobial drugs;
- resorption of lollipops, tablets with antiseptic action;
- vitamin therapy;
- aromatherapy with essential oils;
- inhalation.
Taking into account the specifics of the disease and its clinical manifestations, the therapist prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antipyretics, immunomodulators, and antihistamines. In the subacute period, physiotherapy is included - ultraphonophoresis, laser radiation, UV therapy, UHF therapy.
For frequently recurring tonsillitis, the issue of complete removal of the tonsils along with adjacent tissues using a laser, radiofrequency electrode, or ultrasonic scalpel is resolved. If complications develop in the form of a peritonsillar abscess, it is opened.
Complications of tonsillitis
- Labored breathing.
- Sleep apnea (holding your breath during sleep).
- Spread of infection to the tissue near the tonsils (peritonsillitis), peritonsillar abscess - accumulation of pus behind the tonsil.
- Acute cervical lymphadenitis is inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes.
Streptococcal tonsillitis can cause complications such as:
- acute rheumatic fever, affecting the joints, heart and other organs;
- glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys, which can lead to serious consequences, including kidney failure).
Treatment with antibiotics significantly reduces the likelihood of complications after streptococcal sore throat.
The mechanism of development of sore throat in children
The infection reaches the tissues of the lymphoid pharyngeal ring through the respiratory tract, where it adheres, multiplies and releases toxic products. At the site of introduction of the pathogen, an inflammatory focus is formed with local changes - swelling of the lymphoid tissue, accumulation of purulent masses in the lacunae.
With the accumulation of exotoxins, tissue breakdown products and microbial bodies, a toxic and allergic syndrome develops. The infection from the source of inflammation spreads through the bloodstream throughout the body, affecting internal organs and systems. With a strong immune system, early and properly selected treatment, inflammation can be stopped at any stage.
Diagnosis of tonsillitis
- For tonsillitis, the doctor will examine the child's throat, as well as his ears and nose, where there may also be inflammation.
- The doctor will examine the child's skin, since streptococcal sore throat sometimes causes a specific rash. This is what is called “scarlet fever” - it is not some kind of separate disease, but a sign of damage to the body by streptococcus.
- The doctor will feel the cervical lymph nodes - as a rule, with tonsillitis they swell.
- The doctor will feel the spleen to distinguish a sore throat from mononucleosis, which also causes swollen lymph nodes.
- The streptococcal test is a simple and accurate way to distinguish streptococcal tonsillitis from viral tonsillitis. The doctor takes a scraping from the child’s throat and within 24-48 hours the result is ready.
- In some cases, a general blood test may be needed, the results of which can also indicate the viral or bacterial nature of the disease. It is usually taken if the streptococcal test is negative, but the course of the disease leaves the doctor in doubt.
About the clinic
Euromed Clinic is a multidisciplinary family clinic in the center of St. Petersburg.
- Calling a doctor to your home
- 24/7 therapist appointment
- Tests, ultrasound, x-ray
- Whole body diagnostics
- Hospital and surgery
- Vaccination
Find out more about the clinic
Classification
Taking into account the causes of inflammation, sore throat occurs:
- Primary or simple.
Initially develops in the tonsils. In 85% of all cases, the causative agent is streptococcal infection.
- Secondary.
It occurs as a manifestation of any other disease. Mostly occurs against the background of blood pathologies, with typhoid fever, scarlet fever, measles, diphtheria.
- Specific.
Causes a specific infection - pathogens of chlamydia, candidiasis.
Along the way, tonsillitis can be acute, and with frequently recurring inflammation it becomes chronic.
Depending on the nature of the changes in the lymphoid pharyngeal ring, several clinical forms of the disease are distinguished:
- catarrhal;
- lacunar,
- follicular,
- combined,
- herpes,
- phlegmonous,
- ulcerative-membranous,
- fibrinous.
According to the severity, tonsillitis occurs in mild, moderate or severe form. The severe form is characterized by complications, exacerbations of chronic diseases, and the addition of a secondary infection.
Treatment of tonsillitis
The child should be provided with:
- peace and the opportunity to sleep as much as he wants;
- Drink plenty of fluids to relieve sore throats and prevent dehydration;
- air humidification;
- a sore throat can be relieved by both warm drinks and cold ice cream, especially popsicles;
- for a sore throat, it helps to gargle with a solution of table salt and soda - a teaspoon of salt and a small pinch of soda per 250 ml of warm water;
- Children over 4 years old can be offered lozenges for sore throats. Do not give candy to small children - they may choke;
- do not smoke when your child is sick, avoid strong odors that irritate the throat;
- A sore throat and fever can be relieved by medications containing paracetamol and ibuprofen. Don't give children aspirin; in rare cases, it can cause deadly Reye's syndrome.
Confirmed bacterial tonsillitis (usually streptococcal tonsillitis) is treated with antibiotics. It is dangerous to interrupt or stop the course because it increases the likelihood of infection spreading to the joints, heart, kidneys and other organs. Continue taking antibiotics even if your symptoms are completely gone.
