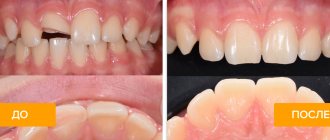
What is tooth flux?
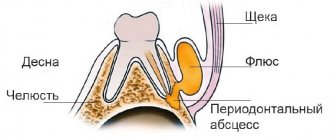
Flux, or, in dentist's language, periostitis, is a very unpleasant pathology, which is characterized by inflammation of the periosteum and soft tissues. The causes of flux on the gums can be different: trauma, gum disease, poor-quality dental treatment - all this can lead to a complication in the form of periostitis. The localization of the disease does not depend on the area of the jaw: flux of the upper and lower teeth occurs equally often.
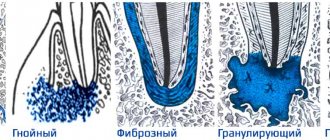
Flux under a tooth (or above a tooth, if we are talking about the upper jaw) visually resembles an inflamed sac. However, this is far from the only possible manifestation of periostitis. There is also a serous form, when the periosteum becomes inflamed as a result of trauma and damage, as well as one of the most unpleasant types - diffuse, when the infection is localized in different parts of the jaw, which requires extensive surgical intervention with the participation of a maxillofacial surgeon.
Why do my gums or cheeks swell?
In most cases, swelling of the gums or cheeks is caused by purely dental reasons:
- Flux
During gumboil, the gums become swollen and painful, and the temperature rises. The development of a tumor begins with an ordinary carious cavity. It gets infected, which eventually leads to tooth decay. Pus accumulates and begins to look for a way out. The cheek swells greatly and a white spot appears on its surface. Without treatment, a fistula forms in this place, and the cheek turns into a huge purulent wound. If you do not seek help from a doctor in time, blood poisoning may occur.
- Removal of a tooth
This operation inevitably involves damage to soft tissue, and swelling is a natural phenomenon. After a while it subsides. If this does not happen, and the gums swell more and more, then you need to urgently visit a doctor. Causes of severe swelling can be:
- a large accumulation of pus,
- incipient periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum),
- infection in the wound.
If you notice swelling of the cheeks and gums, or tissues of the oral cavity, then you need to consult a dentist.
The doctor will determine the exact cause, begin treatment or refer you to another specialist.
Leave your phone number. The clinic administrator will call you back.
By leaving a request on the site, you consent to the processing of personal data
Make an appointment
Initial consultation with a dentist
For free!
- Inflammatory infiltrate
It usually occurs against the background of pulpitis or periodontitis. Pus begins to accumulate in the soft tissues, which causes the appearance of phlegmons and abscesses. It is considered a very dangerous disease because it can lead to big troubles.
- Periodontal disease
Swelling is accompanied by aching or sharp pain. There is no conservative treatment; surgical intervention is necessary. Often it is necessary to remove some teeth and install dentures.
- Teeth chips
The sharp edges of a destroyed tooth begin to scratch the inner walls of the cheek, which leads to inflammation and severe swelling.
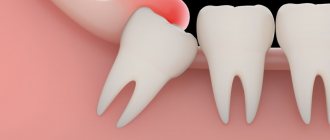
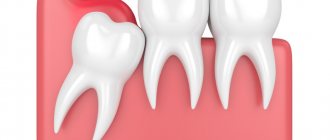
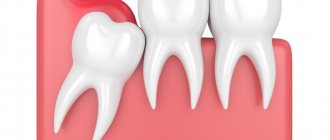
- Wisdom tooth growth, pericoronitis
The eruption of the figure eight often leads to inflammation of the gingival hood. Swelling, as a rule, extends to both the cheek and gum.
- Carious teeth
Advanced caries often causes not only the gums to swell, but also the tonsils and cheeks. After eliminating the cause, the swelling gradually goes away. Folk remedies are useless here; urgent medical help is needed.
