Causes of childhood stomatitis
There are 6 main factors that can provoke the occurrence of stomatitis in the mouth in infants:
- infections;
- mechanical damage;
- physical agents;
- chemical burns;
- allergic reactions;
- poor oral hygiene.
All conditions that cause immunodeficiency in a child predispose to the occurrence of such a pathology: chronic diseases of internal organs, vitamin deficiencies, the presence of foci of chronic infection in the body, stress, climate change. Dr. Komarovsky notes an increase in the incidence of stomatitis in children who often suffer from ARVI.
Infectious forms of the disease are the most widespread. Most often, herpetic stomatitis occurs. Also, lesions of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity can appear against the background of various infections: smallpox, measles, rubella, entero- and adenoviruses. Banal staphylococci and streptococci, which normally live in small quantities in the mouth of every baby, also play a huge role in the development of the inflammatory process. Their effect increases only when the child’s immunological status decreases.
Quite often, after taking antibiotics (especially if the course of treatment is long), infants develop a fungal infection of the oral mucosa - candidiasis or thrush, which can also trigger the development of stomatitis.
Children, especially young children, learn about the world around them through taste. Therefore, babies constantly put into their mouths all the objects that are at their disposal. Thus, mechanical trauma to the mucous membranes simply cannot be avoided. And take into account the fact that objects are not always clean, inflammation forms very quickly. A child can independently injure the mucous membrane by biting it with his teeth. This is observed very often in dreams with neuroses.
When teething, gums are sometimes injured, which, coupled with the baby’s reduced immunity during this period, leads to a strong inflammatory response.
Of the physical agents, the most common cause of stomatitis is exposure to hot food. In this case, microburns occur on the mucous membranes, at the site of which inflammatory foci are formed.
Chemical burns occur due to accidental exposure of the oral mucosa to potent substances. In everyday life, this could be vinegar, high-concentration hydrogen peroxide, alcohol or eau de toilette, perfume, various paint solvents or liquid cleaning products.
Anything can act as an allergic component in the development of stomatitis. For example, harmless candy, toothpaste, chewing gum, various drinks, medications and food. Often, allergic stomatitis occurs in infants during the period of introducing the first complementary foods.
Symptoms of stomatitis in children
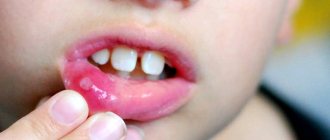
For all types of stomatitis, the common and defining signs are inflammation of the oral mucosa and the appearance on any of its parts, such as the tongue, the inside of the lips, cheeks, pharynx, of various formations in the form of erosions, blisters, characteristic plaque, and in cases of traumatic stomatitis - traces of burns and biting. It is important to understand that stomatitis is not just one acute or chronic disease with certain classic symptoms. Each type of stomatitis has its own specific cause, and it may not manifest itself in the same way. Therefore, they need to be treated differently.
Symptoms and signs
How to recognize stomatitis in children? Despite the abundance of causes that cause this disease, all forms of stomatitis have common clinical symptoms:
- The first signs of such a pathology are slight redness on the mucous membranes, which can be localized both on the gums and on the palate, on the tongue or on the lip.
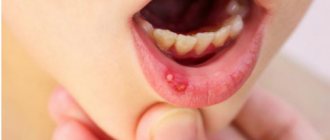
- Gradually, the redness gives way to swelling, round or oval ulcers appear, covered with a whitish or gray coating on top and surrounded by a red cushion. These ulcers are very painful and prevent the child from leading a normal life, eating or sleeping.
- As the inflammatory process becomes more severe, small ulcers merge into one large one.
- Local signs of stomatitis are accompanied by general symptoms: the child’s temperature rises, weakness, and lack of appetite appear.
One of the features of the course of the disease is the appearance of vomiting with stomatitis. It is caused by increased work of the salivary glands and increased excitability of the baby’s nervous system due to severe pain.
Classification of HRAS (chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis)
| CLASSIFICATION | A COMMENT | ||
| classification: | According to the degree of damage to the mucous membrane: | a comment: | 1) Superficial (catarrhal, fibrinous) 2) Deep (ulcerative, necrotic) |
| classification: | According to the clinical course: | a comment: | 1) acute 2) chronic |
All types of stomatitis occur in children, but the most common are: herpetic, candidal and traumatic stomatitis.
