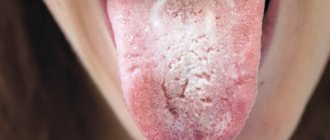
Causes
The exact causes of the pathology are not fully understood. The disease is not an independent disease; it appears against the background of other diseases. Most often, this phenomenon occurs in men over 40 years of age, but is sometimes observed in women. This disease is very rare in children.
The pathology is most often observed in people with gastrointestinal dysfunction, ulcers and gastritis. The development of the disease is greatly facilitated by poor oral hygiene, smoking habits and excessive coffee consumption.
The main causes of the development of the disease are considered:
- long-term use of medications, especially antibiotics;
- fungal infections;
- dehydration;
- chemotherapy;
- metabolic disease;
- weakened immune system;
- Regular rinsing of the mouth with solutions containing astringents.
The risk group also includes people with dental defects and the absence of a large number of teeth, since in this case they are forced to eat only soft food, which does not have the proper abrasive effect on the surface of the tongue.
Geographical language: what to do if you are faced with desquamative glossitis?
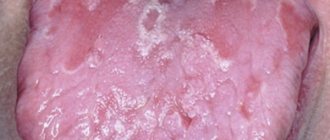
The term “geographic tongue” or “desquamative glossitis” refers to inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tongue, accompanied by sloughing (desquamation) of the epithelium, as a result of which the surface of the tongue becomes covered with bright pink spots with a white rim. The spots are flat, have rounded, distorted outlines, which makes the tongue look like a geographical map. The sites of inflammation are mainly the lateral surfaces and the back of the tongue. Causes Desquamative glossitis is a relatively common disease, although the clear causes of its occurrence have not been fully identified. It is generally accepted that geographic tongue is the body’s response to internal diseases, most often from the digestive and circulatory systems. Other common factors influencing the appearance of desquamative glossitis include:
- heredity;
- oral diseases;
- acute infectious diseases;
- avitaminosis (lack of vitamins);
- puberty in a child;
- exudative diathesis;
- violation of the metabolism of B vitamins;
- autoimmune diseases (disorders of the human immune system);
- endocrine, hormonal changes in the body (pregnancy, menopause, menstruation);
- teething in children.
Symptoms At the beginning of the inflammatory process, grayish-white spots with a diameter of several millimeters appear on the tongue. The papillae in the center of these spots gradually peel off, forming a bright pink or reddish round area. The desquamation (desquamation) zone can be either single or multiple, and can change shape and location. As a rule, geographic tongue occurs without any individual sensations, and therefore is detected by chance as a result of examination of the oral cavity. Sometimes patients experience itching, tingling, changes in the sensitivity and taste of the tongue, which may be due to poor oral hygiene or consumption of irritating foods. Diagnosis Geographic tongue is most often a symptom of serious illnesses, therefore, when it appears, it is necessary to diagnose the gastrointestinal tract, circulatory system, as well as diseases that may be the root cause of desquamative glossitis. It is mandatory to prescribe a general analysis of urine and feces and collect anamnesis (information about previous diseases, living conditions of the patient, etc.). Sometimes geographic tongue develops in children during teething or during puberty in girls. In these cases, no diagnosis is made. Treatment If the patient does not experience pain or discomfort, then no special treatment is prescribed: the geographic tongue will go away on its own after eliminating the root cause of the disease. If you experience a burning sensation, pain or dry mouth, the following is recommended:
- carry out thorough sanitation of the oral cavity;
- exclude excessively spicy, salty, cold or hot foods from the diet;
- rinse your mouth with a decoction of sage, chamomile or St. John's wort;
- give up cigarettes and alcohol for a while;
- apply rosehip oil to the oral mucosa (contains beta-carotene, vitamins A, E, B3)
Prevention This disease requires several preventive measures:
- careful oral care;
- timely diagnosis of somatic diseases;
- Prevention of vitamin deficiency: try to diversify your diet with foods rich in B vitamins.
It is important to remember that desquamative glossitis is a symptom of other very serious diseases, so a person who discovers a geographic tongue should immediately consult a specialist.
Symptoms
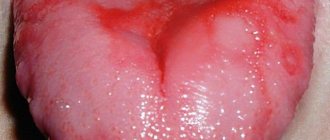
Pathology is immediately detected during a visual examination by a dentist. In the initial stages of the disease, the presence of a foreign object in the mouth is felt, other unpleasant signs gradually appear, then the upper part of the tongue noticeably turns black. In advanced cases, the affected area occupies two-thirds of the tongue. The disease is accompanied by unpleasant odor from the mouth, changes in taste sensations, a metallic taste appears in the mouth, a feeling of tickling and soreness on the surface of the tongue, as well as causeless nausea. In rare cases, there is a burning sensation and severe itching.
What language should be normal?