- Cyst
Depending on the type of cyst, its shape, and location, the doctor decides on conservative or surgical treatment. In some cases, a consultation with an oncologist may be required.
- Gum disease
Swelling is one of the main signs of inflammation of periodontal tissue. Without treatment, the disease quickly becomes chronic and difficult to treat. There is a high chance of losing a tooth.
In addition to the reasons listed, swelling of the gums and cheeks can be caused by:
- inflammation of the facial nerves;
- pathologies of the maxillofacial skeleton;
- allergies;
- disruption of the immune system;
- inflammation of the submandibular and parotid lymph nodes as a result of an infectious disease;
- malignant neoplasm;
- facial injury;
- diseases of internal organs, such as the heart;
- eye diseases;
- blood pathologies.
Symptoms of gumboil
Flux on the gums in adults occurs much more often than in children (approximately 80-90 percent of all cases). A characteristic feature of the pathology is that it does not go unnoticed. This is one of the most unpleasant diseases, causing severe discomfort. The most striking symptoms are the classic purulent flux.
Symptoms
- Severe throbbing pain.
- Inflammation and swelling of soft tissues. At the advanced stage, the side of the face on which the flux is diagnosed swells.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Discomfort and pain when eating and talking.
- Flux of the lower tooth (in the molar area) can lead to numbness of the lip and part of the chin.
- Weakness, headache, fever.
Symptoms of wisdom tooth inflammation
To prevent a problem, you need to immediately notice the symptoms that cause it. To do this, special attention should be paid to the following points:
- there is a prolonged tugging pain;
- the gums become hard;
- the adjacent tooth becomes loose;
- body temperature rises;
- lymph nodes enlarge.
To alleviate his condition, the patient can take an analgin or paracetamol tablet at home before visiting a doctor, rinse his mouth with an antiseptic, and use only liquid food for nutrition.
If the pain is severe, you can take a painkiller pill, but you cannot suppress the pain with pills for a long time. You still need to go to the dentist.
How many days does tooth flux last?
Waiting for the flux to disappear on its own is, to say the least, naive. Some patients believe that if the flux bursts and pus comes out of the wound, then further treatment may not be carried out at all. This is a big mistake, since complete removal of pus requires special drainage, as well as complex therapy and subsequent treatment in the dentist’s chair. With timely and correct treatment, the flux disappears on average in 12-14 days; rehabilitation after severe periostitis can take more than a month.
Treatment of gum inflammation at the Eurodent clinic
Self-medication in case of gum disease is only permissible as a temporary measure to relieve pain. To ensure that the disease does not become chronic, you should definitely contact a dental clinic. When you see a doctor, you will be given an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment will be prescribed.
The Eurodent clinic operates 24/7, so you can contact us for qualified help at any time. We remind you that the initial consultation is free.
We are waiting for you at the following addresses: Zheltoksan, 83, ug.
st. Aiteke bi and Zhandosova, 42, corner. st. Aimanov. Based on: 6 votes
Treatment methods
The attending physician should tell you after the examination how to treat gumboil and what measures need to be taken to achieve a successful result. The mechanism is approximately the same, but each clinical case has its own nuances. Today, several techniques are used aimed at eliminating the disease and its manifestations. As a rule, they come together.
Antibiotics for gumboils
Antibiotic treatment is an important stage of rehabilitation. The most effective antibiotics for fighting inflammation and infection are Metronidazole, Lincomycin, Amoxiclav and their analogues. Any tablets and antibiotics for tooth flux should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor!
Physiotherapy
Used as an additional measure to reduce inflammation and speed up recovery. Recommended procedures include electrophoresis, laser and ultrasound therapy.
Therapeutic treatment
It is carried out if it is decided to save the tooth. This includes endodontic treatment and filling of root canals, as well as resection of the root apex if necessary. If the cause of the flux is periodontitis, then a series of manipulations are carried out to eliminate the accumulation of bacteria in the periodontal pockets.
