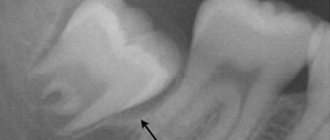
Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck indicate their inflammation - lymphadenitis. It can occur for various reasons, but often develops against the background of dental diseases and their complications. The list of these pathologies also includes caries. In the article we will tell you what lymphadenitis is and what role the carious process plays in its development.
In this article
- What is caries and why does it occur?
- Stages of caries
- Caries and other diseases
- Caries and submandibular lymph nodes - what is the connection?
- Inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes and diseases of the oral cavity
- Gingivitis and lymph nodes
- Periodontitis and lymph nodes
- Pulpitis and inflammation of the lymph nodes
- Stomatitis and inflammation of the lymph nodes
- Purulent tooth abscess and lymph nodes
- Other causes of inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes
- What are the symptoms of inflammation of the lymph nodes?
- Types and forms of submandibular lymphadenitis
- Diagnosis of submandibular lymphadenitis
- The main directions of treatment of submandibular lymphadenitis
- Treatment of submandibular lymphadenitis with caries
- What not to do if you have swollen lymph nodes
Lymph nodes serve as a filter in the body. They accumulate harmful substances and neutralize them, preventing them from passing into other parts of the body. Lymph nodes are located in various parts of the human body: on the arms, legs, neck, behind the ears, etc. An increase in the size of the lymph node indicates the presence of some kind of disease or pathological process. In the presence of inflammation, pain occurs, skin redness, swelling and other symptoms are observed. With their help, this small peripheral organ of the lymphatic system signals the need to check your health.
Often the inflammatory process that originates in the lymph nodes is a consequence of infectious diseases. It can also be provoked by other reasons, for example, caries and other dental ailments: periodontitis, periodontal disease, gingivitis, etc. To understand how this happens and why a carious lesion should not be left untreated, we will talk about its main features.
What is caries and why does it occur?
Caries is a slowly progressive disease in which tooth enamel and dentin are destroyed. It occurs due to the impact of cariogenic microbes and their metabolic products on the teeth. Bacteria feed on carbohydrates and secrete harmful acids that upset the balance of minerals in the oral fluid and enamel, gradually corroding it and leaching calcium, fluorine and other trace elements from it.
It becomes soft, loose and porous, as a result of which it cannot fully resist microorganisms.
- Cariogenic microbes live in the oral cavity of almost every person. But caries occurs only under certain conditions. These include:
- Poor hygiene. Food debris, plaque and tartar stuck between teeth are favorable factors for the spread of bacteria.
- Anatomical features of the teeth and jaw: malocclusion, deep and narrow fissures, crowded teeth, etc. Because of this, it is more difficult to carry out hygiene procedures.
- Presence of braces or other orthodontic structures. They also complicate hygiene: food debris gets stuck between the teeth and braces, which feeds bacteria.
- Disorders of saliva production. It neutralizes acids secreted by cariogenic microbes and maintains the pH of the oral fluid. If saliva is not produced in sufficient quantities, the balance of minerals is disrupted, which makes the enamel vulnerable to external factors.
- Abuse of sweets. The bacteria that cause caries live off carbohydrates, more precisely, sucrose. It is found in large quantities in confectionery products. People who eat a lot of sweet foods are more likely to suffer from tooth decay.
These are the main factors that increase the risk of caries. However, this list cannot be called exhaustive; it can also include poor ecology, genetic predisposition to dental diseases, abrasion of enamel, drinking water with a low mineral content, etc. When diagnosing caries, it is much more important to determine its stage, on which the treatment method depends.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes with carious lesions is not always observed. They often become inflamed due to advanced caries. We will tell you how this pathology occurs and why it causes other diseases that are not directly related to teeth, including lymphadenitis.