A child who is completely healthy has a uniform pink tongue, without areas of inflammation. There should also be no plaque on the mucous membrane normally. Parents should be alert to the following changes in the tongue:
- Limited areas of inflammation;
- Neoplasms of various types;
- Uneven plaque, which consists of tiny particles of food and dead epithelium;
- Excessive growth of the epithelium in certain areas of the uvula.
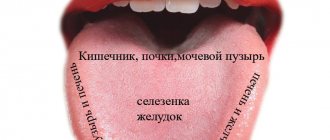
You should pay attention to the localization of spots and areas of inflammation. This also has important diagnostic significance, since each part of the tongue is associated with the work of a specific organ.
- Liver and gallbladder – spots and plaque on the sides of the tongue;
- Intestines - changes affect the base of the uvula;
- Buds - spots located between the root and the middle of the tongue;
- Lungs - there are spots on the front of the tongue;
- The heart is connected to the tip of the organ.
Most often, spots on the tongue are caused by problems with the digestive tract. Such changes are not necessarily a sign of serious illness, but it is worth consulting your doctor about this.
Treatment
It is necessary to contact a dentist or maxillofacial surgeon with such a problem. To obtain a complete clinical picture, it is necessary to undergo examination by a gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, endocrinologist and neurologist. Since the pathology develops against the background of other diseases, a comprehensive treatment regimen is used.
Only treatment of concomitant diseases, professional cleaning and treatment of the oral cavity, taking multivitamin complexes, antifungal medications and, if necessary, sedatives will help eliminate this unpleasant defect. Removal of heavily overgrown papillae can be carried out by cryodestruction (exposure to the pathological focus with liquid nitrogen). It is also necessary to adjust your diet, enriching it with foods with fiber, vitamins and minerals.
The prognosis for black hairy tongue is usually favorable. Elimination of causative factors, as well as appropriate comprehensive treatment of the disease, leads to complete restoration of the surface of the tongue.
Consequences of frenulum anomaly
Hypotrophy due to impaired sucking, poor weight gain in infants.
Malocclusion, the first signs of which during the period of temporary occlusion is the rotation of the central lower incisors to the lingual side.
Impaired development of the lower jaw, as a result, the formation of a distal bite.
Local gingivitis, periodontitis up to exposure of the roots of the teeth in the area of the lower jaw incisors.
Violation of the pronunciation of sounds that require raising the tongue upward: “sh”, “zh”, “sch”.
Impaired language development due to asymmetrical growth. Low mobility of the tongue impairs the articulation of some sounds. Violation of diction (clarity, intelligibility of pronunciation).
Prevention
As such, there is no prevention of black villous tongue. Even with good oral hygiene, you can encounter a similar phenomenon, but with timely treatment of diseases that lead to the development of such a complication, you can minimize the likelihood of the disease occurring.
The following rules must also be observed:
- thoroughly brush your teeth, gums and tongue with a soft brush;
- It is necessary to drink enough water, because if there is a lack of hydration in the oral cavity, it begins to develop; bacteria;
- reduce coffee consumption and quit smoking and alcoholic beverages.
The disease recurs quite rarely. During an exacerbation, the patient is advised to follow a gentle diet; food should be warm and soft in consistency.
When and which doctor to contact about a coating on the tongue
As a rule, tongue coating is not the main symptom.
And it is other symptoms that tell you which doctor you should see. If plaque on the tongue is accompanied by symptoms of ARVI, you should consult a physician. If you have symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases, contact a gastroenterologist. If there are no such symptoms, and the cause of your concern is plaque, in case of white plaque you can consult a dentist, in case of yellowish or gray plaque, you can consult a gastroenterologist. And in any case, you can consult a general practitioner - family doctor or therapist. A child with a persistent coating on the tongue should be shown to a pediatrician.
Reds
The appearance of red spots on a child’s tongue is a sure sign of an infectious or inflammatory process in the oral cavity:
- stomatitis;
- glossitis;
- bacterial dermatosis;
- herpetic infection.
Also, red spots may be due to an allergic reaction or consumption of foods that are bright red in color.
Very often, such formations are accompanied by unpleasant symptoms: pain in the tongue, a feeling of discomfort, increased salivation. Due to pain, children may be capricious and refuse to eat or drink. The general condition may also suffer - body temperature rises.
Only a doctor should treat red spots. After establishing an accurate diagnosis, the following may be prescribed:
- treatment of lesions with antiseptic agents;
- taking antibiotics or antivirals;
- use of anti-inflammatory medications.
Diagnostics
To establish a complete picture of the state of the body, the doctor determines the color of the tongue, its structure, position, motor functions, and possible other pathologies in the oral cavity. Among the laboratory and instrumental research methods aimed at clarifying the characteristics of plaque and the reasons for its appearance, the following may be prescribed:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- sowing on flora from the surface of the tongue;
- determination of antibodies to the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- scatological research.
If you are concerned about the condition of your tongue, plaque on it, pain, unpleasant odor, contact the ENT doctors of our clinic. High-precision equipment and the experience of our specialists allow us to quickly make correct diagnoses and prescribe treatment.