Types of childhood stomatitis and their main manifestations
The classification of childhood stomatitis is based both on the cause of the disease and on some distinctive features in the clinical course of such pathology. We will tell you how to determine this or that type of disease in our article later.
Catarrhal stomatitis
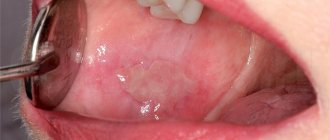
It is the mildest and most common form of the disease. In this case, multiple inflammatory foci appear on the mucous membrane of the gums, cheeks or lips, covered with a whitish coating, but without the formation of aphthae or ulcers. In this case, the child will complain of pain in the mouth when eating, drinking or talking, increased salivation, bad breath, and general weakness.
With catarrhal stomatitis, the mucous membrane is very susceptible to injury and bleeding, even during normal activities: brushing teeth, eating. When inflammatory foci are localized only on the gums, the clinical picture of stomatitis will resemble gingivitis.
Ulcerative stomatitis
The ulcerative form is a consequence of untreated catarrhal stomatitis. In this case, against the background of edematous foci of redness, multiple ulcerations are formed, which gradually increase in size, spread deep into the tissue of the mucous membranes or merge with each other.
The child complains of severe pain in the oral cavity, which intensifies when trying to brush his teeth or eat, and the smell of his breath becomes putrid. General health worsens: body temperature rises, weakness and body aches occur.
Young children are capricious, refuse to eat, and have trouble sleeping.
Gangrenous stomatitis
The gangrenous form of the disease is a continuation of catarrhal and ulcerative forms. A characteristic sign of this pathology is the spread of the inflammatory process deep into the tissues of the jaw with the development of extensive necrosis, which can involve the bones and spread to other anatomical areas.
The condition of a child with gangrenous stomatitis is extremely serious. There may be disturbances of consciousness, severe weakness, and the smell of rotting meat from the mouth. Regional lymph nodes are enlarged and painful on palpation.
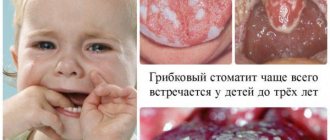
Candidiasis (fungal or milk) stomatitis
Candidal stomatitis is characterized by specific symptoms. At the onset of the disease, children have dry mouth. Subsequently, a burning sensation and an unpleasant aftertaste appear. A white coating in the form of small dots is deposited on the mucous membrane. As the process progresses, the points merge into a large lesion that resembles a curdled mass. Such plaque is difficult to remove, exposing the inflamed surface of the mucous membrane.
Fungal stomatitis often occurs without fever, and the general condition is little affected.
Infectious stomatitis
The phenomenon of stomatitis can also be observed in some infectious diseases. With scarlet fever, the typical picture on the mucous membranes of the mouth will be supplemented by specific manifestations of the disease: a pinpoint rash on the skin and a “crimson tongue” - the surface of the tongue is bright red, shiny with hypertrophied papillae.
With diphtheria, damage to the gums will be combined with the detection of dense grayish films on the tonsils or in the throat. In this case, a paroxysmal cough with episodes of suffocation will be noted.
Allergic stomatitis
The allergic form of stomatitis most often affects children over 4 years of age. It is characterized by a clear connection with the action of the allergen, a rapid increase in symptoms and their rapid extinction with adequate treatment. The clinical picture in this case is similar to the ulcerative version of the disease - ulcers or aphthae form on the mucous membranes, covered with a whitish coating and surrounded by a focus of redness. Quite often, this pathology occurs in the form of chronic stomatitis with periodic episodes of exacerbation.
Traumatic stomatitis
In cases of mechanical trauma, a significant focus of infiltration appears on the mucous membrane, which ulcerates as the inflammation progresses. When burned by hot drinks, a bubble often appears, after opening which a fairly deep ulcer is exposed. A distinctive feature of the traumatic form of the disease is a clear connection with trauma or thermal burn of the oral mucosa and the formation of a single lesion.
In case of severe inflammation, local symptoms may be accompanied by general symptoms: fever, malaise, headache.
