Mothers who have at least once seen a child develop an acute attack of false croup literally before their eyes (and most often on a dark night) are unlikely to forget this episode. At the same time, parents often panic, which, of course, does not solve the problem, but only further frightens the kids. You must act confidently and calmly.
Cough is an unconditional innate protective reflex that facilitates the process of clearing the respiratory tract of foreign bodies, toxins and excess mucus, emphasizes the Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Director of the University Children's Clinical Hospital, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Head of the Department of Childhood Diseases of the Faculty of Medicine of the First Moscow State Medical University. I. M. Sechenova, professor Natalya Geppe . But it is also one of the most common symptoms of many diseases. In addition to colds and ARVI, there are many other reasons for its occurrence. False croup is one of them. An attack of this disease in a child, as a rule, makes a strong impression on parents.
Causes of stomatitis in children
What causes stomatitis in children? The causes of this disease in a child are different. These include dirty hands, fragile children’s immunity, and the peculiarities of thermoregulation, on which the respiratory system directly depends. You need to understand that a child’s mucous membrane, unlike an adult’s, is a very thin and vulnerable substance, so any infection occurs very quickly. At an early age, the child’s salivation is not yet fully formed, but salivary enzymes play a very important role in protecting the body. As a result, the mucous membrane often dries out, cracks appear, infection occurs, followed by stomatitis. It is impossible not to take into account long-term use of medications, for example, antibiotics, as well as neuropsychiatric disorders, unfavorable living conditions, poor child care and poor oral hygiene of the parents themselves.
Often it is the parents who help the doctor find out the cause of the disease. Only they can try to analyze what caused the blister, ulcer or plaque to appear. For example, the child ate something wrong, they bought a new toothpaste or toothbrush, or maybe the baby suffered a temperature change.
What to do if halitosis appears
The variety of causes that cause bad breath proves that in most cases the child requires qualified consultation. Sometimes the cause can be determined without difficulty, sometimes additional examinations (instrumental and laboratory) are required.
If parents detect bad breath in their child, it is important to seek medical help as soon as possible, preferably starting with a dentist. Treatment can be prescribed only after a true diagnosis has been established.
The specialists of the Shifa children's dental clinic have extensive professional experience and regularly undergo internships in Russia and abroad. High professionalism helps dentists establish the root cause of halitosis and draw up an individual treatment plan that is highly effective. Fresh breath guaranteed. Sign your child up for a consultation!
What are the types of stomatitis in a child?
It is more common for everyone to say “stomatitis”, but it would be more correct to say “stomatitis”, since this is a general concept for a whole group of diseases. Depending on the causes, stomatitis can be divided into several types, each of which has a number of characteristics.
Viral, herpes, or herpetic stomatitis in children
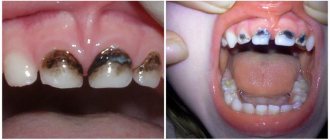
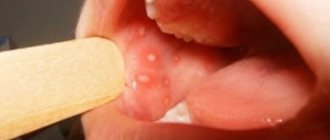
One of the most common types of childhood stomatitis is caused by the herpes simplex virus. Usually a child becomes infected with it through airborne droplets. The virus is also transmitted through dishes, toys, and household items. Most often, herpetic stomatitis appears in a child between the ages of one and four years. The disease begins as a cold, accompanied by lethargy and fever. Sometimes a runny nose and cough occur. Around the second day, small round or oval erosions of a light yellow color with a bright red border appear on the lips, tongue, and inside of the cheeks. Swelling appears, the gums begin to bleed, and the child refuses to eat.
Traumatic stomatitis in a child
The disease is caused by mechanical trauma to the oral cavity. For example, burns from hot food, a too-hard pacifier, the habit of chewing a pencil. Also, traumatic stomatitis often occurs in children with malocclusion due to frequent biting of the cheeks and tongue.
