Correction of dry nasal mucosa
Most modern people quite often experience unpleasant sensations characterized as “dryness of the nasal mucosa.” It is expressed in nasal congestion, often alternating, itching, burning, crusting in the nasal cavity, and decreased sense of smell. In addition to the feeling of discomfort, dryness of the nasal mucosa negatively affects the filtration function of the nose - dust particles, bacteria and viruses contained in the air almost freely enter the lungs during breathing.
Various factors can lead to dryness of the nasal mucosa. Quite often, “dry nose” is a side effect of certain medications, primarily antihistamines and drugs containing atropine. The most common is the adverse effects of climate and ecology, staying in rooms with central heating and air conditioning. The humidity of the nasal mucosa is negatively affected by inhalation of hot air, in particular from smoking, rarefied air (during air travel and vacations in the mountains), dust in the air in a number of industries - cement, chemical, etc. In addition, this condition can also be a symptom of a general disease.
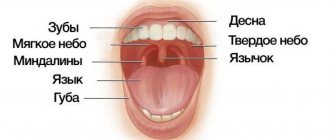
The mucous membrane of the nasal cavity is covered with a special ciliated epithelium, consisting of ciliated cells that ensure the transport of mucous secretions (Fig. 1).
Ciliated cells have 250–300 cilia, 7 microns long and 0.3 microns high. Each cilium consists of 9 pairs of microtubules arranged in a ring and surrounding two unpaired central microtubules. The movement of the cilia of the ciliated epithelium of the nasal mucosa is carried out through the sliding of microtubules (Satir P., 1974). Energy for movement is provided by ATP, which is broken down by dynein. Dynein is a Ca/Mg-dependent ATPase. The motor cycle begins with the addition of ATP to the dynein molecule. Cleavage of the phosphate ring during ATP hydrolysis leads to the connection of the dynein molecule and the tubulin molecule of the adjacent outer doublet and is accompanied by conformational changes in the dynein molecule - bending and displacement of the microtubule at a certain distance. This, in turn, causes a new ATP molecule to attach to dynein and break its bonds with tubulin, causing the dynein handle to return to its original shape. The whole cycle is repeated again (Kiselev A.S., Tkachuk I.V., 2006).
The movement of the cilia is strictly directed - from the vestibule of the nasal cavity towards the nasopharynx. Mucociliary clearance is provided by nasal secretions. The source of the secretion covering the epithelium of the nasal cavity is the mucous glands of the nasal mucosa, goblet cells, extravasation from subepithelial capillaries, lacrimal glands, and the secretion of specialized Bowman glands from the olfactory zone of the nose. The volume of nasal secretion in 24 hours ranges from 100 ml to 1–2 liters. The mucous membrane of the posterior two-thirds of the nose is renewed every 10–15 minutes. The function of the cilia is optimal at a temperature of 28–33 °C, a sufficient amount of secretion with a pH of 5.5–6.5. Loss of moisture, a decrease in temperature to 7–10 °C, and an increase in the pH of the secretion to more than 6.5 causes the cilia to stop vibrating.
Elimination of dryness of the nasal mucosa is facilitated by applying an isotonic solution to it. At the same time, the rheological properties of mucus are normalized. It is believed that trace elements contained in an isotonic solution, such as Ca, Fe, K, Mg, Cu, help to increase the motor activity of cilia, activate reparative processes in the cells of the nasal mucosa and normalize the function of its glands. The listed microelements are contained in preparations that are prepared from sea water, sterilizing it and bringing the salt content to isotonic concentration (Otrivin More, Marimer, Aqua Maris, Salin, etc.), and from mineral spring water, which has medicinal properties (salt).
One of the new drugs in this group is Otrivin More, which is a purified, disinfected isotonic solution of ocean water from Brittany, extracted in an ecologically clean area of the Atlantic Ocean, rich in natural microelements. It contains 18 minerals and trace elements.
We examined and treated 50 patients of both sexes aged from 21 to 43 years with complaints of “dry nose” caused by prolonged stay in rooms with dry and/or rarefied air. In the treatment of the main group (25 patients), Otrivin More was used in the form of irrigation of the nasal mucosa 2 times a day for 10 days; in the second (control) group (25 patients), an oil solution of tocopherol acetate and retinol palmitate in the form of drops 2 times a day. The distribution of patients by gender and age, as well as by the severity of clinical manifestations in both groups was comparable. Every three days, the dynamics of the main symptoms were assessed: difficulty in nasal breathing, dryness in the nasal cavity (including the patient’s subjective sensations), the nature and amount of nasal discharge, the state of mucociliary transport (saccharin test).
At the end of the course of treatment, a positive clinical effect was obtained in 42 patients, of which 23 were from the main group and 19 from the control group. In 8 (16%), including 6 from the control group (24%), no positive dynamics were recorded. In the group of patients receiving Otrivin More, the regression of pathological signs was significantly more rapid compared to the control group, which was confirmed by the results of a study of mucociliary transport. On average, the decrease in mucociliary transport time with the use of the drug was 6.9 minutes. In the control group, this figure was 4.3 minutes (Fig. 2).