Herpetic stomatitis
In herpetic stomatitis, the main morphological element is small blisters located against the background of a hyperemic mucous membrane. They quickly open and erosions form, which are covered with fibrous plaque. The lesions can be localized separately or merge into a single affected area.
Erosion is extremely painful, the child refuses to eat, is capricious, sleep is disturbed, and in severe cases there is a significant increase in body temperature. In this case, typical herpetic lesions can be found not only in the oral cavity, but also on the face or other parts of the body.
Bacterial (purulent) stomatitis
Most often, bacterial stomatitis appears due to constant improper oral care or microbial sore throat. The clinical picture is typical for stomatitis: initially foci of inflammation appear, which then transform into deep ulcers covered with abundant purulent plaque.
At the same time, purulent deposits on the tonsils are detected, the child’s general well-being suffers, body temperature often rises significantly, and the cervical, submandibular and clavicular groups of lymph nodes enlarge.
Vesicular stomatitis
Vesicular stomatitis is an infectious disease. Its causative agent is vesiculovirus, a virus transmitted from sick animals to people. The incubation period of this disease is 5-6 days, during which children may complain of fatigue, weakness, and slight chills. Subsequently, small painful blisters with whitish contents appear on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. Similar elements appear in the area of the feet and hands.
The general symptoms are very similar to a banal acute respiratory infection: the body temperature rises, there may be signs of rhinitis and conjunctivitis. If the intestines are damaged, there may be dyspeptic symptoms: diarrhea or constipation.
Literature
- Khomenko L. A. Therapeutic dentistry of children. Textbook for university / ed. 2007 – pp. 643-722.
- Ismailova G. T. Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis // Bulletin of surgery of Kazakhstan. - 2011. - No. 4. — P. 124-125.
- Drobotko L.N., Strakhova S.Yu. Acute stomatitis in children // Issues of modern pediatrics. - 2010. - T. 9. - No. 2. - P. 146-149.
- Suerkulov E. S., Yuldashev I. M., Mamyraliev A. B., Toktosunova S. A., Tsepeleva A. S., Sooronbaev A. A. Prevalence and structure of the incidence of stomatitis in children // Bulletin of Science and Practice. 2022. T. 4. No. 11. — P. 91-96.
- Suerkulov E. S., Yuldashev I. M., Mamyraliev A. B., Zhumashova N. K., Yuldasheva G. I. Complex therapy of inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa in children // Bulletin of Science and Practice. 2022. T. 5. No. 5. — P. 96-104.
- Pankrusheva T.A., Maravina I.N., Chekmareva M.S. Research on the development of the composition and technology of tablets for the treatment of stomatitis // Scientific result. Medicine and pharmacy. – T.4, No. 1, 2022. – P. 78-87.
- Instructions for medical use of the drug HEXORAL® aerosol: , .
- Instructions for medical use of the drug HEXORAL® solution: , .
- Instructions for medical use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS: , .
- Instructions for medical use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC: , .
- Instructions for medical use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA: , .
Up to contents
Nutritional Features
Due to the fact that painful ulcers appear in the mouth with stomatitis, any meal gives the baby discomfort. Therefore, the diet during the period before recovery should have a number of features.
- All food taken should be warm and at a temperature as close as possible to body temperature. This will prevent unnecessary irritation and will not cause acute pain.
- Since chewing is quite painful, portions should be reduced by about a third, but the frequency of meals should be increased.
- When feeding your baby, you should give preference to dishes with a soft consistency, and it is better to postpone dense and dry foods until complete recovery.
- It is worth giving preference to products with a neutral taste. These are potatoes, bananas, pears, pumpkin.
- Until recovery, spicy, salty and sour foods are completely excluded from the child’s diet.
- To make eating less painful, you can purchase thick straws for cocktails and crush all food so that it can be drunk.
- The emphasis is on healthy foods rich in microelements and vitamins. For example, buckwheat, oatmeal, and rice can be recommended for cereals. It is preferable to give your baby cauliflower and broccoli as vegetables.
Is stomatitis contagious?
Infectious variants of the disease are quite easily transmitted from sick children to healthy ones. Most often, the infection spreads through airborne droplets from saliva during normal talking, coughing or sneezing.
