04.05.2018
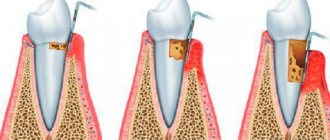
The oral cavity connects the body with the environment and can therefore be subject to a variety of negative influences. Such influences include the influence of too hot or too rough food, the influence of pathogenic microorganisms. In such cases, the first protective barrier is the mucous membrane, which lines the entire oral cavity and has, in addition to protective ones, many other functions. The mucous membrane is well supplied with blood, and its cells divide quickly and frequently. Therefore, wounds on the mucous membrane heal faster than on other parts of the body. However, for a number of reasons, the mucous membrane can be subject to inflammatory processes called stomatitis. Stomatitis is considered separately from such inflammatory processes in the oral cavity as gingivitis (inflammation of the gums; they have their own characteristics) and periodontitis (inflammation of the periodontium). The causes of stomatitis are very diverse.
Infectious causes
Stomatitis can be caused by infection with viruses or bacteria. In these cases, stomatitis is usually considered as an independent disease.
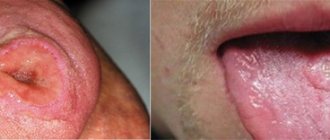
This is especially true for infection with herpes simplex viruses, which leads to very painful inflammation of the mucous membrane. There are two types of herpetic stomatitis - acute herpetic stomatitis (with primary infection) and recurrent herpetic stomatitis (which can pass through the acute stage or manifest itself as a general infection of the body in the presence of provoking factors). Herpetic stomatitis can lead to an aphthous form, in which erosions, aphthae, and even painful ulcers appear on the mucous membrane.
A specific type of stomatitis is chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis, which begins almost immediately with the formation of aphthae, and the nature of which is not yet clear. But viral and bacterial infections and vitamin imbalances are also suggested as initiating factors.
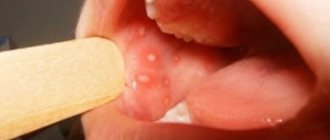
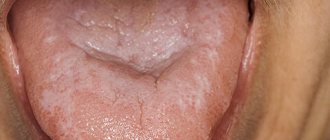
The specific infection that causes stomatitis includes a fungal infection (fungi of the genus Candida) and the disease itself is called candidiasis (thrush). Thrush is characterized by the formation of whitish dots on the mucous membrane, and as the fungal infection multiplies, a whitish coating. Candidiasis develops, as a rule, as a result of violations of hygiene rules, physiological disorders in the body, and the use of certain medications. It is often observed in children and its danger cannot be underestimated. This infection, which initially appears on the oral mucosa, can be spread to all organs and systems of the body, and in this case already poses a significant threat to health.
Purely bacterial causes of stomatitis are less common. As a rule, bacterial infections affecting the oral mucosa accompany viral types of stomatitis (for example, streptostaphylococcal lesions).
Change in structure with fluid accumulation
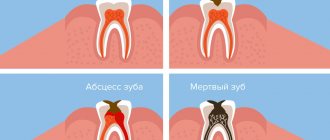
With such lesions, the structure of the mucous tissue changes so that a cavity filled with liquid is formed inside.
Bubbles and bubbles. They are formed in the epithelial layer or under it, filled with serous or hemorrhagic contents, and can be grouped. The cavity is closed by a thin layer of epithelium, which can break through. Bubbles can group and break quickly. Bubbles form and last longer. Both types of lesions provoke the formation of healing ulcers on the surface of the mucous membranes. They arise due to damage by viruses, traumatic injuries, and disturbances in tissue nutrition.
Ulcers. They can form from blisters or on unchanged mucosa. The cavity is filled with purulent exudate (whitish, yellowish, greenish contents with a pungent odor). They can be deep or superficial, often painful. Indicate an inflammatory process, appear after traumatic damage to the mucous membrane, due to infectious, viral diseases.