Changes in mucociliary transport parameters correlated with rhinomanometry data and changes in the clinical picture, which took into account subjective symptoms assessed using a patient questionnaire. The drug was well tolerated by all patients. In addition, all patients noted the ease of use of the drug, while the use of oil drops by the majority of patients in the second group (24 people) was characterized as “inconvenient.”
Thus, Otrivin Sea can be recommended as a means for caring for the nasal cavity not only for patients with rhinitis, including atrophic ones, but also as a means of daily hygienic care for the cavity during the heating season, as well as for people who stay in dry rooms for a long time. and/or rarefied air.
Literature
- Satir P. How cillia move // Scientific American. 1974. Vol. 231. P. 45–46.
- Kiselev A. S., Tkachuk I. V. Spray Aqua Maris for diseases of the nose and paranasal sinuses // Pharmacy Weekly. 2006, March 27, No. 12 (533).
O. V. Zaitseva , Candidate of Medical Sciences, National Research Center of Otorhinolaryngology, Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia , Moscow
Vitamins that protect the body in general and mucous membranes in particular
Severe deficiency of any vitamin negatively affects the immune response, since each of the essential micronutrients is included in several biochemical cascades at once. For example, deficiency of vitamin C causes scurvy, B12 – corresponding anemia, which is accompanied by a significant decrease in protective functions. In this context, the optimal means of increasing the body's defenses are multivitamin complexes. However, some nutrients play a special role in the formation of the immune response, let's talk about them in more detail.
Popular questions about vulvovaginitis
How to diagnose vulvovaginitis yourself?
The first signs of inflammation are itching, burning and pain in the genital area. These symptoms mean you need laboratory testing to determine the type of pathogen. This is the only way the treatment will be effective.
How often does it occur in children?
Vulvovaginitis occurs quite often in children, because due to age and excessive shyness, girls violate the rules of personal hygiene. In addition, babies often put everything they come across into their mouths, which is why they more often suffer from the helminths that cause this disease.
What complications can there be?
Without treatment, the disease becomes chronic, which can lead to the appearance of an oncological lesion. For girls, there is a high risk of fusion of the labia minora, which is why they may have problems with their sex life in the future.
What complications can there be?
Untreated vulvovaginitis can lead to serious consequences. In girls, the formation of dense adhesions of the labia minora is possible. Such a deformation will make sexual life difficult. In addition, this pathology is one of the factors that provoke cystitis.
The disease is especially dangerous during pregnancy. The expectant mother is at risk of spontaneous abortion, endometritis, or the birth of an infected baby.
Chronic vulvovaginitis leads to hardening of the mucous membranes. With this course, cracks and erosions occur more often, and prerequisites for the appearance of oncology appear.
Vulvovaginitis: drugs
Local and oral agents are used for treatment.
Vaginal suppositories and creams (Gynex, Clotrimazole, Lomixin) are indicated as local ones. Doctors also prescribe a course of tablet antibiotics (Pancef, etc.). For candidal etiology, antifungal agents are prescribed: Nystatin, Fluconazole, Itraconazole, Metronidazole.
Upon completion of treatment, doctors recommend taking probiotics (Lactozhinal, etc.) to restore the microflora.
If the cause of the disease is worms, anthelmintic drugs are needed: Aldazole, Pirantel.
Vitamin D
Another fat-soluble vitamin that has a significant effect on the functioning of the immune system is vitamin D. It is known that it [4]:
- stimulates the activity of macrophages;
- induces differentiation [maturation] of immune cells;
- increases monocyte proliferation;
- increases the activity of T-regulatory cells, which regulate the strength and duration of the immune response;
- reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines;
- increases the synthesis of antimicrobial peptides.
It has been proven that with a vitamin D content of more than 50 ng/ml in the blood plasma, the likelihood of developing respiratory infections is 27% lower than with severe deficiency [vitamin D level less than 20 ng/ml] [5]. At higher concentrations of the vitamin in the blood, the risk of developing influenza, respiratory syncytial virus infection, and pneumonia is reduced [6]. The decrease in the likelihood of developing the latter is associated with the beneficial effect of vitamin D on the respiratory tract: it reduces the production of cytokines in epithelial cells, reducing the severity of inflammation, and blocks the proliferation of smooth muscles of the respiratory tract [7].
The daily dose of vitamin D is 600-800 IU. For pregnant and lactating women it reaches 800-1200 IU, and for people over 50 years old 800-1000 IU.
Contraindications and side effects
Methyluracil is prohibited for use in case of malignant diseases of the blood and bone marrow, as well as in case of excessive formation of granulation tissue. It is also necessary to refuse therapy in case of allergic reactions to the components of the drug.
While taking pills, heartburn, headaches, and dizziness may occur. Occasionally, physical weakness occurs. When using suppositories and ointments, a slight burning sensation of the skin and mucous membranes at the sites of contact with the drug is likely.
Drug treatment
Vasoconstrictors (decongestants) are drugs that have a local effect. When used, there is a quick and effective reduction in the swollen vascular networks of the nasal cavity and easier nasal breathing. These medications can be purchased without a doctor's prescription. There are many trade names, but there are only three active ingredients: oxymetazoline, xylometazoline, phenylephrine.