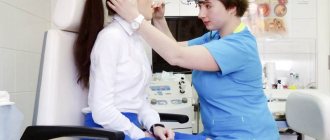
Posterior rhinitis or nasopharyngitis is an inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the nose and pharynx in children.
Normally, the villi of the nasal mucosa clean the inhaled air from dust and harmful substances. Glands located in the mucous membrane produce mucus, which humidifies the air.
With posterior rhinitis, the mucous membrane of the nasal passages swells, and the villi cannot perform their function of purifying the air, as a result of which the child breathes through the mouth and cold, unpurified and unhumidified air enters his respiratory tract.
This may cause bronchitis or pneumonia.
To eliminate the risk of developing serious complications when treating posterior rhinitis, you should consult a doctor.
Content
- Types of enteroviruses
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostic methods
- Treatment methods for enterovirus infection
- Prevention
Enterovirus infection is a group of viral diseases that affect various body systems (usually the skin, digestive tract and respiratory organs). After an illness, stable immunity is formed (up to several years), but only to the specific virus that caused the disease.
Therefore, a child can get sick several times. Because of this, in addition, there is no vaccine for this disease. Breastfed babies have immunity from their mother . But it is not persistent and goes away quickly after stopping breastfeeding. Most often, children from 3 to 10 years old and adolescents suffer . The younger the age, the greater the danger the disease poses.
Enterovirus infection is caused by viruses of the ECHO (Echovirus) and Coxsackie groups. They are characterized by a variety of symptoms - from conjunctivitis to diarrhea. The source of infection is another person . It is transmitted by the fecal-oral and airborne routes. In regions with a temperate climate, the disease is seasonal - people get sick more often in early autumn and late summer. Enteroviruses live in water for a long time: 18 days in tap water, 33 in river water, 65 in treated wastewater. Source: G.P. Martynova Enterovirus (non-polio) infection in children // Siberian Medical Review, 2014, No. 3
Scarlet fever: symptoms and signs
The disease begins acutely, with a sharp rise in temperature. Headache, muscle and joint pain, body aches, rapid heartbeat, and general weakness increase. Intoxication can cause vomiting.
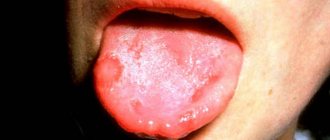
The tonsils, arches, pharynx and palate are excessively red, sometimes a coating appears like a sore throat (whitish, gray, purulent). The jaw and parotid lymph nodes become inflamed and enlarged, swallowing becomes painful and difficult. On days 4-5, the tongue becomes bright crimson with hypertrophied papillae.
Atypical forms of scarlet fever:
- extrabuccal - the pathogen penetrates through damaged skin, a purulent-necrotic focus is formed at the site of penetration with a most concentrated rash around, the pharynx is not affected;
- erased (in adults) - with symptoms of mild to moderate respiratory infection;
- scarlet fever with toxic-septic shock - develops more often in adulthood with severe cardiovascular and renal complications.
What type of rash occurs with scarlet fever depends on the nature of the infection and the age of the patient. In typical cases, the first elements of the rash appear on the 1-2 day in the face, upper torso, then on the elbows, groin folds. The nature of the rash is multiple dark dots turning into dark red stripes. Sometimes the elements merge into a large erythema (redness of a large area). On the face, rashes are observed on the forehead, temples, and cheeks.
Types of enteroviruses
There are more than 100 causative agents of this infection. The main ones are ECHO, polioviruses (the causative agents of polio), Coxsackie viruses A and B, and enteroviruses that cannot be classified.
Coxsackie viruses are several serotypes of the pathogen belonging to groups A, B and C. Coxsackie viruses type A are the cause of severe forms of enteroviral diseases. These are hemorrhagic conjunctivitis, herpetic sore throat, aseptic meningitis. Type B is more dangerous because it provokes hepatitis, myocarditis, and pericarditis. Source: V.V. Botvinyeva, L.S. Namazova-Baranova, O.B. Gordeeva, O.K. Botvinyev, T.N. Konopleva Modern possibilities for diagnosis, prevention and treatment of Coxsackie enterovirus infection in children // Pediatric pharmacology, article received: 01/22/2012, accepted for publication: 05/12/2012.
ECHO viruses are most dangerous for newborns. In them they cause meningitis, myocarditis, and hepatitis. This often causes death. There are no complications in older children.