Diagnostics
Children with suspected acute tonsillitis need to consult a therapist or pediatric otolaryngologist. At the stage of primary diagnosis, the doctor studies and analyzes complaints, conducts a visual examination of the mucous membrane of the throat, and palpates regional lymph nodes.
Characteristic signs of tonsillitis are detected when examining the pharynx - swollen, red tonsils and arches, infiltration, white plaque, and sometimes pus with an unpleasant odor. Plaque on the tonsils is easily removed with a spatula and does not leave bleeding marks.
To identify the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs, sputum culture is performed for flora. All children are prescribed a clinical blood test to determine the activity of the inflammatory process.
Reference!
An alternative to the bacteriological method is a rapid test.
The analysis is characterized by a reliable level of sensitivity and high speed of execution, which makes it possible to make a diagnosis in 15–20 minutes and begin treatment immediately. If necessary, additional instrumental studies are prescribed: ultrasound of the kidneys, radiography of the paranasal sinuses, electrocardiography of the heart. Differential diagnosis is carried out with acute respiratory infections, acute pharyngitis, and pharyngeal diphtheria.
Clinical recommendations for disease prevention
The main methods of preventing tonsillitis in children are compliance with sanitary and hygienic measures (avoiding contact with patients and their things, washing hands, using a scarf and hand sanitizers) and strengthening the immune system (hardening, playing sports, etc.).
Tonsillitis is a common disease in children and adults, which without proper treatment can become chronic. If you notice symptoms of illness in your child, immediately contact the children's medical department.
Sources:
- HELL. Vetrova. Acute tonsillitis in children: a pediatrician’s point of view // Pediatric pharmacology, 2014, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 61-64.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6248716/ Raja Kalaiarasi, Kalaivani S Subramanian, Chellappa Vijayakumar and Ramakrishnan Venkataramanan. Microbiological Profile of Chronic Tonsillitis in the Pediatric Age Group // Cureus. 2022 Sep; 10(9): e3343.
- T.V. Spichak. Diagnosis and treatment of tonsillitis in children from the standpoint of evidence-based medicine // Issues of modern pediatrics, 2010, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 130-135.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Chronic tonsillitis in a child: treatment methods
This disease is diagnosed in children if inflammation of the tonsils occurs more than twice a year. In case of chronic disease, the tonsils themselves become a source of infection. The immune system weakens, and the child is often exposed to illness.
Chronic tonsillitis should be treated by an experienced otolaryngologist. Some ENT doctors recommend removing the tonsils immediately. But you need to remember, by removing the tonsils, you lose the body’s natural defenses against bacteria and viruses forever!
At the ENT Clinic of Doctor Zaitsev, we treat chronic tonsillitis, and we resort to removal of the tonsils only in the most extreme cases, when conservative treatment methods have been completely exhausted.
The procedures for ultrasonic medicinal irrigation of the tonsils using the “Tonsillor” apparatus (it can be seen in the photo) have a good therapeutic effect. Our clinic also has a unique vacuum attachment for this device, which has no analogues in other medical institutions. This attachment is painless, safe and can be used to treat children starting from school age.
The degree of enlargement of the tonsils in a child
There are 4 stages of hypertrophy of the glands:
- At the first stage, the inflamed tissue of the tonsils covers no more than 30% of the lumen between the pharynx and the sky. In this state, it causes almost no discomfort, so it is difficult to detect at this stage.
- At the second stage, hypertrophied tissue covers half of the lumen. The child begins to have difficulty swallowing and breathing freely, and a sensation of a foreign body in the throat.
- At the third stage, there is severe difficulty in breathing and swallowing.
- On the fourth, the pharynx is almost completely blocked by inflamed tonsil tissue. It is difficult to bring the condition to this stage, since already at the third stage the child’s well-being requires immediate medical attention.
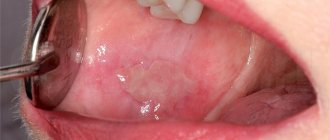
Causes of white plaque in a child
Young mothers panic when they see a white coating on their baby’s tongue. First of all, this is due to ignorance of the causes of the condition, which are divided into natural and dangerous to health.
When there is no reason to worry
Babies may experience a white coating after feeding
Babies who are breastfed may develop a white coating in their mouth after feeding. This is normal.
The same situation is observed in babies who are fed artificial formulas.
In both cases, the plaque disappears 10–15 minutes after finishing the meal. The oral cavity again acquires a healthy pink tint.
Such plaque on the tongue, inner surface of the cheeks and palate also forms after regurgitation. It is lumps of undigested milk and looks like cottage cheese.
Important! Plaque can be easily removed. To do this, wrap a clean finger in a bandage and rub it over the surface covered with the white formation.
When to see a doctor
When white plaque is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, you need to consult a doctor.
You need to visit a pediatrician in the following cases:
- the baby refuses to eat, is capricious, sleeps restlessly;
- there are diaper rashes on the body;
- there is an increase in body temperature;
- there is a lot of plaque in the oral cavity, it is difficult, but still not completely, to be removed;
- white mass appears regularly;
- plaque forms on the genitals.