Stages of caries
There are 4 stages of carious lesions, each of which differs in the number and intensity of symptoms. The first (initial) stage is called the chalky (or white) stain stage, in which an area of demineralization forms on the tooth surface. Outwardly, it looks like a white speck, lacking shine. Under a microscope, you can see that in this area the enamel is rough, loose and porous. However, there is no carious cavity yet, so it is possible to cure the tooth without filling. The person is not bothered by any symptoms. Caries can be detected at the initial stage only during an examination.
At the second (superficial) stage, the carious process penetrates into the deep layers of the enamel, but remains within its limits, without spreading to the dentin. The white spot darkens and becomes brownish. The pathology can already be noticed independently if it develops on the outside of the tooth or fissures. Complaints appear: tooth sensitivity to sweets increases, sometimes to hot and cold, and there is discomfort when chewing food. However, it disappears as soon as the irritating factor is eliminated.
The third (middle) stage of caries is characterized by the penetration of the carious process into dentin. A brown or dark yellow cavity is formed, which is easy to see with the naked eye. Discomfort while eating is an almost constant concern, especially when a diseased tooth interacts with sour or sweet foods. The sensitivity of dental tissues to temperature changes also increases. The pulp is not yet involved in the pathological process, but this stage of caries can already be considered complex. At this stage it will not be possible to avoid preparation and filling. There is a risk of complications, possibly inflammation of the lymph nodes.
The fourth (deep) stage of caries is considered an advanced form of the disease, in which the carious cavity covers almost half of the tooth. It usually looks like a black hole with sharp edges. Pain occurs not only when eating, brushing teeth or temperature changes, but also at rest. The likelihood that caries will spread to nerve tissue and cause pulpitis is quite high. Moreover, the tooth may break into several parts, resulting in the need to remove it. This happens in cases where there is no treatment for the disease.
You can cure caries and save your tooth at any stage. But its loss is not the only complication of the carious process. There is a risk of developing other pathologies that are not dental.
Caries and other diseases
With caries, especially advanced ones, cariogenic microbes actively multiply in the oral cavity. There are several types of them, many of them are dangerous not only because they cause the development of caries. These bacteria can end up on the tonsils, get into the lymph nodes, soft tissues, pulp, etc. Caries can be complicated by pulpitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, meningitis and chronic tonsillitis.
Such a combination of circumstances is facilitated by factors such as weak immunity and high susceptibility to certain pathologies. For example, people with chronic tonsillitis who do not treat caries are more likely to suffer from tonsillitis. There are other patterns that are determined by the interconnectedness of all processes occurring in the body.
In some cases, for example, with diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and problems with the digestive system, treating caries alone is not enough. Carious lesions and other oral diseases will constantly recur. For this reason, an integrated approach to treatment is required. Of course, caries rarely causes complications, but it is better to reduce the likelihood of their occurrence as much as possible than to then deal with the treatment of several pathologies.
Let's move on to the next question and find out why inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs, what role dental diseases, including caries, play in this.
Teeth and inflamed lymph nodes: what is the relationship? Symptoms of pathology, causes, treatment methods
When inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs after tooth extraction, not everyone is ready for such a turn of events. People who have not gone through the extraction procedure (removal) are even less likely to expect an inflammatory process in this important system for the body. However, this phenomenon is not uncommon. At the same time, doctors often find a connection in it with teeth. Let's look at the nuances of this difficult topic together.
Caries and submandibular lymph nodes - what is the connection?
The main function performed by the lymph nodes is to filter and protect a person from harmful microbes that enter the body from the external environment. The virus that enters it causes a reaction from the immune system, and it begins to resist the onslaught of the pathogenic agent, producing a large amount of lymph. Because of this, the size of the lymph nodes changes. In a normal state, it is almost impossible to see or feel them; they are no larger in size than a pea. In an inflamed state, the lymph nodes can be felt by palpation. Plus they start to get sick. If we are talking about the submandibular lymph nodes, then pain occurs when swallowing, as with a sore throat.
But inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes develops not only due to viruses. There are many diseases that are also accompanied by an inflammatory process in the lymph nodes, that is, lymphadenitis. These include caries. Nodes with carious lesions, especially deep ones, become inflamed under the jaw and behind the ears. If the carious process develops on the right side, then the lymph node also begins to increase in size on the right.
Thus, lymphadenitis, which is not an independent disease, tells a person that pathology is beginning to develop and he needs to undergo examination. Many patients do the wrong thing when they begin to rub, massage, warm and lubricate the skin in the area of the inflamed lymph nodes. This can cause bacteria to spread even more and increase inflammation. To take treatment measures, you must first accurately determine the cause of lymphadenitis.
Possible reasons
The lymphatic system is the basis of immunity . It prevents the spread of pathological microorganisms and blocks the occurrence of many disease processes. In various diseases, lymphocytes begin to actively multiply to slow down inflammation. Then the lymph nodes enlarge.
If structures localized under the jaw and in the neck area “grow,” it is most likely an infection, that is, the disorder is caused by bacteria. But sometimes the condition occurs in the absence of infection.
Among the most common infectious causes:
- Colds, viruses. Their pathogens affect the ENT organs, and general intoxication is observed. In this scenario, sore throats, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, sinusitis, otitis media, etc. occur.
- Tuberculosis. With lymphadenitis, the entire neck swells. In advanced cases, lymphoid tissues located in the abdominal cavity and chest increase. The pathology is treated conservatively and surgically.
- Dental problems. Pulpitis, caries, periodontitis - all these are provoking diseases.
- Toxoplasmosis. People become infected with it from domestic animals (most often from cats). In addition to the growth of nodes, with this diagnosis the following are observed: high body temperature, headaches, an increase in the size of the spleen and liver. But very often the disease is asymptomatic.
- Venereal pathologies. Transmitted sexually. The body reacts very sharply to most of them, so already in the first days the patient notices that the lymph nodes have become enlarged and began to hurt, and severe weakness has appeared.
- Herpes. It manifests itself as an increase in the volume of lymphoid tissue in the neck, under the jaw and in the groin. Requires competent antiviral therapy.
Among the factors of a non-infectious nature that lead to the appearance of an unfavorable symptom:
- Oncology. It does not matter whether cancer of the lymphatic system or any internal organ is diagnosed. But in the first case, cancer cells quickly spread with the lymph flow, which contributes to the formation of metastases.
- Autoimmune pathologies. These are conditions in which the immune system begins to malfunction, causing serious damage to the body. This group includes systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, etc.
- Allergy. It manifests itself differently in all people. The most common symptoms are skin rashes and itching. But lymph can also be involved in the allergic process.
- Traumatic injuries to the head and face. If a strong pathological process occurs, lymphocytes begin to be actively produced.
Gingivitis and lymph nodes
Gingivitis is an inflammatory disease of the gums that occurs due to the formation of plaque on the teeth and the spread of microbes. It often develops in people who do not take good care of their oral hygiene. Typical symptoms of gingivitis are itching and bleeding of the gums, swelling, and pain, especially when soft tissue comes into contact with hard objects, such as a toothbrush.
This pathology can occur in various forms. If the lymph node is inflamed, it may be ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis. Its other signs are:
- strong pain;
- copious amounts of saliva;
- formation of ulcers;
- increased body temperature;
- loss of appetite;
- headache.
One of the complications of gingivitis if left untreated is periodontitis.
Periodontitis and lymph nodes
Periodontitis is an inflammation of the connective tissue between the tooth root and the alveolar plate. One of the main reasons for the development of this pathology is untreated caries. If periodontitis is not treated, it takes on a purulent form, which is accompanied by an increase in body temperature to 38 degrees, severe pain in the tooth and the formation of an abscess from which pus can flow directly from the jaw. Also characteristic signs of purulent periodontitis are an increase in the size of the lymph nodes and painful sensations under the jaw during palpation.
