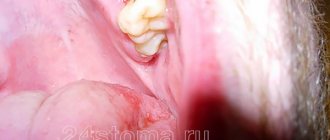
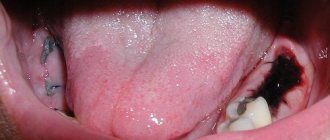
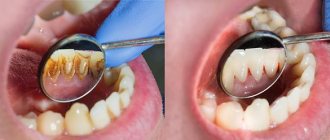
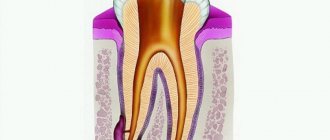
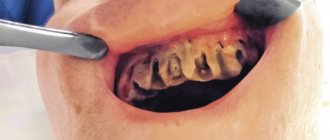
A purulent formation on the gum is popularly called gumboil. Very often it is not taken seriously, but it is not just a small swelling that will go away on its own. Flux is an ontogenic periostitis, a complex infectious disease that affects the periosteum and jaw bone. Periostitis occurs quite often, but without adequate treatment it is fraught with serious complications, including blood poisoning.
It is almost impossible to cure gumboil without the help of a dentist. The treatment program includes therapeutic, physiotherapeutic, and surgical methods.
Have you noticed purulent formations on your gums and swelling of your cheeks? Do you have acute pain in your tooth or gum? Come for a consultation with a dentist at our clinic. Timely treatment of flux allows you to get rid of the problem within about 7 days.
Why does flux form?
Dental diseases are always the precursor to gumboil. Most often lead to suppuration:
- Untreated caries. If caries is not treated, the inflammatory process begins to spread to other tissues. Pulpitis and periodontitis gradually develop.
- Mechanical injury. Injury can lead to more than just crown destruction. Very often, an inflammatory process develops in injured tooth or gum tissues. Without treatment, purulent processes develop and gumboil forms.
- Periodontitis. In more than half of the cases, gumboil develops precisely against the background of periodontitis, as its complication. This is due to the fact that purulent processes from periodontal pockets can spread to the neck of the tooth.
- Poorly sealed canals. Before filling, the canals must be completely cleaned and the filling material must completely fill the cavity. If at least one of the conditions is violated, the infection from the canal spreads to other tissues.
Features and risk factors
During difficult and prolonged eruption, the tooth germ practically does not change its position, and a significant part of its chewing surface is covered with a flap of gingival or mucoperiosteal tissue, the so-called “hood”. The flap covering the tooth germ forms a kind of pocket in which food debris and bacterial plaque accumulate. A moist nutrient medium creates optimal conditions for the intensive reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms, which, in turn, actively secrete waste products that are toxic to our body. This provokes the development of an infectious-inflammatory process in the tissues surrounding the problematic tooth germ.
Most often, inflammation of the gums occurs when a wisdom tooth erupts in the lower jaw, which is due to the anatomical structure of the jaw and the lack of space for third molars. In modern people, the jaw arch is approximately 1-1.2 cm smaller than in our distant ancestors, but the size of the teeth has remained the same. This is why the “eights” are cut much later, when the body as a whole and the dental system in particular have already formed - and because of this, it is difficult for the new tooth to find the “right” place on the dental arch.
Since wisdom tooth pericoronitis is the most common type of disease, people over the age of 18 are primarily at risk (usually “eights” are cut at the age of 20-25, but for some this process can take up to 30 years) . As for pericoronitis in children, it usually occurs against the background of insufficient oral hygiene in a child or with infectious diseases of the oral cavity (caries, gingivitis, stomatitis), which complicate teething in children and require treatment. Accumulations of plaque and hard dental deposits significantly increase the risk of developing the disease, so timely and regular removal of tartar can serve as a good preventative method.
When do you need dental help?
Flux has pronounced symptoms. The main one is the appearance of an abscess on the gum next to the diseased tooth. The abscess develops gradually. At first, the gums swell a little and a small red or whitish bump is noticeable on it. After some time, a noticeable fistulous tract forms on the lump, from which pus flows. The development of periostitis is accompanied by other symptoms:
- Swelling and swelling of the gums, lips, cheeks. Sometimes they can be so large that facial features are distorted.