Causes
The group of enteroviruses is very diverse. They are distributed everywhere: in water and soil, food and the bodies of people and animals, in feces (they remain viable for up to 6 months). They are resistant to environmental factors and the chemical effects of a number of agents, but die at temperatures above 50 degrees, drying, exposure to formaldehyde and chlorine. Outbreaks of the disease are typical for the warm season.
Main routes of infection:
- fecal-oral;
- contact and household;
- airborne;
- vertical (from the pregnant woman to the fetus);
- water (there are known cases of infection even through bottled water).
Causes of rhinopharyngitis in children
- Bacteria (staphylococci, pneumococci, streptococci).
- Viruses (adenovirus, influenza virus, ARVI)
- Severe hypothermia, diathesis.
- Scarlet fever, measles.
With the development of this pathology, the inflammatory process is localized in the nasopharynx, affecting the third tonsil of Pirogov’s lymphatic ring.
Rhinopharyngitis is a neuroreflex reaction of the mucous membrane of the pharynx or nose to an irritant. The irritant can be bacterial, mechanical, thermal and chemical.
The occurrence of posterior rhinitis in infants is due to the fact that infants easily react to environmental changes and malnutrition.
Acute nasopharyngitis in children from six months to 2 years old can be caused by an adenovirus infection, which is transmitted by airborne droplets.
Symptoms
Depending on the type of virus, there are different symptoms of enterovirus infection in a child. Some of them are relatively mild, while others can cause serious complications. The disease has an incubation period of up to 10 days . Most of the signs of enterovirus infection are similar to the manifestations of colds:
- high temperature (sharp increase to 38-39 degrees);
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- general malaise;
- headache.
Depending on the type of virus, the following are possible:
- diarrhea;
- nausea and vomiting;
- exanthema (a specific rash in the form of red spots, sometimes with blisters containing liquid);
- redness and pain in the throat and eyes;
- increased pulse and heart rate;
- pain in the chest or limbs;
- pressure change;
- nasal and sinus congestion, runny nose;
- numbness of the limbs, spasms, muscle twitching;
- numbness and tingling of the face;
- rapid weight loss;
- gastric disorders, including reflux;
- bloating;
- muscle, bone, joint pain, especially in the legs;
- feeling of chest tightness;
- wheezing, shortness of breath, cough;
- pain in the pelvis and testicles, reproductive dysfunction;
- decreased visual acuity, “foggyness”;
- depression, anxiety;
- ulcers or blisters in the mouth, throat, cervix, vagina;
- short-term memory impairment;
- decreased concentration;
- sleep disorders;
- in rare cases - convulsions.
There are a number of symptoms that appear as complications of enterovirus infection:
- “Summer flu”, or enteroviral fever, is the most common form of infection. First, the body temperature suddenly rises and stays within 38.5-40.0℃. Signs of the flu appear - muscle pain, sore throat, general weakness, headache, conjunctivitis, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. There may be inflammation of the testicular tissue and its epididymis. The duration of symptoms is 3-7 days.
- Viral pemphigus of the extremities and oral cavity is small, fluid-filled blisters on the skin. They appear on the palms of the hands, in the mouth, throat, on the soles of the feet, and in preschoolers and schoolchildren - between the fingers. There may be a fever for 1-2 days, and small red spots may appear on the legs and arms.
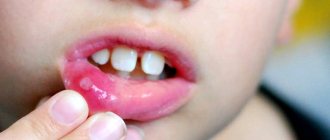
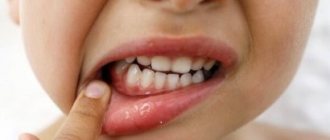
- Herpetic sore throat - blisters filled with light liquid with a red border on the back wall of the pharynx and tonsils. They are accompanied by a sore throat, fever, and pain when swallowing. Children may refuse to eat due to ulcers. Symptoms last 3-7 days.
- Viral exanthems - similar to the rash of roseola or rubella, appear in the summer. Usually occurs in children under 5 years of age. They pass in 3-5 days.
- Pleurodynia – it is characterized by severe muscle pain in the abdomen and chest. The pain worsens when coughing and breathing, the child sweats profusely. The duration of convulsive muscle pain is 15-30 minutes. There may be difficulty breathing. The condition is accompanied by headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss. Symptoms disappear within 2 days.
- Hemorrhagic conjunctivitis in acute form. With it, vision becomes blurred, pain occurs, visual acuity decreases, discharge comes from the eyes, and photophobia develops. The duration of the disease is 10 days.
