Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
The taste of blood in the mouth is quite common. However, this symptom should never be ignored. Of course, the reasons for its appearance can be quite harmless, for example, a slight injury to the gums or eating food from clay dishes. However, an unpleasant taste can also indicate very dangerous pathologies. Let's figure out why a metallic taste may appear in the mouth and what to do to eliminate it as soon as possible, and most importantly, remove the reasons for its appearance.
Conventionally, all the causes of a pronounced metallic taste can be divided into three groups:
- Dental problems are usually associated with increased bleeding of the gums.
- Oral injuries.
- Internal pathologies.
Taking various medications often leads to a taste of blood in the mouth.
Oral injuries
If the mucous membrane is damaged, a little blood may enter the taste buds and, accordingly, a metallic taste appears in the mouth.
The causes of mucosal injury may be:
- tartar in the mouth;
- improper dental care, for example, using a brush that is too hard;
- incorrectly installed dentures;
- incorrectly installed braces.
Often the cause of the taste of blood in the mouth is a more significant injury, such as to the esophagus or throat. For example, a strong cough often leads to mucosal injuries. After an injury, a small amount of blood enters the mouth and causes an unpleasant taste.
When to see a doctor
An emergency medical team must be called in the following cases:
- the bleeding is massive and continues for too long;
- there is a suspicion of traumatic injury or entry of a foreign body;
- any diseases associated with impaired hemostasis have been diagnosed.
Age may also influence the difficulty of treatment. The older the patient, the more difficult it is to stop the bleeding and the more severe the consequences of blood loss.
Those who constantly have nosebleeds, when blood pressure rises or against the background of exacerbation of other systemic diseases also need medical advice. First of all, nasal bleeding is the profile of an otolaryngologist (ENT), but endocrinologists, hematologists and other specialists may also be interested in such a patient.
Diagnosis and treatment
The evaluation of epistaxis begins with a history and general physical examination using a nasal dilator and nasopharyngeal speculum.
To accurately identify the cause of the pathology, additional diagnostic methods are used:
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- coagulogram;
- Ultrasound;
- ECG;
- X-ray, CT, MRI.
When bleeding from the nose, treatment begins with rapid relief of the pathological condition in order to prevent large blood loss. Then the cause that caused the epistaxis is eliminated and the possible consequences of acute blood loss are prevented.
If the bleeding cannot be stopped through the use of anterior or posterior tamponade and the use of hemostatic drugs, then resort to the following manipulations:
- radio wave method - the vessels are cauterized using the Surgitron apparatus, which emits high-frequency radio waves through electrodes, instantly evaporating moisture in the cells and promoting coagulation.
- electrocoagulation - vessels are cauterized under the influence of electric current;
- cryocoagulation - cauterization of the mucous membrane using liquid nitrogen;
- laser coagulation - the vessel is evaporated under the influence of high temperature of a narrowly directed laser beam;
If epistaxis is associated with a blood clotting disorder, the patient is prescribed hemostatic agents. If the reason lies in hypovitaminosis, then the patient is given a multivitamin complex.
Internal pathologies
The most common diseases of internal organs that lead to the taste of blood in the mouth include:
- bronchitis;
- pneumonia (pneumonia);
- lung abscess;
- lungs' cancer;
- cystic fibrosis;
- tuberculosis;
- dysfunction of the heart;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT);
- diseases of the ENT organs.
Neurological diseases can also cause the taste of blood in the mouth. A signal travels through the nerve fibers of the brain to the taste buds; if its transmission is disrupted, an unusual taste may appear in the mouth.
However, neurological problems accompanied by a blood taste usually have other unpleasant manifestations. For example, they may be accompanied by headaches, hearing problems, hand tremors, trembling eyelids, and lumbago in certain areas of the face.
In very rare cases, the taste of blood in the mouth is caused by heavy metal poisoning. A similar problem often awaits workers in chemical laboratories and metal processing plants. Intoxication of the body is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms - attacks of dry cough, nausea, aching limbs, swelling of the gums, and lack of appetite. Dysbacteriosis is also rarely the cause.
Prevention
To avoid bleeding in adults or children, it is useful to adhere to the following rules:
- get rid of the habit of picking your nose;
- against the background of allergic or cold nasal congestion, do not blow your nose too often;
- when practicing dangerous sports (boxing, rugby), wear a protective helmet;
- use vasoconstrictors strictly according to instructions (no longer than 7 days);
- to reduce pressure in the nasal cavity, you should sneeze with your mouth open;
- If coagulants previously caused nasal bleeding, then the next time they are prescribed, be sure to inform your doctor about this.
It is also important not to rip off the crusts in the nose formed after bleeding until the mucous membrane recovers on its own. Otherwise, bleeding in this case may recur every day.
When working in production with polluted air, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment. To prevent bleeding, it is useful to undergo regular preventive examinations. With the next episode of epistaxis, it is important to see an otolaryngologist to find out the cause of the bleeding and receive recommendations for the future.