Surgical procedures
This includes tooth extraction and periostotomy - the main procedure for treating flux. The doctor makes an incision into the purulent sac, and then installs a drain through which the purulent exudate comes out.
Local therapy and rinsing for tooth flux
For better release of pus, pain relief and reduction of swelling, gels and ointments are used topically: Metrogyl Denta, Levomekol, Cholisal. Many people are interested in how to rinse gumboil on the gums. Miramistin and soda solution are usually used for rinsing. As an alternative, you can use folk remedies: decoctions and tinctures of propolis, chamomile, sage or calendula. A tooth after gumboil is still very vulnerable: to minimize the risk of re-infection, these treatment and preventive procedures are very important.
Contraindicated actions for swelling:
- Under no circumstances should you heat the swollen area, or touch the wound with your hands and tongue;
- rinsing on the first day after tooth extraction is not recommended, as it can wash away the blood clot that protects the socket from infections. In the future, you can rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions - miramistin, furatsilin, or decoctions of chamomile, sage;
- the first two to three hours after the removal operation, you should refrain from smoking, drinking and eating;
- Until the wound is completely healed, you should not consume solid food, hot and carbonated drinks, or alcohol.
If you follow these simple rules, the swelling will go away quickly enough and there will be no need to visit the dentist.
Is a tooth removed during gumboil?
A tooth can be removed due to flux, but in modern dentistry the emphasis is on tooth-preserving manipulations. This also applies to flux. A tooth must be removed when its crown is seriously damaged and cannot be restored with a pin or inlays. If an infection occurs under the crown, then re-prosthetics are often difficult. In some cases, a tooth has to be removed because it is impossible to unfill the canals after a previous unsuccessful treatment, but this happens extremely rarely. In any case, the doctor makes the decision to remove a tooth based on the clinical picture.
Other diseases that give similar symptoms
It was already said above that 90% of patient requests fall into one of the three cases already described. But there remains another 10% of calls with the complaint that “the gums are swollen.” Edema or conditions similar to them in appearance can cause precancerous diseases, hormonal changes, cancer itself, HIV infection, diabetes and many other diseases. And with everyone there will be swelling, perhaps there will be pain. Therefore, it is very important if you detect any swelling, growths, or bulges on the gums to consult a doctor to find out the cause of this phenomenon and timely treatment.
Why is tooth flux dangerous?
An inflammatory process of this type tends to develop and, as it spreads, affects deeper layers of tissue. If left untreated, flux often develops into phlegmon - a serious purulent inflammation that has no definite boundaries. The most severe forms of flux provoke the development of sepsis, which can lead to infection of the entire body and even death. It is important not only to know how to cure gumboil and visit the dentist on time, but also to follow a number of preventive measures so that the likelihood of complications developing is minimal.
- Regular and high-quality hygiene.
- Treatment of caries at the initial stage. Flux, dental cysts and other complications often arise due to untreated pulpitis and periodontitis.
- Preventative visits to the clinic to assess the condition of the oral cavity and carry out professional cleaning.
Home treatments
While the patient is waiting to visit the doctor, he can alleviate his condition by using some home remedies. Among them are:
- an aqueous solution of salt and baking soda to rinse your mouth several times a day;
- decoctions of medicinal herbs such as sage and chamomile, which are used to rinse the mouth;
- a three percent solution of hydrogen peroxide half and half with water also helps in reducing swelling;
- a cold compress of ice on the outside of the cheek, it is important not to chill the tooth.
If after 24 hours the above methods have not had any effect, you should contact your dentist as soon as possible.
The inflammatory process left untreated can ultimately cause blood poisoning and painful death.
How to remove swelling from the cheek due to tooth disease?
Most people are familiar with toothache. Most often, the patient seeks help immediately after the appearance of unpleasant pain or when swelling appears. In the latter case, you should know what to do, what actions will help relieve swelling. Experts emphasize that in this case you should not self-medicate. The best option is to visit a dentist.