- Pericarditis and/or myocarditis – coverings around the pericardium and infections of the myocardium. Infants and preschoolers are most susceptible to the disease. 2/3 of the cases are boys. First there is shortness of breath, cough, fever. Then chest pain, heart rhythm disturbances, increased shortness of breath, and heart failure may appear.
- Aseptic meningoencephalitis - affects children and adolescents, it causes pain in the eyes and head, fear of light, and fever. There may be a sore throat, drowsiness, muscle pain, and rash. Everything goes away in about 7 days.
Symptoms of the disease
Herpes sore throat in a child does not manifest itself for seven to fourteen days. This is the incubation period for the disease. Then symptoms appear that are similar to those of other infectious diseases: acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, intestinal infections - therefore, at the initial stage, herpetic sore throat is difficult to diagnose:
- high temperature up to 40°C
- severe sore throat, sore throat, cough
- Gastrointestinal disorders (vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain)
- muscle pain
- enlarged lymph nodes in the neck
- In infants, convulsions are possible.
Abdominal pain and digestive disorders are associated with the activity of enteroviruses in the intestines that cause herpes sore throat - they affect the intestinal and stomach mucosa, thereby disrupting their functioning. On the second or third day of illness, a characteristic rash appears on the palate and tonsils, similar to blisters with liquid. The appearance of these rashes is a sign that we are dealing with herpetic sore throat. When these bubbles burst, they form ulcers, which create discomfort and pain in the mouth. A child experiencing severe sore throat may refuse not only food, but also drink. Increased salivation is possible, since the receptors that affect saliva production are constantly irritated.
If the baby has a weak immune system, the formation of bubbles can occur in several “passes” and with a break of two to three days, accompanied by a repeated increase in temperature and symptoms of intoxication. There are cases when rashes appear on the legs, arms and body, but not on the face.
The fever usually subsides on the third to fifth day, and mouth ulcers disappear within a week. When the peak of the disease passes, the child feels significant relief - improvement occurs on the sixth or seventh day after the appearance of the first symptoms. But we must remember that for a certain period the child remains a source of infection! One of the differences between herpes sore throat and acute respiratory infections is the absence of nasal discharge, although swelling of the mucous membrane is present. Also, outbreaks of acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections in the summer, as a rule, do not happen, which cannot be said about this type of sore throat. In summer, heat contributes to the rapid spread and high activity of enteroviruses, and the number of cases of herpangina increases accordingly.
Normally, herpetic sore throat in children lasts from eight to ten days.
Dear parents! Diagnosis and treatment of herpetic sore throat in children must be carried out under the supervision of an otorhinolaryngologist, since it is not always possible to make a correct diagnosis on your own (due to the similarity of the initial symptoms of the disease with other viral diseases). Failure to start proper treatment on time can result in a protracted illness and complications!
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis in most cases can be made by characteristic symptoms, physical examination, and medical history.
After examining and collecting complaints, the pediatrician will prescribe a series of tests aimed at identifying the type of virus. The doctor may prescribe:
- general urine analysis;
- stool analysis;
- blood tests (general, biochemical, serological, etc.);
- immunohistochemical analysis of tissues (to detect antibodies to enterovirus infection);
- cultures of biomaterial (saliva, throat scrapings, etc.).
An accurate diagnosis may also require a differential diagnosis to exclude other diseases with a similar clinical picture.
Other diagnostic tests are also performed:
- Laboratory Serology is a blood test that detects an increased amount of antibodies. The body produces them to fight the virus in the acute period and during the recovery stage. The analysis allows you to determine ECHO 6, 7, 9, 11, 30 and Coxsackie B1-B6. A negative result does not necessarily mean that you do not have the disease; it just does not detect other types of viruses. PCR is a highly sensitive (100%) and specific (97%) test. Allows the detection of enterovirus RNA in the cerebrospinal fluid. Blood PCR detects the virus in 30% of patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Source: A.V. Demina, V.A. TERNOVOY, N.I. Shulgina, S.V. Netesov Enteroviruses. Part 3. Laboratory diagnostics, treatment, immunoprophylaxis // Bulletin of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, volume 31, No. 3, 2011. An analysis of cerebrospinal fluid is needed if there are symptoms of damage to the spinal cord, brain and their membranes. The fluid is collected by puncturing. With aseptic meningitis, the level of leukocytes is increased. Glucose is normal or slightly reduced. Protein is normal or slightly increased. Troponin I and cardiac enzymes is a blood test to determine the level of these indicators. If they are elevated, it means the heart is damaged. Normally, the serum troponin I level should be from 0 to 0.5 ng/ml. RT-PCR is an analysis to detect common regions of enterovirus RNA. The test has a sensitivity of 95% and specificity of 97%. Approved for the diagnosis of enteroviral meningitis. The best results are obtained if the material for research is cerebrospinal fluid. Sputum, blood and mucus from the respiratory tract, and feces can be examined. However, the result will not be as accurate.