Dental diseases
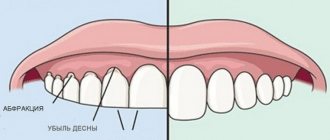
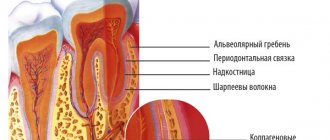
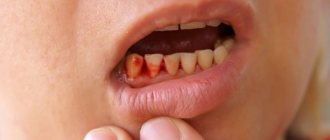
The most common cause of the taste of blood in the mouth remains dental diseases and lip lesions. Diseases are easily recognized by reddish-colored saliva, inflamed oral mucosa, and the presence of ulcers and erosions.
The main dental problems that cause the taste of blood in the mouth are:
- gingivitis - inflammation of the gums;
- stomatitis - damage to the mucous membranes;
- cheilitis - lip injuries;
- periodontitis is inflammation of the periodontal tissues.
Main causes of bleeding from the mouth
Blood from the mouth: for gum disease
For bleeding from the mouth to occur, you need really serious reasons. Of course, it does not always mean that something terrible has happened to the body, but only a doctor can determine the real cause, therefore, if a problem such as blood from the mouth occurs, you must immediately seek help. Blood from the mouth indicates the possible occurrence of diseases such as:
- Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that is quite common in the world and is caused by a certain group of mycobacteria. The disease mainly affects the lungs, but sometimes it can affect other organs as well. Tuberculosis poses a great danger in terms of infecting others, as it is transmitted by airborne droplets.
- cancer of various internal organs and tissues. Bleeding can occur in case of disease of the tongue, oral mucosa, pharynx, lungs, and stomach.
- stomach ulcer
- gum disease
You should pay attention to the color of the blood coming from the mouth. If it has a dark color, as if it was mixed with coffee, then this may indicate that it is coming from the stomach and, quite possibly, the cause is cancer. If the blood is bright red and there are food particles mixed in with it, then this indicates a high probability of a stomach ulcer in a person. Other reasons are less dangerous, but in any case you should not refuse the help of a specialist.
Bleeding from the mouth can occur for various reasons. In some cases, its appearance indicates serious diseases of some internal organs and systems of a person. If bleeding from the mouth occurs, you should not put off seeking qualified help.
What to do if you taste blood in your mouth?
First, you should contact your dentist. The doctor will confirm or deny dental diseases, prescribe effective gum treatment or refer you to another specialist.
If the taste of blood in the mouth appears for a short time, you can eliminate it using traditional methods of treatment. For example, rinse your mouth with water and lemon juice or a water-salt solution. You can also get rid of the unpleasant taste using a chamomile solution. To prepare it, you need to pour 5 g of dried flowers into 500 ml of water and cook for 7-10 minutes in an enamel bowl. The product must be infused for an hour.
A decoction of oak bark will also help get rid of the taste of blood in your mouth. To prepare it, 10 grams of raw material should be steamed with boiling water and left for about an hour.
An effective means of treating gum inflammation and eliminating such unpleasant symptoms as the taste of blood in the mouth is ASEPTA Active mouth rinse. This combined action remedy is used for infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, and also quickly relieves bleeding and inflammation of the gums. The rinse has an antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, does not contain alcohol, fluorine and dyes, so it is perfect for treating even those with the most sensitive tissues.
Types of nosebleeds
There are 2 types of nosebleeds and are classified by location:
- Anterior - blood flows from one or both nostrils in the form of drops or streams. Most often, this deviation from the norm affects the capillaries. This epistaxis is not dangerous and usually stops without outside help.
- Posterior section - blood does not appear from the nasal canals, but flows into the pharynx and enters the digestive tract. It is provoked by damage to large blood vessels localized in the lower parts of the nose. They usually require medical attention to resolve.
Posterior bleeding is a rarer occurrence than anterior bleeding, but is more life-threatening. Bleeding from the nasal cavity is also divided according to frequency into: one-time, recurrent or habitual.
Clinical researches
The effectiveness of various ASEPTA mouth rinses has been repeatedly proven clinically.
For example, it has been clinically proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- The effectiveness of complex therapy in the treatment of periodontal diseases. (Department of Periodontology of the SF State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education MGMSUIM.A.I. Evdokimova. Moscow.) Nemeryuk D.A. - Associate Professor, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Dikinova B.S. - Postgraduate Student of the Department of Periodontology of the SF Tsargasova M.O. - Postgraduate Student of the Department periodontology SF Yashkova V.V. - postgraduate student of the Department of Periodontology of the SF Department of Periodontology of the SF State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education MGMSUIM.A.I.Evdokimova. Moscow
Symptoms
The main symptom of nosebleeds is the discharge of blood from the nostrils or its flow into the mouth from the nasopharynx. However, depending on the blood loss, there are also accompanying signs:
- Nausea.
- Spitting blood.
- Pallor of the skin.
- Weakness.
- Noise in ears.
- Thirst.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Flashing of flies before the eyes.
- Dizziness.
Reference! With posterior bleeding, the patient may experience tarry stools, and if blood enters the stomach, vomiting interspersed with blood clots.