- What kind of disease is candidiasis?
- Symptoms
- Causes
- Treatment
- Therapy methods
- Preventive measures
Many parents are aware of such a common problem in children as thrush, which is characterized by the appearance of a white coating on the tissues of the oral cavity. In medicine, this pathological condition is called “candidiasis” and refers to fungal diseases. Candidiasis most often develops in a child’s mouth in the first year of life. The symptoms of thrush are very disturbing for the baby, but timely treatment allows you to get rid of the fungus quickly and without consequences.
What kind of disease is candidiasis?
According to statistics, about 30% of infants experience candidiasis. The causative agent of the disease is Candida fungus. These specific microorganisms are normally present in the body of every person, even in the absence of health problems, but only in small quantities.
Oral candidiasis in children is much more common, since the immune system of children is not yet formed and is not able to resist pathogenic microorganisms and the effects of negative external factors.
With weakened immunity and the concomitant influence of provoking factors, the fungus begins to actively multiply, affecting the mucous membranes. Without therapeutic treatment, candidiasis is eliminated in exceptional cases. Much more often, if thrush is not treated, complications arise, and the infection itself spreads throughout the body.
How is the disease diagnosed?
Visual methods for diagnosing candidiasis. Upon examination, inflammation of areas of the skin is revealed, limited to a border of exfoliating, macerated epidermis, and a whitish coating on the mucous membranes.
Laboratory diagnostics. Contrary to popular belief, the main method for diagnosing candidiasis is still microscopy of a smear from the affected areas of the mucosa. PCR (DNA diagnostics), which has become popular recently, is usually poorly suited for diagnosing candidiasis.
Laboratory diagnosis of the disease includes:
- microscopy of discharge smear
- cultural diagnostics (seeding)
- enzyme immunoassay (ELISA)
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Symptoms
Oral candidiasis in children can have different forms of manifestation and severity of symptoms: mild, moderate and severe. As a rule, each form corresponds to the stage of development of the disease. If therapy is not carried out in a timely manner, the signs of fungal infection become more intense and the number of symptoms increases.
In mild forms of the disease, a red rash appears on the oral mucosa, which is covered with a white coating on top. At the next stage, the child experiences swelling of the tissues and the formation of localized white spots with a coating of curd consistency. Gradually these spots merge into a larger affected area. When plaque is removed, bleeding ulcers open. If thrush starts, the fungus spreads to the entire oral cavity, including the lips, tongue and throat. All fabrics are completely covered with a curd coating.
Common symptoms of candidiasis in children include:
- burning and itching sensation in the mouth;
- discomfort and pain when eating;
- frequent regurgitation in babies;
- formation of cracks in the corners of the lips;
- temperature increase.
Children in the first two years of life report their condition by refusing to eat, constant whims and crying for no reason. It is not difficult to see the signs of candidiasis, so if a child has a sharp rise in temperature or refuses to eat, pediatricians and dentists recommend checking the oral cavity for the presence of white plaque. If you suspect thrush, it is not advisable to delay a visit to a specialist, since the fungal infection progresses quickly.
Complications of thrush
Thrush (candidiasis) is a disease, so its appearance requires special measures for immediate treatment. A mild form of candidiasis can develop into a more severe form if left untreated. The child’s body is designed in such a way that an infection from one place quickly spreads to another. Therefore, thrush as a disease cannot be underestimated. In weakened children, Candida fungi can spread into the intestines and disrupt its natural environment.
Fungi can enter the intestines, where they will also begin to multiply
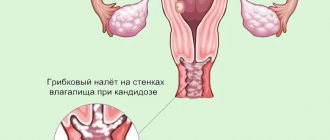
Manifestations of thrush in the genitals of girls can become especially difficult to treat. Delayed treatment can lead to serious consequences: a fungus in the vagina can cause vulvovaginitis, which leads to fusion of the labia or vaginal mucosa (synechia). Treatment of this problem occurs only surgically. Therefore, treatment of white plaque in the mouth of girls should be accompanied by constant parental monitoring of the condition of the genital organs.
- How long does it take for drugs to leave the body?
Important! At the slightest sign of complications in the form of redness and discharge, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Synechia
The presence of a large number of bacteria in the oral cavity can cause them to enter the child’s blood, lymphatic system, and from them to all organs. It is necessary to start treatment on time to prevent such a serious complication of thrush.
Important! Treatment should continue until the child recovers completely. Otherwise, the disease can become chronic, which will significantly weaken the immune system, and this will cause the development of allergies and other diseases.
Bacteria can also enter the blood
Causes
The main reason for the development of candidiasis of the oral mucosa in children is weakened immunity. If a baby is born premature, the likelihood of developing thrush is very high. Children who are breastfed or have congenital pathologies are also often exposed to fungal infections.