Cysts. A formation with dense walls that form a cavity. It is filled with transparent contents (can become purulent, serous, bloody). Appear due to blockage of gland ducts on the mucous membranes or as a symptom of periodontal diseases.
Other causes of stomatitis
In addition to infections, there is a whole range of other causes that can cause inflammation of the oral mucosa: • allergic reactions of a local and general nature (for example, to certain foods, medications, filling materials, oral care products) • the presence of soft and hard dental plaque, multiple caries • incorrectly installed dentures or orthodontic devices (braces) • irritation and trauma to the mucous membrane (mechanical injuries, burns) • deficiency conditions in the body (vitamins A, B and C, iron, folic acid); • intoxication with nicotine, alcohol, metal compounds.
Stomatitis can be manifestations and side effects of common infectious diseases (measles, diphtheria) or internal and general diseases and pathologies (blood and skin diseases, hormonal fluctuations, metabolic disorders).
Inflammation of the oral mucosa occurs especially often when the body's immune system is weakened and due to insufficient oral hygiene. The danger of stomatitis may also be associated with increased and constant dryness of the mouth, in which the protective functions of the mucous membrane are sharply weakened. The salivary glands produce on average up to 1.5 liters of fluid per day, and its deficiency leads to an imbalance in the acidity of the environment, an imbalance of inorganic components and, ultimately, has a depressing effect on the immune defense of the mucous membrane.
Main symptoms of stomatitis
Symptoms of stomatitis depend on its type and form, are very diverse and specific. General symptoms include redness, swelling of the mucous membrane, burning and pain in the mouth (including when eating hot, sour or spicy foods), an increase (or, conversely, a decrease) in salivation, bad breath, as well as the manifestation, in depending on the severity of the disease, specific lesions - erosions, af, ulcers.
Therapy for diseases of the oral mucosa
Prevention measures:
- Visiting the dentist twice a year to promptly identify and eliminate dental problems;
- Careful observance of local hygiene;
- To give up smoking;
- Avoiding too hot and spicy foods;
- Rinsing the mouth with disinfectant solutions and herbal decoctions;
Oral hygiene should be carried out regularly. Failure to comply with basic rules can provoke the occurrence of sore throat, problems with the gastrointestinal tract and other pathologies.
The health of the oral mucosa largely depends on the condition of a person’s teeth.
To successfully cure any disease of the oral mucosa, it is necessary to suppress the factors that influenced its development. If you suspect any problems in the oral cavity, you should contact a specialist. It is categorically unacceptable to get too carried away with self-medication and resort to non-standard methods of treatment. If you do not see a doctor for a long time, a minor problem can develop into a more serious one, lead to complications and worsen a person’s overall health. In addition, some oral diseases can develop into malignant ones. You should not put off visiting a specialist and expect the disease to go away on its own. Timely diagnosis and treatment will help avoid many problems in the future.
Treatment
The primary diagnosis of the disease based on clinical manifestations is carried out by a dentist, who also carries out local symptomatic treatment based on the primary diagnosis. But in complex and unobvious cases, laboratory diagnostics are carried out, and doctors of other specialties (allergists, dermatologists, immunologists) are brought in for treatment.
Local symptomatic treatment usually involves the use of rinses with solutions of painkillers and antiseptic drugs (including herbal origin), the use of drugs for tissue regeneration (after the acute phase subsides), if necessary, the elimination of irritating and provoking factors (removal of dental plaque, hard deposits, treatment dental caries).
Local drug treatment is carried out only after an accurate diagnosis has been established (the cause of stomatitis) and usually includes treatment with antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal drugs in the form of ointments and applications.
General treatment is carried out, as a rule, in a hospital and is aimed at eliminating the internal causes of stomatitis (treatment of internal pathologies), taking therapeutic drugs according to special regimens, and physiotherapy.
Stomatitis - symptoms and treatment
The main goal of treating stomatitis is to prevent the lesion from spreading throughout the entire oral mucosa and to prevent the disease from becoming chronic. First of all, it is necessary to determine the form and stage of the disease, since treatment tactics will depend on this. Treatment is complex: both local and general.
