Causes Possible complications What to do about pain?
How to relieve pain? Prevention The vitality of a tooth, in particular its sensitivity, is ensured by the neurovascular bundle (pulp). Removal of the pulp (depulpation) is a forced measure, which is resorted to for serious indications (pulpitis, hilar cyst, damage to the pulp chamber due to trauma, etc.). Painful discomfort for several days after depulpation is a normal tissue reaction to the intervention. But if a tooth hurts after removing the nerve and filling the canals 2-3 weeks later
or pain occurs suddenly long after endodontic treatment, this is a good reason to see a dentist.
Even treated teeth should be examined every year to diagnose or rule out complications at an early stage. A pulpless tooth does not hurt, but it is like a time bomb. Poor-quality canal treatment can provoke complications that destroy the jaw bone and cause purulent processes (cysts, abscesses) that are life-threatening. Properly treated canals are the foundation of any restoration. The more modern and high-quality the materials used for their processing, the less likely there are complications.
Can a tooth hurt after nerve removal?
A tooth from which the nerve has been removed is called “dead.” According to logic, a tooth without a nerve cannot hurt. But tissues need time to recover after endodontic treatment. Therefore, reactive pain after dental treatment can normally persist for several days. Over time, it weakens and goes away on its own. Painful sensations usually occur when pressure is applied or while eating - they can last 1-3 days
,
a week maximum
.
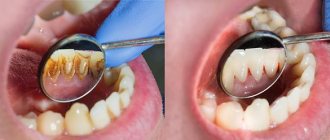
The picture is completely different when the pain increases, becomes throbbing, the gums are swollen, red, swollen, and symptoms of intoxication appear - headache, fever, weakness. Such symptoms indicate the development of complications and require immediate attention to the dentist. The doctor will determine why the dead tooth hurts and provide effective treatment.
Natural cause
After the nerve is removed and the canals are sealed, the pain syndrome persists for up to a week, since the soft tissues located near the apex of the root are injured. Unpleasant sensations arise at the moment when the effect of the anesthetic injection ends. Such pains are of a specific nature, and it is almost impossible to confuse them with pathological ones.
Constant pain in a tooth is rare. Most often it appears at the moment of pressure when eating, or when touching the tongue. The patient has the feeling that the tooth has grown sharply upward and rises above the others, which is why it hurts. Gradually, the unpleasant syndrome subsides, and after 3-4 days, painful sensations appear only from strong pressure, and then completely disappear.
If the pain does not begin to subside after 5 days or the discomfort intensifies, both are cause for concern. Usually in such cases there is an error on the part of the doctor who was unable to pass the canal correctly and violated the technique prescribed for such a procedure. The dentist will identify the cause of the pain and provide the necessary assistance. You should not delay a visit to a specialist, as this can cause a serious deterioration of the condition and the development of acute suppuration.
Reasons why a tooth without a nerve hurts
- Re-infection
- not all affected tissues were removed, the source of infection remained, and the inflammation began to spread again. This can happen if endodontic treatment is performed without a dental microscope or if the dental canals have a very complex structure, which does not allow for high-quality cleaning and disinfection. - Poor-quality filling
- when filling the canal, there are voids left in the canal, areas not filled with material, in which pathogenic microorganisms begin to multiply, which leads to inflammation, the development of periodontitis, the formation of cysts, granulomas. - The exit of the filling masses
beyond the root apex - the filling material, having exited through the apical foramen, hardens in the periodontal tissues, compresses the nerve endings, and disrupts blood circulation. Inflammation develops in the periodontium, accompanied by severe pain. - Perforation of the canal walls
– in the area of perforation, the dental tissue becomes infected and inflamed; during filling, the composite may escape beyond the boundaries of the canal. - Incomplete depulpation - due to the complex structure of the canals, the doctor was unable to remove one of the nerve endings. The use of a dental microscope with good optics significantly improves access to the prepared cavity and facilitates the detection of the canal orifices and all nerve branches.
- A fragment of an instrument
in the canal - during expansion, cleaning, filling, a piece of the instrument could break off and remain in the dental canal. The presence of a foreign object contributes to the formation of voids, where conditions are created for the proliferation of bacteria and the development of inflammation. - An allergy
to filling materials or a drug is accompanied by pain, swelling, and discomfort in the area of the dental unit. - A filling that is too high
– the opposite tooth (antagonist) puts excessive pressure on the filling, which leads to the appearance of pain. - Damage to the adjacent unit
- pain spreads (radiates) along the gum from the adjacent tooth.
In what cases may depulpation be required?
- Advanced caries, when the pathological process affects not only dentin, but also spreads to the pulp.
- Preparation for upcoming prosthetics.
- Various chronic gum diseases. If treatment is not treated in time, the inflammation progresses, affecting the roots and nerve endings, which requires radical measures.
- An injury as a result of which a sufficiently large part of the tooth has broken off, and its restoration is impossible with conventional filling materials.