- Severe cutting pain in the tooth area. Innervates the temporal region, orbits.
- The diseased tooth begins to become very loose, even if there was no mobility before or it was insignificant.
Since flux is caused by infection, it is characterized by symptoms that appear during any infectious process. The patient feels unwell, his temperature rises, his head hurts, and weakness appears. Lymph nodes on the head and neck become enlarged.
Any of these symptoms is a reason to consult a doctor. The more advanced the case, the higher the risk of complications. This disease is often accompanied by other pathological processes. For example, a cyst may form in tissues affected by infection.
Occurrence of complications
Operations to pull out figure eights are considered complex dental procedures, which are due to:
- difficult access;
- frequent retention;
- unpredictable structure;
- features of the location of the mandibular alveolar nerve.
Such procedures are very traumatic, which creates the preconditions for the occurrence of general and specific types of complications.
Are common
The nature of complications largely depends on the location of the tooth: on the upper or lower jaw. But there are also general complications that arise in almost everyone, regardless of the location of the figure eight and its initial condition. The most common overall effects are listed below.
Painful sensations
Approximately 2-3 hours after molar extraction, you will experience noticeable pain in the gums. This is a normal reaction of the body to trauma, which is dental surgery. During it, soft tissues are torn or cut, the bone is injured (if the tooth is located under it), blood vessels and nerves are damaged. Painful sensations should completely disappear after 2-4 days, and for some people disappear within a few hours. They can be reduced with the help of painkillers prescribed by the dentist. If the pain does not go away, and the cheek is very swollen, it means that the gum healing process is proceeding with complications.
Swelling of the tissues of the face and neck
Often after figure eight extraction, especially impacted ones, swelling of the soft tissues of the gums or cheeks is observed. This is also a reaction to injury, which can be called a normal consequence of a dental procedure. In addition to swelling, the following symptoms may occur:
- swelling of the lymph nodes;
- discomfort when swallowing;
- painful sensations during mouth movements, radiating to the ear.
Normally, severe swelling should go away completely in 2-3 days, and if it doesn’t go away, then we can talk about more dangerous consequences. If the condition worsens every day, difficulties arise when breathing, fainting, the temperature rises and the skin becomes covered with a rash, then such swelling is provoked by an allergy and it can lead to anaphylactic shock.
Hematomas
Hematoma due to extraction is usually expressed by minimal bluishness of the cheek, which goes away after a few days. But there are situations when the appearance of a bruise is accompanied by severe pain, swelling, and an increase in temperature. In such a situation, medical attention is needed. Hematomas form after vascular damage in people with increased capillary fragility, as well as when the patient has hypertension.
Alveolitis
complications after wisdom teeth removal
Alveolitis is often provoked by non-compliance with doctor’s recommendations after treatment procedures. It is a local inflammation of the gums with the following additional symptoms:
- the gums swell and turn red;
- local pain and headache are observed;
- sore throat;
- the temperature rises, muscle aches appear;
- lymph nodes become inflamed, most often the submandibular ones.
If inflammation occurs, the cause is often the loss of a blood clot from the socket and infection. Various infections that enter the wound due to poor hygiene can provoke extensive inflammation. In advanced cases, the above complication develops into osteomyelitis, which is expressed by:
- increased persistent temperature;
- poor general health;
- severe migraine-like pain;
- nausea;
- other signs of intoxication of the body.
Increased body temperature
A slight increase in body temperature to 37.5-38 °C also often occurs in the postoperative period. This complication occurs due to a reaction to inflammation. The temperature should completely return to normal within the first day, and if it continues to rise and rise, it means that more serious pathologies have arisen and you need to go to the hospital again.
Bleeding
The dentist will never dismiss a patient with severe bleeding, especially if it is complicated. After removing the figure eight, the bleeding is stopped in the hospital, and then sent home with a gauze pad on the hole. If blood clotting is normal, then the bleeding will stop within 10-15 minutes, after which the tampon must be removed. Severe prolonged bleeding is provoked by:
- rupture of large vessels;
- capillary fragility;
- hypertension.
