From this article you will learn:
- stages of caries,
- what are the signs of caries?
- how to identify caries yourself.
Caries is the process of destruction of hard tooth tissues with the active participation of cariogenic microorganisms of the oral cavity, such as streptococci, actinomycetes and lactobacilli. The main conditions for its development are irregular or insufficient oral hygiene, which leads to the accumulation of soft microbial plaque on the teeth, as well as food debris between the teeth. Depending on the depth of damage to the hard tissues of the tooth, caries is usually divided into several types, which, in fact, are successive stages of its development.
The initial stage is always spot-shaped caries (foci of demineralization in the form of white spots on the surface of tooth enamel), and if left untreated, it gradually goes through the stages of superficial, medium and deep caries. Symptoms of dental caries, where we include patient complaints and data from a visual examination of the carious cavity, will be slightly different at each stage, and below we will consider them in detail.
What is caries
Caries, translated from Latin, means “rotting,” which quite accurately describes the disease - the decay of tooth tissue under the influence of aggressive factors.
The process may affect the nerve, which is accompanied by severe pain. Many people have bad breath, which also corresponds to the name of the disease. The pathogenesis of caries is based on demineralization - the loss of minerals and, accordingly, the hardness of dental tissue due to the action of organic acids. The occurrence of these chemical compounds has two ways:
- Acids are formed in the cavities of teeth from food stuck in them - simple carbohydrates break down and change the alkaline balance.
- Microorganisms are active on the surface of the enamel, resulting in the release of acidic substances.
As a result, the hardest tissue of the human body is destroyed, causing pain that interferes with normal chewing of food.
Competition “Bio/Mol/Text”-2020/2021
This work was published in the “Free Topic” category of the “Bio/Mol/Text” competition 2020/2021.
The general partner of the competition is the annual biotechnology conference BiotechClub, organized by the international innovative biotechnology company BIOCAD.
The sponsor of the competition is SkyGen: a leading distributor of life science products on the Russian market.
Competition sponsor: the largest supplier of equipment, reagents and consumables for biological research and production.
"Book" sponsor of the competition - "Alpina Non-Fiction"
We would all like to have brilliant, healthy white teeth so that we can proudly show them off to others, and those around us would immediately fall into delight from such a demonstration. But, alas and ah, the problem of caries lies in wait for our teeth literally around every corner. However, if you are “armed and dangerous”, namely, you know where the roots of caries come from, that’s already half the victory! Therefore, let's understand the biological subtleties of its occurrence.
Causes of caries development
Negative factors lead to the appearance of defects; these can be both external influences and changes in the body. Caries - causes: Eating sweets, especially in large quantities. First of all, we are talking about candies, cookies, baked goods, carbonated water - quickly broken down carbohydrates that change the alkaline environment of the oral cavity to an acidic one. Also, these products are a breeding ground for microorganisms, whose vital activity destroys teeth.
- Poor oral hygiene. Lack of habit of regularly brushing your teeth twice a day after meals for at least three minutes accelerates the demineralization process, and the remaining food particles begin to rot, damaging the enamel and emitting an unpleasant odor.
- Bad habits. Smoking and alcohol negatively affect the condition of teeth.
Not only the causes that provoke dental caries lead to the development of the process - there are factors whose presence increases the likelihood of pathology occurring. Risk factors include:
- pregnancy - if there is insufficient calcium intake, the mother’s body takes the element from the dental and bone tissues and transfers it through the bloodstream to the growing baby;
- heredity – predisposition to caries is inherited;
- low quality water;
- food low in vitamins and minerals, primarily calcium, phosphorus, colecalciferol;
- congenital disorder of enamel maturation.
Lifestyle
If you have learned about the risk group for root caries (older age), this does not mean that you can relax. Caries has many causes and can occur at any age if basic precautions are not followed.
Those at risk include smokers, diabetics, pregnant women and even children. The provoking factors in this case are:
- smoking and lack of oral hygiene;
- infrequent brushing of teeth and lack of fluoride;
- poor nutrition with preference for desserts;
- frequent stress;
- alternating hot and cold;
- structural features of the oral cavity;
- alcohol abuse - alcohol breaks down into sugars and acids;
- abuse of coffee and strong tea, which creates an acidic environment in the oral cavity;
- lack of water intake, and therefore lack of saliva;
- gum injuries.
Stages of caries development
During the pathological process, four stages are distinguished. Caries – stages of development:
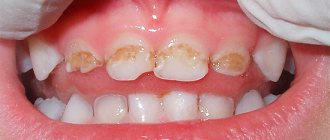
- With initial caries or the stain stage, it is manifested by local darkening of the enamel, which is often perceived as plaque. With early treatment, remineralization is possible - restoration of the mineral composition of the tooth.
- With superficial caries, the destruction of the enamel begins, as a result, the nerve in the affected tooth reacts to cold, hot and sour - a person experiences unpleasant sensations when eating ice cream, an orange or drinking tea. Since the destruction does not affect the deep layers, there is no severe pain, but there is noticeable discomfort close to pain.
- With average caries, dentin is affected, a cavity is formed in which food particles get stuck. The layer between the nerve ending and thermal, mechanical or chemical irritants, which is food, becomes thinner and thinner, as a result the person feels pain, lumbago and tries to avoid certain foods.