Sometimes depulpation has to be resorted to after unsuccessful caries therapy. Incorrect processing and violations of the filling process lead to softening of the dentin, but already under the installed filling. The patient does not notice this immediately, and turns to the dentist after the onset of acute pain. And in such situations one has to resort to radical methods of solving the problem.
Possible complications
- Periodontitis;
- formation of granuloma, hilar cyst;
- periostitis (flux);
- complete destruction and/or loss of the tooth;
- osteomyelitis.
To exclude complications associated with poor-quality endodontic treatment, control radiography is performed at the RUTT clinic in Moscow, and an apex locator is used to assess the depth of the canals. The use of computed tomography and an operating microscope provide more opportunities for accurate diagnosis and quality treatment.
Missed channel
The number of nerves in the roots of the teeth is not the same, and therefore an inexperienced dentist may miss one of the canals. It is also possible that there are branches in the dental canal that may also be missed. In such a situation, acute inflammation and severe pain occur. To eliminate them, it is necessary to unseal the canal, clean it and close it.
A canal can also be missed if it is very thin and for this reason is not reflected on an x-ray. In such a situation, the doctor must carefully examine the tooth cavity, since excessively thin canals can only be determined externally.
What to do if a pulpless tooth hurts?
Soreness after depulpation is a normal tissue response to the intervention. But such symptoms should subside within a couple of days after endodontic treatment. If the canal of a tooth without a nerve hurts and the pain does not subside, but rather increases, you need to consult a dentist. The pain can be different - pressing, aching, throbbing, radiating to the eye socket, temple, cheek. In addition to pain, redness and swelling may occur. An allergy to a material or an antiseptic drug is usually accompanied by a burning sensation, fever, general weakness, and a feeling that the tooth “rises” above neighboring units.
The deeper the pathological process goes, the more pronounced the symptoms. As soon as the inflammation spreads to the periodontium, a person begins to feel pain when biting or pressing on a tooth. When pus accumulates on the gum, a fistula is formed, through which the outflow of purulent contents is ensured, temporarily alleviating the condition. The presence of a fistula is a direct indicator that there is a problem with the roots of the tooth.
The doctor will conduct a diagnosis and determine the exact cause of the pain. To do this, an examination is carried out and a number of x-ray studies are performed:
- targeted photographs of the affected tooth in different projections;
- orthopantomogram;
- 3D tomography.
The doctor selects therapeutic tactics according to the clinical picture. If the pain occurs due to re-infection, an allergy to the material, or errors in the initial treatment, re-treatment is carried out - the root canals are opened, processed and filled. If the pain is caused by pulpitis or deep caries of an adjacent dental unit, treat it. Cysts, flux, osteomyelitis are treated surgically - the gums are cut, cleaned, and the affected areas are removed along with part of the tooth root (according to indications). If it is not practical to save a tooth, it is removed followed by prosthetics.
Treatment of a dead tooth in dentistry
During the first visit to the dentist, the patient is usually sent for an x-ray, which will help determine the possible causes of pain in the pulpless tooth. Next, the doctor acts based on the current clinical situation:
- The dead tooth is opened and the remaining filling is removed from the canals.
- If there are remnants of nerve endings in the pulp, complete depulpation is performed.
- The root canals are thoroughly disinfected.
- Finishing the channels, cleaning and polishing them.
- Filling of root canals. If there is a one-stage treatment, the doctor uses a filling paste. If there is a need to eliminate the source of infection and inflammation, the dentist will install a temporary filling, which will be replaced with a permanent one in 2-3 weeks.
- Restoring the final shape of the tooth. Restoration work is no less complex a process than canal filling. If the permanent filling turns out to be higher than it should be, an additional chewing load will be placed on the tooth, which may cause discomfort and pain to arise again over time.
It may seem that treating a dead tooth is much easier than depulping a live one. In fact, the opposite is true - finding and eliminating an existing defect is much more difficult than doing all the work on treating a tooth “from scratch.”
How to relieve pain
If a tooth hurts severely after treatment of pulpitis, taking a pain reliever (Analgin, Ibuprofen, Ketolac, etc.), rinsing the mouth with an antiseptic solution or a warm herbal decoction of lemon balm, sage, oak bark, chamomile, will help temporarily relieve the pain symptom and alleviate the condition. calendula.
It is strictly forbidden to heat a sore tooth, apply alcohol or garlic compresses to the gums, or take antibiotics or aspirin.
How to alleviate the condition and prevent the problem
How many days can a tooth hurt after nerve removal? No longer than 7, otherwise this is no longer the norm, but a pathological condition requiring medical attention. After the manipulations, the dentist may prescribe a pain reliever, which must be taken immediately after the anesthesia wears off - this can be Tempalgin, Ketorol and others. On the first day after nerve removal and filling, you need to rinse your mouth with a soda-iodine solution; it will relieve irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane and have a disinfecting effect.