Candidal stomatitis
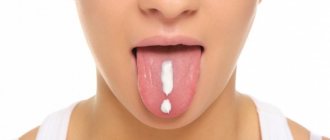
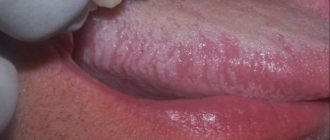
Appears in children under one year of age. The cause is fungi of the Candida species. The main symptom is the appearance of white plaque in the baby’s mouth. It is worth noting that it should not be confused with the usual plaque after feeding. A cause for alarm is if the plaque does not go away and the child refuses to eat.
Drug-induced or allergic stomatitis in children
Caused by certain allergies or reactions to medications. If this type of disease is suspected, the allergen should be identified and removed, otherwise there is a risk of unpleasant consequences, including anaphylactic shock.
Each type of stomatitis is characterized by a certain childhood age. In young children, candidal or fungal infections (thrush) are often observed. At the age of “I want to know everything” in a child of 3-4 years, stomatitis, as a rule, is infectious in nature, when the infection gets through dirty hands or objects. From one year to four years, we often observe an acute herpetic type of disease.
Night guest
False croup, or stenosing laryngotracheitis, is one of the manifestations of ARVI. It occurs in the larynx, where swelling forms, which interferes with the breathing process. A viral disease does not necessarily have to be severe for an attack to develop. Sometimes the child had only a slight runny nose and a slight cough the day before.
As a rule, false croup occurs closer to the night, but a few hours before this, the child already begins to experience warning signs. Due to the narrowing of the airways, the baby's voice becomes hoarse and a whistling sound appears when breathing. Hearing this, sometimes parents begin to suspect that their child has begun to develop bronchial asthma. But in fact, any doctor who hears such a sound will understand that this is not so. Indeed, with obstruction of the lower respiratory tract (bronchial asthma), the patient inhales normally (problems arise only with exhalation), but with false croup, on the contrary, it is not exhalation that is difficult, but inhalation. The child inhales noisily, making the so-called inspiratory breath. In addition, with false croup, a special cough occurs - barking. For some, it resembles the caw of a crow or even the sound of iron on glass. As the airway narrows, symptoms increase, requiring emergency medical attention. If necessary, emergency doctors will give the child an injection of glucocorticosteroids. Of course, not every child’s false croup can reach the suffocation phase, but if there is a predisposition to such a complication, it is better to have such drugs in your home medicine cabinet.
Symptoms of stomatitis in children
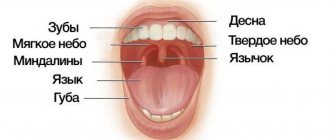
For all types of stomatitis, the common and defining signs are inflammation of the oral mucosa and the appearance on any of its parts, such as the tongue, the inside of the lips, cheeks, pharynx, of various formations in the form of erosions, blisters, characteristic plaque, and in cases of traumatic stomatitis - traces of burns and biting. It is important to understand that stomatitis is not just one acute or chronic disease with certain classic symptoms. Each type of stomatitis has its own specific cause, and it may not manifest itself in the same way. Therefore, they need to be treated differently.
Is this bronchospasm?
With asthma, a special paroxysmal dry cough with shortness of breath and wheezing also occurs. A child suffering from such a cough should definitely be shown to a pulmonologist, although it may not be asthma, but, for example, bronchospasm. Some children (usually preschool age) are prone to its development. This is a feature of their physiology. But you still can’t ignore such a symptom; you need to deal with it carefully, without putting it off for later. After all, 80% of children with bronchial asthma develop the disease in the first 5 years of life.
It is important to listen to the exhalation. If, as you exhale, the patient emits a high, thin whistle that can be heard even from a distance, you can already suspect that this is not a case of an ordinary ARVI. Although viral infections can become a trigger for asthma.
To alleviate the child’s condition, doctors can use glucocorticoid drugs (can be administered in the form of tablets orally, intravenously or through a nebulizer, as well as rectally in suppositories). Usually on the second day the child feels better, and after a week the baby recovers.