The reasons for this lie in diseases.
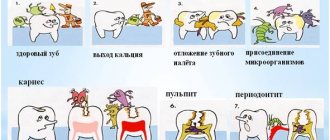
Diseases of infectious and dental origin
Such diseases include:
Types of disease
- Spicy. Most often, the acute form develops after suffering from acute respiratory viral infection, due to reduced immunity. Source: A.D. Vetrova Acute tonsillitis in children: a pediatrician’s point of view // Pediatric pharmacology, 2014, v. 11, no. 2, pp. 61-64
- Chronic. Occurs after relapses if the patient has not fully recovered. Diseases in the mouth, nose, and structural features of the tonsils contribute to the development of chronic tonsillitis. Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6248716/ Raja Kalaiarasi, Kalaivani S Subramanian, Chellappa Vijayakumar and Ramakrishnan Venkataramanan Microbiological Profile of Chronic Tonsillitis in the Pediatric Age Group // Cureus. 2022 Sep; 10(9): e3343
Causes of tonsillitis
As a rule, the cause of the disease is bacteria and viruses (usually streptococcus). Typically, infection occurs through airborne droplets, especially when children are in large groups (kindergarten, school, various clubs and sports sections). If the causative agent of the disease is bacteria, you can become infected through dishes, a handshake, or through the patient’s personal items (towel, spoon). A child only needs to play with the toys of another sick child to become infected. Alas, acute tonsillitis is a highly contagious disease; and it is very easy to become infected with it.
Another cause of the disease is microorganisms that constantly live on the mucous membranes. This is the norm. A healthy body controls their amount and does not allow them to be exceeded. But as soon as the immune system weakens, the number of pathogenic microorganisms begins to increase: and in essence it turns out that the body infects itself. That is, the development of inflammation can occur with prolonged exposure to unfavorable factors on the child’s body that cause a decrease in immunity: dry indoor air, cigarette smoke, polluted air in big cities, etc.
Prevention of tonsillitis
To reduce the risk of developing the disease, you need to devote time to preventing this disease and strengthening the immune system. It is necessary to accustom children to hardening procedures. Hardening will bring positive results if you do it gradually, and at the same time consistently and regularly.
It is important to eat healthy and varied, eat foods rich in vitamins and avoid seasonings that irritate the throat. You also need to remember the relationship between the ENT organs and the surrounding tissue. Therefore, it is extremely necessary to promptly treat dental diseases and any inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx and larynx.
From an early age, children should be taught sanitary standards: washing hands, washing fruits, covering their mouths when coughing with a handkerchief or napkin. During periods of epidemics, it is advisable to avoid places with large crowds of people.
Following these simple measures will help avoid inflammation and the unpleasant consequences of this disease.
Diagnostic methods
During the consultation, the doctor will examine the patient’s throat and palpate the lymph nodes. The examination should be carried out by a pediatrician and pediatric ENT specialist. In case of decompensation of the chronic form, the child requires consultation with a pediatric cardiologist, rheumatologist, nephrologist, because tonsillitis can cause concomitant diseases. To rule out pockets of infection in the oral cavity, the child should be examined by a dentist. Laboratory and instrumental studies are also prescribed:
- blood and urine tests;
- pharyngoscopy;
- blood test to determine C-reactive protein;
- definition of ASL-O;
- bacterial culture from the pharynx for flora.
If there are difficulties in making a diagnosis, additional studies may be required - ECG, x-ray of the sinuses, etc.
How is inflammation treated?
The tactics for treating enlarged tonsils in a child consists of treating the underlying disease that caused this symptom (taking antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal drugs), and influencing them directly to regenerate the affected tissues. The latter includes:
- washing the tonsils from pathogenic microorganisms and mucus with antiseptic solutions;
- reducing swelling - taking antihistamines and ultraviolet irradiation;
- UHF therapy, which improves blood microcirculation;
- exposure to ultrasound to free the lacunae of the tonsils from pus, which can accumulate in them;
- laser exposure to destroy infection and its pathogens.
"ENT Clinic of Doctor Zaitsev"
Treatment of tonsillitis in children in Moscow is offered by many medical institutions: from district clinics and multidisciplinary centers to private clinics. The main thing is to make the right choice!
Our clinic accepts patients from the age of three. The ENT clinic has everything necessary for the successful treatment of sore throat and chronic tonsillitis: the most modern equipment and instruments, its own treatment methods, and most importantly, highly qualified ENT specialists with extensive practical experience. A visit to a doctor for a small patient is always stressful, and our task is to make the appointment as calm and easy as possible for the child. The examination takes place in a playful way: the baby no longer perceives the treatment as something scary and unpleasant, and the mother’s saved nerves are worth a lot. Our clinic is equipped with a children's corner where a child can play, read, or just drink tea and cookies while the mother and the doctor discuss the treatment regimen. Prices for our services have not changed for more than three years and remain one of the best in Moscow.
If you have discovered the first signs of a sore throat in your child, or he has been suffering from relapses of chronic tonsillitis for several years, please do not delay and make an appointment. We will help you cope with this illness.