Propolis is considered a good remedy - a small piece can be applied to the treated tooth and held for about an hour. Relief from soreness in the mouth will be brought by a cool compress of ice, wrapped in several layers of fabric and cellophane; it is not recommended to hold it for a long time, in order to avoid colds and pinching of the trigeminal nerve. It is not recommended to treat pain with warm compresses - perhaps this measure will help alleviate the condition, but it is considered pathologically dangerous.
Under the influence of heat, active proliferation of microbes begins, as a result, purulent contents accumulate in the tissues. It will enter the general bloodstream and cause blood poisoning (sepsis).
Now it is clear for what reasons a tooth may hurt after removal of a nerve, and which of them are considered normal and which require immediate treatment. It is not recommended to engage in therapy on your own at all, and in particular, you should run to the dentist if you begin to experience discomfort when swallowing saliva and water, there is an unpleasant odor coming from your mouth, and the gum tissue is very swollen. If symptoms are observed after the removal of a wisdom tooth or nerve, the matter may take a serious turn and require medical intervention.
Prevention of complications
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups, contact your dentist immediately if your tooth hurts after root canal cleaning;
- consult a doctor immediately if there are signs of an allergy to the filling material, increased pain, fever, swelling of the gums or face;
- follow the doctor’s recommendations after endodontic treatment regarding oral care and medications;
- do not self-medicate.
Author of the article Voznyuk Vladimir Aleksandrovich Maxillofacial surgeon-implantologist of the highest category
Work experience: 28 years.
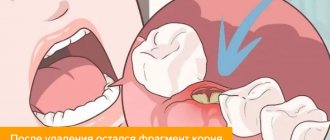
The mechano-medical treatment and filling of the tooth canals has not been fully completed
Post-filling pain may also occur due to the fact that the canal was not fully cleaned before closing. As a result, when the paste is introduced, a void is formed, which is a source of infection. In such a situation, in the first 5-10 days after visiting the dentist, the pain completely disappears. After this, the tooth becomes sore only when pressing on it. At the beginning, the discomfort is not strong, but soon becomes acute. It is also possible for a tumor to appear on the gums and a general deterioration in the victim’s condition, which is sometimes accompanied by an increase in temperature.
An x-ray is taken to determine the problem. If a void is detected, the filling material is removed and the canal is cleaned again. After this, it is sealed again. Treatment should not be delayed in such a situation.
Pulsating pain in a tooth can be caused by non-dental problems.
Trigeminal neuralgia
Unbearable, throbbing pain covers the teeth on one side (on the upper and lower jaws on the right or left). At the same time, half of the head hurts, “shoots” in the ear, eye and under the jaw. In severe cases, the tongue becomes temporarily numb, the patient complains of tingling of the face and twitching of facial muscles. The pain usually appears at night. During the day, an attack can be triggered by eating, talking, brushing your teeth, combing your hair, and even yawning. Without treatment, the patient's condition worsens due to the destruction of the protective myelin sheath of the nerve. If you have the slightest suspicion of trigeminal neuralgia, consult a neurologist.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Pulsation of teeth without pain may indicate a dysfunction of the liver, diseases of the stomach and intestines. Characteristic signs of gastrointestinal pathology are a coated tongue, bad breath and an unpleasant taste in the morning, abdominal pain, flatulence, constipation or diarrhea. After successful treatment of the underlying disease, discomfort in the mouth disappears.
Sinusitis
Inflammation of the maxillary sinuses is manifested by prolonged nasal congestion, discharge of purulent mucus and headache. The patient breathes through his mouth, his face is puffy. Often, a nagging pain in the area of the maxillary sinuses radiates to the cheekbones and provokes pulsation in the teeth. An ENT doctor treats sinusitis.
Perforation of the tooth root
With this problem, holes appear in the root. Perforation causes very sharp and severe pain that occurs immediately after the anesthesia wears off. The discomfort does not go away, even if you wait a month or more. In the soft tissues near the holes, inflammation develops, which can also provoke a purulent process.
If there is perforation, first all pathological holes are closed with calcium-containing compounds, and only after that the diseased tooth is filled. Without such treatment, the canal cannot be closed with paste.
When to sound the alarm
Mild soreness after nerve tissue removal is normal. After all, the canals are expanded, their shape is changed in order to be densely filled with a filling compound.
Mild discomfort that persists in the first few days is what doctors call post-filling pain. It does not require special treatment. If necessary, the patient can take painkillers.
During the depulpation procedure, microtraumas are inevitable. The tissues need to be given time to recover. Within two or three days there will be no trace of post-filling discomfort.
This is what the symptoms look like, indicating that the regeneration processes are not going according to plan:
- the pain persists after five to seven days, it is sharp, severe, and interferes with leading a normal lifestyle;
- analgesics do not relieve symptoms immediately and for a short time (sometimes they are completely useless);
- body temperature is increased;
- the gums in the area of the problem unit become inflamed and swollen;
- headache;
- the pain spreads to neighboring teeth, sometimes it is difficult to understand which zone is its source.
With these signs, you need to determine the cause of the problem as soon as possible. To do this, you should seek medical help. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis and tell you what to do to speed up regeneration.