For all types of stomatitis, professional oral hygiene . It is the removal of dental deposits such as tartar and soft pigmented plaque.
Effective drugs for the treatment of stomatitis in adults
Next, it is necessary to eliminate chronic foci of infection and predisposing factors. For painful ulcers, anesthesia of the oral mucosa :
- applications of a 2% solution of procaine (Novocaine);
- applications of 2% lidocaine solution [7].
The affected mucous membrane is treated with antiseptics (0.02% Furacilin solution; 0.06% chlorhexidine solution; 0.1% Dimexide solution).
Applications of collagen films with various medicinal substances, for example, corticosteroid drugs, Diphenhydramine, and anesthetics, are also used. This film attaches to the erosion and has anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects, after which it dissolves on its own. To accelerate the healing of the mucosal epithelium, an oil solution of vitamin A, rosehip oil, and dental adhesive paste with solcoseryl are used.
How can you rinse your mouth for stomatitis?
When treating stomatitis, it is very important to identify the cause and eliminate it. Rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions (0.02% Furacilin solution, 0.06% Chlorhexidine solution) or herbal decoctions will reduce swelling and inflammation, but this is not the main method of treatment.
General treatment
Includes adherence to a diet (it is not recommended to consume spicy, spicy, rough foods, alcoholic beverages), as well as the use of antihistamines, antivirals, antibacterial, antifungal drugs (depending on the form of stomatitis) and sometimes glucocorticosteroids (GCS) - analogues of natural hormones of the adrenal cortex [6 ].
Desensitizing therapy : orally “Tavegil”, “Diphenhydramine”, “Suprastin”, 1 tablet 2 times a day for a month.
Antifungal therapy is carried out for candidal stomatitis: tablets “Nystatin”, “Nizoral”, “Diflucan” [9].
For viral stomatitis, antiviral drugs are prescribed: Lavomax, Valtrex, Bonafton. In severe forms of stomatitis, corticosteroids can be prescribed: prednisolone 15-20 mg per day, the dose of the drug is reduced by 5 mg per week from the moment of epithelization of erosions and ulcers.
For stomatitis, restorative therapy . Vitamins of group B, C, PP. Imudon tablets have an antiseptic effect, normalize microflora, and increase local immunity [11].
From the first day of the patient’s treatment until complete epithelialization, physiotherapy : ultraviolet irradiation, helium-neon laser, laser biostimulation of blood.
Laser treatment of stomatitis
Laser in the treatment of stomatitis is especially effective if the oral mucosa is affected by bacteria, viruses or fungi. The laser beam is targeted specifically at the affected area of the mucous membrane without damaging healthy tissue. The method allows you to destroy microbial cells, reduce pain and swelling, improve microcirculation, which promotes healing. The procedure is painless and safe.
How to cure stomatitis in a child
The principles of treating stomatitis in children and adults are similar, but it is important for the doctor to take into account the age of the child and correctly calculate the dosage of drugs. Another feature is that young children will not be able to rinse their mouths or use mouth baths. Therefore, antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity is carried out by parents with a finger wrapped in several layers of gauze and soaked in an antiseptic solution.
Treatment of stomatitis at home
If symptoms of stomatitis appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Self-diagnosis and treatment with folk remedies often aggravate the disease.
Prevention
In general, it is quite difficult to avoid this disease in the presence of predisposing causes; you can only take some general measures to possibly prevent the disease or complication in the form of stomatitis.
Since the herpetic virus, especially in acute primary forms, is extremely contagious, a certain isolation of the patient is required to prevent the spread of infection by airborne droplets and contact. The difficulty here is that there is a rather long incubation period, up to 26 days, and the first signs of stomatitis may escape attention.
Other preventive measures are of a general nature and consist of proper and complete oral hygiene, regular professional cleanings in a dental clinic (removal of soft and hard plaque), timely treatment of mucosal injuries, and measures to generally strengthen the immune system.
Posted in Useful information | Tags: teeth, diabetes, care