- In case of deep caries, it is accompanied by demineralization and a large amount of damage to the hard tissues of the tooth, often by pulpitis - inflammation of the dental nerve. Due to the resulting cavity, the tooth becomes fragile, its walls can crumble when pressed with food, and not necessarily hard food.
Based on the area where the defect is located, four types of caries are distinguished:
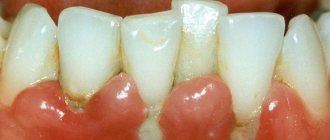
- Cervical. The part of the tooth near the gum is affected. Noticeable upon examination, including with the help of a mirror.
- Root. It is characterized by destruction of the tooth and roots and is diagnosed by opening the pulp and using x-rays.
- Fissure. The cavities are located on the chewing surfaces and are clearly visible upon examination.
- Proximal or interdental. Spots and cavities form between adjacent teeth and are one of the most difficult types of tooth decay to diagnose.
Complications
Untimely treatment of caries leads to inevitable complications:
- development of pulpitis (the carious process gradually spreads to the deep layers of dentin surrounding the pulp of the tooth);
- if pulpitis is not treated, necrosis of the pulp occurs (i.e. it dies), as a result, a focus of inflammation appears at the apex of the tooth root;
- development of gum “flux” (a purulent process occurs between the jaw and periosteum);
- the appearance of a cyst at the apex of the tooth root (the bone tissue is resorbed, and inflammation forms in its place).
Diagnosis of the disease
Detecting caries is not difficult if the patient is able to open his mouth on his own - the doctor uses a mirror and a probe for visualization. In mental and paralyzed patients, there is a need to resort to the use of various means with a sedative, relaxing effect, which facilitates the procedure for examining the oral cavity.
What caries looks like on teeth - signs:
- a white spot on the surface of the tooth at the initial stage;
- darkening of the enamel and a defect of varying depth in other stages;
- pain when probing the cavity is characteristic of medium and deep, less often superficial caries.
- In order to clarify the condition of the tooth root and the presence of a nerve (if the patient does not remember whether the nerve was removed during previous treatment), an x-ray of the upper or lower jaw is prescribed. This examination method also helps determine how tightly the canals are sealed.
How to determine the presence of a carious infection
Often this disease is accompanied by such symptoms as:
- pain when cold or hot;
- increased sensitivity of the affected part;
- aching pain that increases at night;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- change in tooth color.
In order to determine the presence of carious bacteria, it is best to contact trusted Dent Prestige dentists. Specialists diagnose the disease through a thorough examination and x-rays.
The presence of professional equipment contributes to the high-quality and quick implementation of the necessary procedures aimed at eliminating the problem.
Features of pathology in children
It is common for children to replace baby teeth with permanent ones, but this does not mean that temporary teeth do not need to be treated - firstly, the baby will be bothered by pain, and secondly, it is important to eliminate the source of chronic infection.
Distinctive features of caries in children:
Children need help brushing their teeth; adults must constantly monitor the process, otherwise caries may occur.
Treatment
Treatment tactics depend on the stage of caries development:
Caries in the spot stage allows you to carry out activities without turning on the drill. The patient is prescribed a special diet high in calcium, and a mineral composition is applied topically to the area of the spot. The only stage of the disease that is reversible.
Modern filling materials that harden under ultraviolet rays make it possible to treat deep caries in one visit, but the doctor may need 25–40 minutes depending on the complexity of the situation and the location of the tooth. In many cases, troubleshooting occurs in two stages:
- On the first day - removal of dead tissue, installation of an analgesic, application of a temporary filling.
- After 2–3 days, remove the temporary filling, rinse the cavity with antiseptic solutions, open the pulp (if necessary) and then, as described above, until the filling is polished.
Anesthesia is required for the third and fourth stages of caries; anesthesia can also be administered at the second stage if the patient has a low pain threshold.
Prevention
The causes of caries are well studied and known, which helps to develop preventive measures. Prevention of the development of the disease includes the following measures:
- daily brushing of teeth twice a day;
- replacing your toothbrush every three months – with longer use, the bristles wear out and do not perform their functions;
- rinsing your mouth with warm water, using dental floss after eating;
- To remove deeply stuck pieces, use a toothpick, not knives, needles or other objects - the enamel on the teeth can be easily damaged:
- reducing consumption of sweet and sour foods;
- preventive visits to the dentist twice a year, if complaints arise - immediately.
Brushing your teeth should be done with toothpaste, and its duration should be at least three minutes - during this time, remineralization processes occur, i.e., replenishment of minerals in the enamel.
Cleaning in dentistry from stone and plaque
1243900247100
Professional teeth cleaning involves removing the accumulation of all pathogenic microflora around the root.
It involves not only removing plaque, but also stones. This elimination of negative factors protects teeth for a long time.
Antiseptic treatment of affected areas
Treatment of root caries involves drilling out all affected areas with a drill and treating the carious cavity with antiseptics and special preparations. A 2% chlorhexidine solution or a gel based on it is used as an antiseptic for the treatment of carious cavities.