Damage to the roots of adjacent teeth
Such a complication is observed extremely rarely and only if the patient did not undergo X-ray diagnostics before the procedure. This procedure is mandatory for all people with indications for the removal of figure eights and allows you to fully assess the condition, location, as well as other features of the tooth and its roots.
Flux
Flux in the postoperative period develops in cases where the gums become infected due to the fault of the dentist or patient, after which the infection quickly reaches the periosteum and provokes its inflammation. This complication is not considered normal and acceptable and must be treated. Main signs of flux:
- redness, suppuration and swelling of the gums;
- severe shooting pain;
- temperature increase;
- weakness.
Others
Among other common complications, the most commonly observed are:
- displacement of the seventh tooth (2 molars);
- mouth rupture; cut gums or cheeks;
- jaw injuries.
In addition, complex extraction of the 8th tooth can cause the formation of a cyst. This is a small tumor located at the root of the tooth and filled with fluid. The cyst often serves as an insulator for infected cells from healthy ones. To prevent its occurrence, the dentist prescribes antibiotics, and the treatment in this case (if the cyst is located at the roots of the tooth) will be resection.
Flux treatment methods
Treatment should be started as early as possible. If an abscess on the gum opens spontaneously, there is a risk of infection entering the bloodstream. With such an infection, blood poisoning develops, and such a complication can lead to serious consequences, including the death of the patient.
Flux treatment is always complex. The treatment program depends on the degree of tooth decay and the spread of infection.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
Types of gingivitis
Gingivitis differs in the nature of its course:
- Acute gingivitis is a disease whose symptoms appear suddenly and progress quite quickly.
- Chronic gingivitis is a sluggish process, the symptoms of which increase gradually.
- Aggravated gingivitis (recurrent stage of a chronic process) is an increase in the symptoms of a chronic disease.
- Gingivitis in remission is the moment of complete relief of all symptoms.
The form is:
- catarrhal gingivitis, which is manifested by swelling and redness;
- ulcerative (ulcerative-necrotic) gingivitis, with necrotic (dead) areas of the gums;
- hypertrophic gingivitis, in which there is a significant increase in the volume of gum tissue and its bleeding;
- atrophic gingivitis, on the contrary, is characterized by a decrease in the volume of gingival tissue;
- desquamative (geographic) gingivitis, which is manifested by intense redness and abundant desquamation of the epithelium of the mucous membrane.
According to its distribution in the oral cavity, gingivitis can also be local (affects some areas of the teeth) and generalized (the process affects the gums of the entire jaw or both jaws). And according to severity - mild, moderate and severe gingivitis.
Opening an abscess on the gum
The abscess is always opened. This reduces the risk of spontaneous opening, which can cause complications. The flux is opened under local anesthesia. If the patient has panic or other indications, the doctor may choose a different method of anesthesia.
A small incision is made on the anesthetized gum in the area of the gumboil, no more than 2 cm in length. After the dissection, the doctor completely cleans and sterilizes the purulent cavity and treats it with antiseptics. A crust should not be allowed to form in the area of the incision, as it will interfere with the outflow of ichor and purulent contents. To do this, a drainage is inserted into the incision. After the cavity is cleared of pus, you can begin general treatment, the purpose of which is to eliminate the causes that caused periostitis.
General treatment
Methods depend on the reasons that caused the flux. The only exception is periostitis, which develops against the background of periodontitis. In this case, immediately after opening the abscess, the doctor begins periodontal treatment. No medical manipulations with the tooth are required. In other cases of dental disease you need to treat:
- Pulpitis. First, the dentist drills out carious cavities and performs pulp removal. After this, endodontic canal treatment is performed.
- Periodontitis. Treatment depends on whether depulpation and canal filling have been previously performed. If periodontitis has developed for the first time, the doctor will remove the pulp, clean and fill the canals. If filling of the canals has already been performed previously, they need to be unfilled and treated again. Since it is very important that the pus comes out of the flux completely, when treating complicated pulpitis and periodontitis, a temporary filling is not placed.