How to treat stomatitis in children
As we have already found out, there is no single algorithm for treating stomatitis in children. Each case is individual in its own way. Very often it happens like this: a mother comes in the hope that the doctor will prescribe an ointment, and she will immediately cure the child with it. This doesn't happen! It is necessary to understand what preceded the inflammation, taking into account the child’s age, stage and severity of the disease. Treatment is carried out both locally and symptomatically, i.e. symptoms are relieved. Doctors—a pediatric dentist and a pediatrician—give their recommendations, and it is possible to involve highly specialized specialists such as an ENT specialist, a mycologist, or a dermatologist. Of course, there are some textbook principles that experts follow to relieve or ease pain and prevent complications. We are talking about observing the rules of oral hygiene, diet and sleep, treating the mucous membrane with special gels, solutions and applications. For example, for allergic stomatitis in children, antihistamines are recommended, for herpetic forms - antiviral drugs, and if there is a fever - antipyretics. It is important to immediately contact a specialist when you discover a problem.
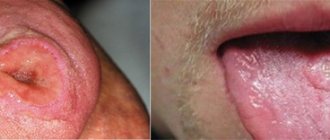
Afta Bednara
This is an inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa of a non-infectious nature, occurring in weak, bottle-fed infants in the first months of life.
Causes of the disease:
- permanent mechanical injury to the mucous membrane of the palate due to a nipple that is too long and too hard;
- may occur in breastfed children if the mother's nipple is very rough.
Main signs of the disease:
round or oval erosions, covered with loose plaque and located symmetrically at the border of the hard and soft palate, redness of the surrounding mucous membrane. The child becomes restless, eats and sleeps poorly.
In order to prevent the occurrence of the disease, it is necessary
promptly replace the pacifier or pacifier if irritation occurs on the oral mucosa.
If there are signs of disease, you should consult a pediatric dentist!
If any changes appear on the oral mucosa, you should visit a pediatric dentist to avoid complications and conduct a comprehensive examination and treatment!!!
Caring for a child with stomatitis
The participation of parents in treatment and proper care of the child is not just important - they are decisive. With stomatitis, it is necessary to strictly follow the treatment plan, which is often very labor-intensive, so the result depends on parental care and control. The oral cavity is a kind of epicenter of pain, so it is not surprising that the child will be capricious a lot. Therefore, it is important for parents to be patient and persistent.
Nutritional Features
Most mothers and fathers are concerned about the question of how to feed a child with stomatitis. Firstly, it is necessary to eat only soft, warm and mushy foods, for example, in the form of purees. The main thing is that the food is high in calories and not heavy, because the child’s immunity is already weakened. After eating, be sure to rinse your mouth so as not to provoke the development of stomatitis and not to add any additional infection. If a child is ill, the diet should include the exclusion of spicy, sour, sweet foods and citrus fruits.
Pain relief and care
For stomatitis in children, pain relief is necessary. It is carried out with the help of various medications in order to avoid food refusal and poor sleep. In addition, for stomatitis in children, proper treatment of the oral cavity is very important. A doctor should recommend what to treat and rinse a child’s mouth with.
Physiological change in bad breath
If parents smell a child’s breath, the doctor looks for the reasons for this phenomenon in three completely different directions.
Physiological disorders associated with a temporary decrease in saliva production.
This can happen if:
- eating spicy or fried foods;
- large intervals between meals;
- insufficient amount of fluid drunk;
- long outdoor games;
- being in a stuffy room;
- excessively wrapping the child;
- strong excitement;
- taking certain medications.
The mechanism for the appearance of odor is due to the fact that it is saliva that has a bactericidal effect, regulating the number and composition of microflora in the mouth. When the mucous membrane is dry, the activity of bacteria is activated. This produces hydrogen sulfide, which has a pronounced tint.
Physiological disorders leading to halitosis can be easily eliminated without medical intervention. It is important to change the child's lifestyle. Increase the amount of fluid you drink, optimize your diet, normalize the psycho-emotional background in the family and reduce the duration of outdoor games. But in some cases, an unpleasant odor turns out to be the first alarm signal indicating a developing pathology.
How to treat stomatitis in children at home?
On the Internet you can find descriptions of many ways to treat stomatitis in children at home. However, experts consider many of these virtual tips not only useless, but also dangerous. There is always a risk of allergies, so you should not use infusions and decoctions, even if you are absolutely sure that it will not harm the child. Instead of wasting time, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics and consultation with a dentist and pediatrician, who will prescribe the correct treatment regimen.