Diagnostic search
Table 1: Diagnostic measures to identify the causes of pain in the gum and lymph node:
| Purpose of diagnosis | Ways to achieve |
| Patient Interview | Collecting anamnesis of life, illness, clarification of complaints, symptoms of diseases, how long ago symptoms appeared and the characteristics of their manifestation, determining the presence of concomitant diseases |
| Oral examination | Determining the presence of diseases of the gums, mucous membranes, teeth |
| Lymph node examination | Inspection, palpation, determination of the location and mobility of the lymph node |
| General facial examination | Determining the presence of other inflammatory processes |
| Examination of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx | Determining the presence of diseases of the respiratory system |
| Definition of infectious agent | Determine what is causing an enlarged lymph node |
| Consultations with other specialists if necessary | ENT specialist, dentist, ophthalmologist, infectious disease specialist, oncologist. |
Differential diagnosis
Attention, to make a correct diagnosis and treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary. Only a doctor can conduct differential diagnosis, clinical and additional examinations, establish connections between diseases and prescribe treatment. Pain and inflammation in the lymph node is a secondary and easier to diagnose disease.
To determine gum disease, it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of possible diseases:
| Name of the disease | Definition | Accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes | Symptoms | Treatment |
| Gingivitis | Gum inflammation | In acute form, with herpetic and aphthous lesions | Pain, swelling, redness, swelling, increased gum size | Local, etiotropic, anti-inflammatory |
| Periodontitis | Inflammation of the tooth ligament | In good shape | Pain, swelling, redness, swelling, exudate from the gums | Professional oral hygiene, anti-inflammatory therapy of gum tissue |
| Periodontal disease | Dystrophic damage to the tissues around the tooth | Rarely | Pain, discomfort, itching in the gums | General and local effects on gum tissue. |
| Periodontitis | Inflammation of the tissue behind the apex of the periodontal tooth | Rarely, in acute inflammation | Pain when biting on a tooth, pain and redness of the gums | Removal of the tooth nerve and medicinal treatment of the inflammation site. |
| Periostitis | Inflammation of the periosteum and gums | Yes | Sharp pain in the alveolar process, gums, swelling, facial asymmetry, increased temperature | Removal or treatment of a tooth, incision of the gum and periosteum. Local and general drug treatment. |
| Pericoronitis | Inflammation of the gums above or near the wisdom tooth | In purulent form | Pain in the gums and jaw in the area of the last teeth, swelling and redness of the gums | Tooth extraction or excision of the gum above the tooth, drug therapy. |
| Stomatitis | Inflammation of the mucous membrane of various etiologies | In acute form, with herpetic and aphthous lesions | The presence of lesions on the mucous membrane, gums, and tongue. Painful sensations. | Professional oral hygiene, local and general treatment with medications. |
Pain in the gums and pain in the lymph node brings discomfort
Pulpitis and inflammation of the lymph nodes
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the pulp - the nerve tissue inside the tooth. It often occurs in people with advanced caries at a deep stage. The following symptoms are characteristic of pulpitis:
- Acute pain that occurs both at rest and when the tooth is exposed to various irritants: food, brushes, water, etc. After eliminating the factor that provoked the pain, the symptom persists for some time, but gradually subsides. The pain is usually sharp and intense; it cannot be eliminated with analgesics.
- Headaches, pain in the ear area from the affected tooth, general malaise and increased fatigue. The pain may radiate to the temple and eyebrow.
- Increase in local and general temperature. In adults it can rise to 38°C, and in children even higher.
- Swelling of the submandibular lymph nodes, pain when swallowing and chewing food.
With pulpitis, as a rule, it is necessary to remove the diseased nerve, after which the tooth becomes dead and noticeably darkens.
Stomatitis and inflammation of the lymph nodes
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa that occurs against the background of infectious diseases, after burns, as a result of trauma, due to an allergic reaction, etc. Traumatic stomatitis is often diagnosed, for example, when the mucous membrane is injured by crowns or braces.
After an injury, bacteria enter the wound and cause inflammation, which is accompanied by:
- painful sensations;
- the appearance of rashes and ulcers on the mucous membrane;
- release of translucent exudate;
- the formation of a white film on the surface of the wound;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- high temperature, chills and fever;
- hyperemia and swelling of the gums.
As a rule, stomatitis goes away without consequences. However, it can be complicated due to weak immunity, alcoholism or smoking. There is a risk that the disease will cause inflammation of the lymphatic system.
Main dental problems leading to pathology
- abundant accumulation of bacterial plaque on and under the gums,
- gingivitis and periodontitis,
- advanced caries, pulpitis, periodontitis,
- purulent-inflammatory processes: flux, fistula, abscess, festering cyst and granuloma, osteomyelitis, phlegmon,
- damage to the oral mucosa by stomatitis, especially in acute and recurrent [1] varieties caused by the herpes virus or Candida fungus,
- glossitis of the tongue,
- poorly installed, old fillings and crowns under which inflammation has developed,
- long-term lack of sanitation of the oral cavity: during the sanitation process, the doctor applies a set of measures aimed at eliminating all dental pathologies.
This is interesting! The submandibular lymph nodes are responsible for the condition of the nose, throat, teeth and ears. If they are the ones that become inflamed, then you need to look for pathology in the listed organs, and to eliminate the problem, contact a dentist (in 60% of cases, dental pathologies are detected) or an ENT doctor.
Purulent tooth abscess and lymph nodes
A tooth abscess is a purulent inflammation that is localized inside the tooth after pulp removal, in the periodontal area or under the gum. This pathology is characterized by shooting, throbbing pains that intensify with pressure and heat on the tooth. Inflammation of the lymph nodes under the jaw is possible, which is sometimes even noticeable from the outside: the patient develops a slight swelling in the neck. In rare cases, the abscess spreads to the bone tissue and causes swelling on the face. Some complain of migraines. The disease is complicated by the presence of other dental diseases, such as caries.
Other causes of inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes
The lymph node is an important component of the entire lymphatic system, which performs many different functions. It is involved in maintaining immunity, protects against pathogenic microorganisms, transports nutrients, and removes harmful components from the body, for example, dead red blood cells and bacteria. Lymph nodes respond to many changes that occur in the human body. Almost any pathology or its complications can provoke lymphadenitis. We list the common causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes:
- Infectious diseases: chronic tonsillitis and tonsillitis, otitis, sinusitis, mumps, alveolitis, streptococcal infections.
- Pathologies that strongly affect the state of the immune system: lupus, HIV and AIDS, leukemia, arthritis, tuberculosis.
- Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease that often occurs in a chronic form and is accompanied by symptoms such as low-grade fever, swollen lymph nodes, decreased performance due to fatigue, headache, etc.
- Diseases that usually occur in childhood: chickenpox, measles, mumps. They affect the state of the entire lymphatic system.
- Tumors. If the lymph node is inflamed, but the person does not notice any other symptoms, has not been injured and does not suffer from chronic diseases, then it is necessary to undergo a systemic examination. Lymphadenitis can be the initial symptom of oncology.
If your lymph node is inflamed, do not try to eliminate the inflammation using folk remedies. Thus, the inflammatory process may be a consequence of the development of a bacterial infection, which must be treated with antibiotics. Many people apply cold or, on the contrary, hot lotions to the swollen area, and this causes even more active growth of bacteria. As a result, complications may develop. There are many causes of lymphadenitis, so deciding on self-treatment is dangerous.
What are the symptoms of inflammation of the lymph nodes?
The submandibular lymph nodes become inflamed against the background of other pathologies, each of which has its own specific symptoms. We list the most common signs of lymphadenitis:
- sudden enlargement of the lymph nodes under the lower jaw, their pain when pressed and hardening;
- first slight and then severe redness of the inflamed areas, they become burgundy and sometimes bluish;
- swelling at the site of inflammation on one or both sides, depending on the etiology of lymphadenitis;
- sharp and short-term attacks of pain that radiate to the ear, temple or eyebrow;
- discomfort when chewing food, increased pain during swallowing;
- inflammation of the oral mucosa, which is accompanied by redness and increased sensitivity;
- increased body temperature, general weakness, sleep disturbance, fatigue.
To make a diagnosis, it is important to determine not only the cause, but also the type of lymphadenitis, since the clinical picture of each of them may be different.
Measures to eliminate the problem
Dental treatment
In order for the lymph nodes to return to normal, it is first necessary to get rid of the main problem that caused their enlargement and inflammation. Depending on the pathology, the dentist can perform the following manipulations:
- cleaning teeth from plaque and tartar,
- treatment and filling of root canals,
- surgical opening and drainage of ulcers (with flux, abscess),
- cleaning the socket (for alveolitis),
- tooth-preserving operations: cystectomy and cystotomy, resection of the root apex for cysts and granulomas,
- replacement of unsuitable fillings and crowns.
After treatment of dental pathologies, the lymph nodes do not disappear immediately. Swelling may persist for the next 7-10 days. In order for the patient’s condition to normalize faster, he is additionally prescribed physiotherapy (for example, UHF therapy) and prescribed medicinal support.
“I once had a tooth removed with periodontitis on the lower jaw. A few days after this, I noticed that the lymph node was a little swollen and painful. I didn’t want to go to the dentist again, I hoped that it would go away on its own. Then the hole healed safely, but the swelling under the jaw sometimes appeared again. In general, I started this case, and when more frightening symptoms appeared, I ran to the doctors. I was told that there was pus inside the lymph nodes and it needed to be cut out. There was no choice, I had surgery, then took antibiotics. Now I regret that I didn’t go to the clinic right away...”
S. Tsareva, review from gidpozubam.ru
Drug therapy
The doctor will prescribe medications to take at home. In case of inflammation of the lymph nodes, as well as in advanced dental diseases, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed for 7-10 days. The patient is also recommended ointments for applying external lotions and applications to the affected areas. Additionally, immunostimulants and multivitamin preparations are prescribed, which must include vitamin C to boost immunity.
Symptomatic treatment is also prescribed. For fever, antipyretics are taken, and for pain, painkillers are taken.
Types and forms of submandibular lymphadenitis
Inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs in acute or chronic form. The first is characterized by high intensity of symptoms, the disease develops quickly, and it is almost impossible to ignore it. The patient suffers from pain, fever and other symptoms. Immediate medical intervention is required, especially if the pain increases and cannot be relieved with painkillers.
Chronic submandibular lymphadenitis is characterized by a long incubation period, during which a person may not be bothered by any symptoms. In such cases, he usually does not see a doctor, which allows the pathology to progress. An exacerbation may occur at any time, which will require urgent diagnosis and treatment.
Depending on the nature of the contents of the lymph nodes, inflammation can be purulent or non-purulent. The first occurs with great complications and is accompanied by an increase in temperature, the second - in a milder form. Based on the causes of inflammation, it is divided into simple, hyperplastic and destructive. Downtime is accompanied by classic symptoms and tends to become chronic.
Hyperplastic submandibular lymphadenitis is a more complex type of inflammatory process, which is accompanied by redness of the skin and significant enlargement of the lymph nodes. Pathology covers not only the node, but also the tissues surrounding it.
Destructive lymphadenitis is characterized by the destruction of lymph nodes, as well as adjacent tissues, which occurs against the background of a purulent process. This is the most dangerous type of disease that requires urgent treatment.
In most cases, the type and form of inflammation of the lymph nodes is determined by etiological factors and the patient’s state of health, his immunity. Let's consider how it is possible to identify the cause of the inflammatory process in the lymph nodes.
Why does the problem occur after tooth extraction?
Let us list the main reasons why nodes become swollen after tooth extraction.
1. The body's reaction to surgery
It is not uncommon for a lymph node in the neck or under the jaw to slightly increase in size immediately after tooth extraction. Some experts believe that after surgery such a reaction is quite natural, because the body has activated all its forces in order to quickly cope with the physiological trauma inflicted on it.
If you have removed a wisdom tooth and then felt an enlarged lymph node in your neck, then you should not panic ahead of time. Procedures for extracting “eights” are always complex, large-scale and quite traumatic. Therefore, after them, a non-infectious inflammatory process almost always occurs, accompanied by a number of characteristic symptoms: increased body temperature, pain, limited jaw mobility and the inability to open the mouth wide, general weakness.
The procedure was carried out against the background of a purulent-inflammatory process
Typically, patients come for extraction (removal) if there are advanced dental diseases in the mouth that cannot be restored. Often the operation is performed urgently, against the background of an acute inflammatory process. Therefore, enlarged lymph nodes after tooth extraction with periodontitis, gumboil, fistula, cyst, granuloma are a common story. After all, the inflammatory process in this case had already been going on for some time. And it does not go away immediately after eliminating the problematic element; you still have to fight it by taking antibiotics and other medications, lotions, antiseptic rinses, and physiotherapy.
Extraction complications occurred
If several days have passed after tooth extraction, and you notice that the lymph node under the jaw hurts and is inflamed, this may indicate the development of the following complications of extraction:
- alveolitis: this is where it all begins. This is an inflammation of the socket that occurs due to a medical error or due to a violation of the postoperative regimen on the part of the patient. Actually, the complications that we will list below appear because the patient develops alveolitis, or tries to cure the disease on his own and does not seek medical help,
- flux, abscess, phlegmon, osteomyelitis.
Diagnosis of submandibular lymphadenitis
You can determine that inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes has begun on your own. It is enough to simply feel the areas of the neck directly under the lower jaw, closer to the ears. Normally, the nodes are almost impossible to palpate; they are small, have a dense structure, do not hurt and move easily under the fingers. If you notice a change in the structure of the lymph nodes, or feel discomfort or pain during palpation, you should consult a doctor. It is impossible to independently identify the cause of inflammation. First, you can go to a therapist. After the initial examination, which includes examination and collection of tests, he will refer you to another specialist: otolaryngologist, phthisiatrician, surgeon, infectious disease specialist, immunologist or dentist. If caries is suspected, the doctor will diagnose using the following methods:
- Coloring. A solution is applied to the tooth enamel, which turns the areas of demineralization purple.
- X-ray. Photographs of the teeth or the entire jaw are taken, from which the location and extent of the caries process can be determined.
- Laser diagnostics. This method is the most modern. It allows you to accurately identify the extent of the spread of pathology.
Based on the results of the examination, treatment is prescribed. First, we will describe the general features of the treatment of submandibular lymphadenitis, after which we will tell you what to do if the lymph nodes become inflamed due to caries.
Diagnostic measures
Detecting the problem is very simple - the doctor just needs to feel the area under the chin and carefully examine it. To establish the exact cause of the disease, you need:
- Take blood and urine tests. From them you can understand the nature of the “provocateur” (viral or bacterial).
- Donate blood biochemistry.
- Get an ultrasound of the lymph nodes.
If the doctor suspects oncology, the patient is referred for a computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging scan or a puncture biopsy. These diagnostic measures allow you to make a correct diagnosis and select adequate treatment.
The main directions of treatment of submandibular lymphadenitis
The direction of treatment is determined by the etiology of the inflammatory process. If the disease is infectious, antibiotics, antifungal and anti-inflammatory drugs, sprays and ointments are prescribed. Purulent inflammations are treated promptly under local anesthesia. The doctor cleans the lymph node of purulent masses and installs drainage. After this, the patient is prescribed appropriate medications.