- Instrumental Electroencephalography – assesses the degree and severity of the disease. Chest X-ray - may reveal an increase in cardiac volume in patients with myopericarditis. Echocardiography – performed if myocarditis is suspected. Shows abnormal movement of the walls of the heart chambers. May reveal acute reduction in ejection fraction and ventricular dilatation in severe cases. Examination by an ophthalmologist using a slit lamp is indicated for those children who have hemorrhagic conjunctivitis and corneal erosions. Coxsackie A24 and Enterovirus 70 viruses can be detected from conjunctival smears within 3 days of infection.
Symptoms of posterior rhinitis in children
- dryness, burning, tingling in the nasopharynx;
- difficulty in nasal breathing, nasal tone of voice;
- possible headache in the occipital region;
- as the disease progresses, ear pain and hearing loss may occur;
- temperature increase;
- tenderness of the occipital and cervical lymph nodes upon palpation;
- mucous or purulent nasal discharge;
- In newborns, due to difficulty breathing, vomiting and flatulence are possible.
Hearing may decrease due to illness
Treatment methods for enterovirus infection
Drug therapy is:
- medications to relieve symptoms (antipyretics, painkillers, etc.).
- vitamins and microelements.
To relieve symptoms, a child may be prescribed medications from different groups:
Painkillers and antipyretics to relieve headaches, muscle pain, and fever. These are “Ibuprofen”, “Paracetamol”, “Ibuklin”, “Nurofen for children”, etc.
Immunoglobulins stimulate the child's immunity. They are administered by injection - intramuscularly or intravenously. The second option is more effective and common.
Important! Antiviral drugs have not been shown to be highly effective in later stages and are not included in the formal treatment plan. They help at a very early stage, when 5-10 hours have passed since infection. But identifying the disease at this stage is almost impossible.
Vitamins (especially vitamin D) and supplements containing essential microelements (magnesium, zinc, potassium, selenium, calcium) help fight the virus well support the child’s body during this difficult period
Important! Antibiotics do not work against enterovirus infection, since they are antibacterial, not antiviral drugs.
The child should be provided with bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids using solutions to restore water and electrolyte balance, and a special gentle diet. The main purpose of the diet is to reduce intoxication and increase immunity, while being gentle on the digestive system. The diet should have enough vitamins, minerals, and protein.
Prevention
The basis for the prevention of enterovirus infection in a child is compliance with the rules of hygiene:
- washing hands and food before consumption;
- boiling water;
- avoiding places where large numbers of people gather during an epidemic.
- It is extremely important to take measures to increase immunity: follow a routine, eat right, and harden yourself.
In the pediatric medical department, all conditions have been created for the diagnosis and treatment of enterovirus infection in a child. For seriously ill patients, the department operates a 24-hour hospital, where the small patient will be under the constant supervision of qualified medical personnel and doctors. Remember that the sooner the correct diagnosis is made and the type of virus is determined, the easier it will be to cure the child and avoid complications.
Sources:
- G.P. Martynov. Enterovirus (non-polio) infection in children // Siberian Medical Review, 2014.
- V.V. Botvinyeva, L.S. Namazova-Baranova, O.B. Gordeeva, O.K. Botvinyev, T.N. Konopleva. Modern possibilities for diagnosis, prevention and treatment of Coxsackie enterovirus infection in children // Pediatric pharmacology, article received: 01/22/2012, accepted for publication: 05/12/2012.
- A.V. Demina, V.A. Ternova, N.I. Shulgina, S.V. Netesov. Enteroviruses. Part 3. Laboratory diagnostics, treatment, immunoprophylaxis // Bulletin of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, volume 31, No. 3, 2011.
Markova Daria Olegovna Clinic
Author of the article
Markova Daria Olegovna
Specialty: pediatrician
Experience: 15 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Online opinion of a pediatrician (SPECIAL) | 0 rub. |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a pediatrician, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |