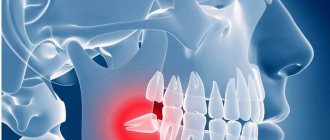
Formally, from the point of view of classification, wisdom teeth (“eights”) are the same molars (large molars) used for chewing and grinding food. However, in fact, for a number of reasons, these teeth have a special attitude: both among dentists and their patients.
The reason for this attitude lies in several points:
- Rudimentary. Science has proven that the outer molars in the mouth are the legacy of very distant ancestors, whose jaw was much larger; the current “wisdom teeth” fit on it without problems and were functionally very important for primitive man. Currently, their value has decreased to almost zero.
- Late eruption. In modern humans, wisdom teeth appear in adulthood (from 17 to 25 years), when bone tissue is already formed. Moreover, they do not replace dairy products, but grow for the first time. As a result, the pain is much stronger than usual, and in search of “its place” on the jaw, an erupting wisdom tooth can lead to rupture of soft tissues, the risk of infection and even more serious consequences, including malocclusion and disease of neighboring teeth.
- Difficult to reach position. Wisdom teeth occupy an extreme position in the dentition, which makes it difficult to properly clean them and, in case of illness, to treat them.
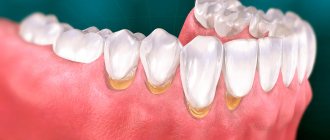
What is a wisdom tooth
In everyday life, wisdom teeth are the third molars, or the last, eighth teeth in a row, that is, “eights.”
The upper third molars can vary in shape and size, and are usually smaller than other molars and lower 8s. They have two or three roots, which sometimes grow together into one. But they always have three channels.
The lower wisdom teeth can also vary in shape and size, but, as a rule, they are larger than the upper “eights”. The roots of these teeth are short, sometimes fused, and often have a curved shape.
Indications for removal
Wisdom teeth removal is carried out if the following indications are present:
- Horizontal growth of the molar (promotes displacement of teeth in a row);
- the figure eight occupies an anatomically incorrect position and harms neighboring units;
- incomplete eruption (impacted tooth);
- pulpitis, periodontitis;
- impossibility or inappropriateness of endodontic treatment.
If the wisdom tooth on top hurts, it is easier to remove it than the lower third molar. The lower eights are distinguished by large, developed, often tangled roots, and the mandibular bone itself has a more dense structure. The complexity of surgical extraction depends on:
- Wisdom tooth positions;
- the position of neighboring units that complicate extraction;
- degree of eruption;
- the number of roots, their confusion.
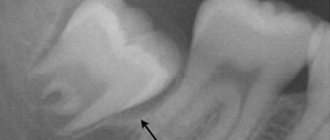
An orthopantomogram gives the doctor the necessary information about the position of the figure eight and its condition.
Features of cutting through “eights”
A characteristic feature of the third molars is the very late time of their eruption - as a rule, this occurs between 16 and 24 years, and sometimes later [1]. That is why in many languages they are called “wisdom teeth”. Late eruption determines the difficulties that many patients face during the development and appearance of “eights.”
The fact is that by this age the upper and lower jaws, as a rule, are already formed. Therefore, the eruption of “eights” is often associated with unpleasant or painful sensations, and often serious complications. Additional difficulties are caused by individual features of the anatomy of the facial skull, for example, the small size of the jaws, in which there is not enough space for the third molars to fully develop. The reason for this, according to most experts, is the evolution of the structure of the human body [2].
Due to the lack of space for full growth, third molars may not fully erupt (retention) or even change the direction of growth (dystopia). Often they begin to grow not vertically up or down, but at an angle to the dentition. Moreover, the size of the slope can be different and largely determines the possible complications of teething. Both retention and dystopia are considered pathological processes [3].
Among the complications of eruption and development of third molars are [3]:
- acute inflammatory process, up to phlegmon (purulent inflammation);
- formation of pathological bone pockets;
- destruction of hard tissues of the adjacent tooth;
- formation of follicular cysts;
- neuralgic pain;
- osteomyelitis and others.
Prevention of teething diseases consists of monitoring the correct development of the jaws and teething, sanitation of the oral cavity and timely orthodontic treatment, compliance with the rules of oral hygiene
“Retention, dystopia. Teething diseases”, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of the Department of Surgical Dentistry of Moscow State Medical University Panin A. M.
In what cases is wisdom teeth removal recommended?
The wisdom tooth removal procedure is carried out in several cases:
- as a prevention of complications of eruption and development;
- in the presence of complications;
- with severe tissue damage.
Various complications of eruption (inflammation, difficult eruption, retention, etc.) occur in almost 75% of owners of third molars [3]. These pathologies more often occur with “eights” on the lower jaw. Moreover, in women such complications occur twice as often as in men, which experts explain by the lack of space behind the teeth (retromolar region) in the lower jaw.
The difficult-to-reach location of the third molars means that even regular hygiene procedures do not clean them completely. Therefore, even if they have grown in accordance with the norm, they are often affected by caries. It also affects the lower (69.05%) “eights” more [3].
In the vast majority of cases, regardless of the gender and age of the patient, wisdom teeth are removed for pulp, periodontal and periodontal diseases. Indications for the procedure are [1]:
- the presence of inflammatory processes;
- impossibility of further prosthetics;
- prevention of the healthy state of second molars;
- maintaining gum health.
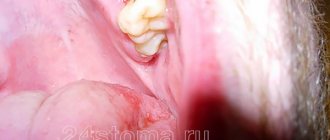
There are frequent cases of removal of an uncut “eight”. This procedure is performed to prevent complications during teething, as well as the development of crowding of teeth.
When choosing a treatment tactic for a “figure of eight”, specialists evaluate the location of the molar or its rudiment. For an accurate diagnosis, an x-ray examination is performed; it helps to assess the location of the tooth and identify changes in the tissues. In addition, radiation examination helps prevent complications during surgery.
If the eruption of third molars is difficult, the dentist will evaluate the possibility of saving them. As a rule, they try to maintain the “eight” if [3]:
- the tooth is in the correct vertical position;
- its roots are straight;
- periodontal tissues have no changes;
- there is enough space in the dental arch;
- The angle of inclination of the molar does not exceed 150 degrees.
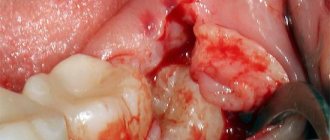
The operation to remove the figure eight is performed under local conduction anesthesia. The specialist may prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics 40 minutes before the procedure. The oral cavity is treated with antiseptics. The surgeon then performs the removal procedure. After this, the wound is treated and sutured tightly or openly, depending on the dentist’s decision.
Wisdom tooth removal is often associated with various complications. Therefore, there are a number of special techniques that are used by surgeons during the operation. This may be an incision of soft tissue, if necessary, sawing a tooth or other manipulations.
What happens in the oral cavity during the extraction of the eighth tooth?
When deciding how to treat a particular patient, the doctor takes into account the characteristics of his physical and emotional state. Particular attention is paid to the presence of allergies to medications.
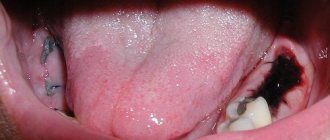
If there are no contraindications to extraction, the doctor administers an anesthetic. When the area becomes insensitive, the gum bends back and grabs the wisdom tooth with forceps. Begins to make rocking movements, allowing you to loosen the periodontal connection and extract the diseased tooth.
Since during the operation the vessels through which blood flows to the pulp tissues are damaged, bleeding occurs. Nerve impulses indicating trauma are transmitted to the brain. Then pain appears. But due to the action of the anesthetic, the patient does not feel it at first.
The hole formed as a result of the operation is heavily supplied with blood. Leukocytes rush here. Swelling occurs and inflammation develops.
Immediately after surgery, the doctor closes the wound with a sterile cotton swab. It helps stop bleeding and creates conditions for the formation of a dense blood clot. The latter is needed to prevent the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the tissues of the wound surface. Do not remove the tampon before the doctor says!
Contraindications for wisdom tooth removal
The surgeon assesses the patient’s condition before surgery based on the medical history and the results of preliminary studies. Removal of wisdom teeth is postponed in the presence of infectious diseases in the acute and subacute periods. These include, among others, influenza, tonsillitis, stomatitis, ARVI and others [1].
If complications of the eruption of “eights”, for example, an inflammatory process, can worsen the patient’s condition, tooth extraction is forced. In such cases, the operation is performed against the background of antibiotic therapy and other anti-inflammatory drugs.
A separate decision is required in cases where wisdom tooth removal is required for cardiovascular diseases, such as a previous myocardial infarction and hypertensive crisis, extrasystole and others. In such situations, the acute condition is usually treated.
The “eight” tooth is removed with special care in case of concomitant blood diseases: hemophilia, thrombopenia, acute leukemia and others. As a rule, the removal procedure is carried out in specialized hospitals.
What to do after wisdom tooth removal
After the removal of third molars, complications are more common than with the removal of other teeth. This is due to the peculiarities of their anatomical structure, retention, complexity and traumaticity of surgical intervention. The most common complications after removal: socket bleeding, “dry socket” and others [9].
After the procedure, it is not recommended to do anything that could remove the blood clot from the wound and impair healing or cause bleeding. The patient is advised to refrain from eating for 2 hours after surgery. At the same time, hot food and drinks are prohibited throughout the day after the procedure, and mouth rinsing is prohibited for the next 24 hours. It is not advisable to smoke, eat sweet, sticky, hard foods or drink with a straw.
List of sources
1. Dentistry. Textbook Aleksandrov M. T., Bazhanov N. N., Medvedev Yu. A., Platonova V. V., Sergeev Yu. N. / Ed. N. N. Bazhanova. - M.: GEOTAR, 2008.
2. Iordanishvili A.K., Ponomarev A.A., Gaivoronskaya M.G., Korovin N.V. Age-related features of wisdom teeth diseases // Kursk scientific and practical bulletin “Man and his health”. 2015. No. 4. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/vozrastnye-osobennosti-zabolevaniy-zubov-mudrosti (date of access: 06/13/2020).
3. Marugina T. L., Kan V. V., Fedotov V. V., Zagorodnikh E. S. Diagnosis, prevention and treatment of diseases of the eruption of the lower eighth teeth // Russian Journal of Education and Psychology. 2012. No. 4. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/diagnostika-profilaktika-i-lechenie-bolezney-prorezyvaniya-nizhnih-vosmyh-zubov (date of access: 06.13.2020).
4. Iordanishvili A.K., Ponomarev A.A., Korovin N.V., Lyskov N.V. Complications after removal of wisdom teeth and their treatment // Kursk scientific and practical bulletin “Man and his health”. 2022. No. 2. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/oslozhneniya-posle-udaleniya-zubov-mudrosti-i-ih-lechenie (date of access: 06/13/2020).
How does a postoperative wound heal?
How long the area hurts after tooth extraction depends on many factors. The healing process after tooth extraction is a complex and lengthy process. Removal occurs with a rupture of the dentofacial connection, namely the connection with the alveolar process and the jaw bone.
The recovery process lasts about two to three weeks. Much depends on the surgical protocol, the clinical situation and the characteristics of the body.
Main stages:
- Formation of a blood clot. Forms 1.5-3 hours after extraction. The function of the clot is to protect the wound area from pathogens and secondary infection.
- Active tissue regeneration. The affected mucous membranes are restored, after 3-4 days swelling and inflammation decrease.
- Formation of granulation tissue. After 4-6 days, granulation tissue forms on top of the clot - the basis of a new epithelial layer.
- Granulation proliferation. After a week, the granulation tissue grows, completely covering the socket.
Already on the eighth to tenth day, the wound is completely healed and by the end of the second week a new epithelial layer is formed.
After two weeks, bone tissue begins to renew. After six months, the bone tissue in the area of removal becomes completely healthy.