Often, after eliminating the underlying pathology that led to inflammation of the lymph nodes, all its symptoms, including lymphadenitis, disappear. If this does not happen, the patient undergoes a course of physical therapy. Immune-boosting therapy may be needed. The patient needs to stop smoking, start eating right and taking vitamins.
Treatment of submandibular lymphadenitis with caries
Caries is treated with various methods depending on the stage. At the first stage, in which you only need to eliminate the white spot, remineralization of the tooth surface is carried out. With the help of special preparations, the enamel is saturated with minerals - calcium and fluorine. Therapy is prescribed in a course lasting 5-15 procedures. For home use, the patient is prescribed hygiene products that help restore enamel and the balance of microelements in the oral fluid. Such means include:
- toothpastes: Marvis Orange Blossom Bloom, Dentissimo Complete care, Apadent Perio;
- gels: Stomysens® Desensitizing Repairing Treatment 4, DRC ROCS (ROCS) Medical Minerals, Dental Resources Inc Sorbet Revive;
- rinses: Vivax “Remineralization”, CURAPROX Perio Plus Forte chx 0.20%, Biorepair Delicate Gums Mouthwash.
If a carious cavity has formed on a tooth, then remineralization will not help; filling is necessary. First, the dentist cleans the hole from necrotic tissue and food debris, after which he places a protective gasket and fills the cavity with filling material. If caries is complicated by pulpitis, the nerve has to be removed.
After treatment of the carious process, the inflamed lymph node should return to normal. If this does not happen, it is necessary to re-diagnose. Perhaps the inflammation is not a consequence of caries, but of another disease.
More often, the submandibular lymph nodes become inflamed during the chronic course of the carious process, in which slow tooth destruction is observed. It is not accompanied by severe symptoms, but with exacerbations or the presence of certain factors, inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs.
What not to do if you have swollen lymph nodes
On the one hand, lymph nodes become inflamed quite often, and often the inflammation goes away on its own without any treatment, so many people do not take this problem seriously. In most cases, it really does not cause any consequences.
On the other hand, submandibular lymph nodes can make themselves felt in severe pathologies that cannot be left without treatment. Doctors recommend not delaying a visit to the hospital if inflammation and pain do not go away within 2 days or occur systematically. Experts also advise:
- Do not try to cure inflammation on your own. It is not possible to find out what caused it at home. In some cases, this cannot always be done quickly and in a medical institution, as a result of which the patient undergoes many examinations. Attempts to cure inflammation with folk remedies can lead to the development of complications.
- Do not heat inflamed lymph nodes. They cannot be heated even in the absence of elevated temperature. Warming up can increase swelling and pain. With the bacterial nature of lymphadenitis, heat stimulates the proliferation of bacteria and causes the infection to spread through the lymphatic system.
- Do not apply ice to the sore area. Cold is contraindicated in inflammatory and infectious processes, since hypothermia can greatly aggravate the situation and lead to even more severe inflammation.
However, a person can take certain measures on his own. You need to switch to proper nutrition, quit smoking and alcohol and make an appointment with a doctor. To reduce the risk of developing inflammation of the lymph nodes, treat all diseases in a timely manner, visit the dentist every six months, exercise and carefully observe hygiene rules.
Treatment
If a person has a toothache or is starting to erupt, he will be disturbed by an enlargement of the nearby lymph node. When teething, the development of cervical lymphadenitis is not excluded, which should not be left to chance.
Therapy for an inflamed tooth, gum and lymph node includes taking medications. Only the doctor decides what means to treat the disease. He will also tell you what procedures to carry out after treatment in order to consolidate the result achieved with its help.
The following therapeutic measures can contribute to recovery:
- Sanitation of the oral cavity.
- Rinse with Burov's solution.
- Opening abscesses if present.
- Antibacterial therapy.
- Vitamin therapy.
- UHF.
A surgeon may be needed if the patient needs to have swollen lymph nodes cleaned.