- Tooth after restoration. At the first stage, the doctor is faced with the task of completely removing inflammation. After this, the damaged tissue of the root apex is removed. If the condition of the root allows, the tooth is restored again using a core tab or pin and an artificial crown. When the damage is very severe, it is more advisable to remove the tooth.
How to avoid negative consequences
- The choice of clinic and specialist should be conscious. To do this, you need to get acquainted with the opinions of other patients about the work of doctors, study certificates for equipment and other materials that will be used during implantation.
- At the preparation stage, you should not refuse additional examinations to identify all problematic issues that may become contraindications to the procedure.
- It is necessary to provide accurate information about your state of health, medication use, existing diseases (without hiding their exacerbation).
- Complete restoration of the dentition in just 4 days!
more detailsRoott Pterygoid Implants Sinus lift is no longer needed!
more details
Once and for life! Express implantation in 4 days with a permanent ReSmile prosthesis
more details
All-on-4, All-on-6, ReSmile, Zygomatic implantation We use all modern methods of dentition restoration
more details
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are used as additional ones. They allow you to quickly cope with the infection and stop the inflammatory process. The following methods can achieve good results:
- Fluctuarization. The inflamed tissues are exposed to low voltage current.
- Electrophoresis with lidase. Electrical current is applied to the tissue, allowing the drug to be effectively distributed.
- Ultrahigh frequency therapy. The method is based on the influence of an electromagnetic field.
- Ultrasound therapy. The effect of ultrasound on infected tissues accelerates their regeneration.
- Laser therapy. Damaged tooth tissue is treated with a laser beam.
Prevention
In some cases, especially when it comes to inflammation of the gums during teething in children, preventive measures will help prevent the disease: careful regular oral hygiene, timely removal of tartar and soft deposits, visits to the dentist for diagnostic examinations at least once every six months.
If pericoronitis is caused by the anatomical features of the structure of the dental system and the lack of space for the lower “eights” on the dental arch, preventive measures will only smooth out the course of the inflammatory process (due to timely cleaning of the oral cavity from bacterial plaque and food particles that create favorable conditions for inflammation) and identify the problem in time (subject to regular dental examinations).
Rinse
They are used as an additional treatment in order to completely remove pus and ichor from an opened abscess and prevent the infection from spreading to healthy areas. Soda-salt baths and rinsing with antiseptic solutions help make treatment more effective and speed up gum healing. When rinsing, you must adhere to the following rules:
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
Folk remedies
The use of effective folk methods and recipes as a supplement to basic drug treatment can significantly speed up the healing process.
- Rinse with saline solutions. Per liter of boiled water - 4 tbsp. spoons of salt, leave to brew for an hour. Afterwards, warm the solution a little and sanitize the oral cavity. Salt disinfects, relieves swelling, and soothes.
- Gargling with herbal infusions. Chamomile, eucalyptus, calendula, and yarrow are suitable for these purposes. 4 tbsp. l. herbs are brewed in 1 liter of boiling water and infused for half an hour. Herbs have a calming and antiseptic effect on the mucous membrane and promote the resorption of compactions.
- Kalanchoe juice. Nourishes and heals inflamed gum tissue, strengthens tooth enamel. Freshly squeezed juice is rubbed into the gums, or a washed leaf, freed from the outer skin, is simply chewed.
- Salt with honey. Healing tandem - salt softens inflamed tissues and helps remove purulent exudate, and honey disinfects, nourishes, and soothes. A mixture of honey and salt is prepared in a 2:1 ratio.
- Garlic tincture. It removes pus well and is a powerful antiseptic, but to avoid burns it should not be used for more than 3 days. The infusion is prepared from 4 heads of garlic, 5 lemons and 700 grams of vodka. The crushed ingredients are infused in alcohol for 3 days. Then rinse the mouth with the solution every 4 hours.
Important! Traditional methods are auxiliary methods of combating the disease, not a panacea, and will not replace drug treatment prescribed by a dentist.