The herpes virus can pass from an infected mother to the child during childbirth or during breastfeeding in the event of an exacerbation of herpetic inflammation.
We must remember that some forms of infectious stomatitis may well be transmitted through shared objects. This is especially true for cutlery, toys and personal care products. Therefore, if a child gets stomatitis, it is necessary to take measures aimed at preventing the possibility of its transmission to healthy children.
- If there is another child in the family, then it is worth protecting him from communication with the sick baby for at least a few days.
- It is imperative to provide the patient with individual household items that can be processed separately from the belongings of the rest of the family.
- If a case of stomatitis is detected in a kindergarten, it is recommended to disinfect all toys that healthy children may come into contact with.
Homeopathic treatment
Many parents prefer to treat their children with homeopathy. However, such treatment should only be auxiliary and complement traditional methods.
In pediatric practice, the following drugs can be used:
- Borax,
- Mercuriussublimatuscorrosives,
- Natrum muriaticum,
- Arsenicum.
The group of homeopathic medicines also includes the combination remedy Malavit, which combines homeopathic components, natural herbal extracts and water from artesian springs. For rinsing with stomatitis, a solution is prepared from 5 drops of the drug and 100 ml of water (children under 5 years old need only one drop per year of life). The procedure is carried out 3-5 times a day after meals.
How many days do people suffer from stomatitis and what to do at the first signs of it?
How long does stomatitis last? This question is of great concern to parents of sick children, since all the symptoms of the disease are unpleasant and cause discomfort to the child.
The duration of the disease depends on its form. Acute variants of stomatitis with adequate drug treatment resolve within 14 days.
If the disease does not go away for a month or more, then they talk about the chronic course of such a pathology. In this case, it is possible to alternate periods of subsidence of clinical symptoms and their exacerbation - recurrent stomatitis.
If you suspect signs of stomatitis in your child, you should urgently consult a doctor who will tell you how to numb the mucous membrane and prescribe comprehensive treatment. If it is not possible to visit a doctor as soon as the first symptoms of the disease begin, then it is possible to independently numb the mouth with local drugs (Dentinox, Kalgel). And you can’t delay medical consultation!
Hexoral in the treatment of stomatitis
For local treatment of stomatitis in children, drugs from the HEXORAL® line can be used.
For irrigation of the oral cavity, the doctor may recommend aerosol HEXORAL® based on hexethidine, which has antiseptic properties7. Thanks to the fine spray, the drug is evenly distributed over the entire surface of the mucosa7. A solution of HEXORAL®8, similar in composition, is intended for rinsing the mouth. Both medications can be used to treat children 3 years of age and older.
Mint-flavored lozenges HEXORAL® TABS based on chlorhexidine and benzocaine may be suitable for boys and girls over 4 years of age9.
For patients with stomatitis over 6 years of age - HEXORAL® TABS CLASSIC based on the antiseptic amylmetacresol. The assortment includes tablets with lemon, orange, black currant, lemon and honey flavors10.
HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA may be suitable for adolescents aged 12 years and older. The lidocaine it contains can relieve even severe pain11.
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.
Up to contents
Possible complications
The prognosis for the disease is usually favorable. However, incorrect or untimely treatment can lead to the development of complications:
- The addition of a secondary bacterial infection, accompanied by a worsening of the sick child’s condition.
- Sometimes severe necrotizing forms of stomatitis lead to osteomyelitis - destruction of the bone tissue of the jaw.
- Persistent or frequent stomatitis can provoke the loss of teeth from both the primary and permanent sets.
- The presence of a chronic purulent inflammatory focus in a child’s body negatively affects the state of immunity, and also, under the influence of unfavorable factors, can lead to blood poisoning - sepsis.
Prevention in infants
Preventive measures should begin in a newborn child immediately after he is discharged from the maternity hospital. For the first days and months of life, it is necessary to adhere to thorough disinfection of toys, bottles during artificial feeding, or to treat the nipples immediately before applying to the breast.
«
An important point is regular visits to the dentist from the first teeth. It is necessary to carefully care for your baby’s oral cavity and use only special toothbrushes and toothpastes, preferably those recommended by the doctor.