Provoking factors include:
- the presence of vaginal candidiasis in the mother during pregnancy (the child can become infected when passing through the birth canal);
- insufficient hygiene of the female breast during breastfeeding (the fungus is often localized specifically on the nipples due to the environment favorable for it);
- poor handling of the child’s initial things (bottles, pacifiers, etc.);
- parents’ habit of licking nipples (even if the adult has no signs of thrush, there may be a fungus in the mouth that can be passed on to the child);
- long-term use of drugs from the “antibiotics” group (medicines help reduce one’s own immunity);
- frequent regurgitation in infants (after regurgitation, an increased acidic environment will remain inside the oral cavity, favorable for fungus);
- excessive and frequent dry mouth (lack of saliva as a protective agent against the activity of pathological microorganisms).
Infection with Candida fungus in children over 2 years of age can occur as a result of consuming unwashed foods, raw milk or running water. If a child over 3 years of age suddenly shows signs of thrush, they should be examined not only for a fungal infection, but also for other possible diseases that may be accompanied by a “decay” of the immune system.
Causes of black plaque on the tongue in adults
“Stick out your tongue” - probably everyone has heard this phrase in the doctor’s office. “Why is it so important for a doctor to see a patient’s tongue?” – patients are lost in conjecture. The doctor will determine whether the tongue is clean or coated, and can suggest a diagnosis based on the nature and color of the plaque. Dark coating on the tongue is a sign of what disease? Do not be afraid of the appearance of a strange shade of the mucous membrane of the tongue. The reasons for the color change may be temporary and completely harmless.
Causes of black plaque on the tongue in adults:
- changes in bacterial flora after a course of antibiotics;
- poor oral hygiene;
- xerostomia;
- glossitis;
- regular use of mouthwashes containing irritating oxidizing agents;
- smoking or chewing tobacco;
- drinking excessive amounts of coffee or black tea;
- alcohol abuse.
What does brown coating on the tongue mean? Discoloration usually occurs when the papillae on the surface of the tongue grow larger than normal. The waste products of microorganisms accumulate between them, which leads to an unpleasant tint of the tongue. If the root of the tongue is covered with a green coating, the cause may be oral candidiasis (thrush). When taking antibiotics or eating “colored” foods, the white-gray coating characteristic of thrush can turn different shades of green.
What does a red coating on the tongue mean:
- about a lack of folic acid and vitamin B12, which causes a reddish tint;
- about “geographic tongue” (benign migratory glossitis), which is characterized by the appearance of reddish spots on the surface of the tongue;
- about scarlet fever, one of the symptoms of which is “strawberry tongue.” Read more about the symptoms and treatment of scarlet fever on our website Dobrobut.com;
- about Kawasaki syndrome, observed in children under the age of five and characterized by damage to the blood vessels. The syndrome is accompanied by redness of the tongue (“strawberry tongue”).
Treatment
Fungal diseases in children can be treated by a pediatrician, an infectious disease specialist or a dermatologist. If we are talking about the treatment of oral thrush, then therapy can also be carried out by a dentist.
The diagnosis of candidiasis is determined in most cases based on an examination of the oral cavity performed by a specialist. If there is any doubt, the doctor refers the patient for additional examinations. More often, to confirm the disease, a laboratory test is used to test a smear taken from the mouth for the presence of fungus.
Treatment of thrush in children requires an integrated approach. If the disease is not advanced, then local therapy is carried out in combination with measures to strengthen the immune system. In severe cases, oral candidiasis in children is treated with systemic drugs, local agents and compliance with preventive recommendations.
Diagnosis of mycosis
To make a diagnosis, an examination is carried out by a dermatologist or mycologist. The first step is a microscopic examination of the scales of the epidermis, hair and nails.
Laboratory testing allows you to determine the presence of spores or hyphae, which is necessary to clarify the type of pathogen and make an accurate diagnosis. The dermatologist also performs an examination under a Wood's lamp. This approach allows us to determine the type of disease and differentiate it from dermatitis.
Therapy methods
Treatment of candidiasis begins with treatment of the oral cavity. The first procedure is performed by a specialist at the appointment. Antiseptic agents are used to remove plaque. The doctor may then apply an antifungal agent.
The parent should closely monitor the dentist’s actions, since in the future they will have to treat the oral cavity themselves at home. The necessary medications will be prescribed by a specialist. Local antifungal agents are dangerous in case of overdose, especially for children, so you must strictly follow your doctor’s recommendations.
In advanced cases, medications are prescribed in the form of solutions, drops or tablets. There are few drugs available to treat candidiasis in children. Replacing them with adult counterparts is also dangerous. The dosage must be strictly observed.
A mandatory addition to the main therapy is maintaining good hygiene, good sleep, proper nutrition and taking measures to strengthen the immune system (eating healthy foods, taking pharmaceutical vitamins if necessary, walking, etc.).