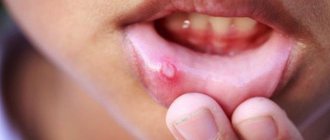
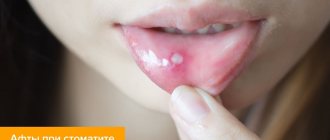
Signs of stomatitis in children
To identify the cause of the child’s nervousness and capricious state, he must be carefully examined. The disease may not appear externally, so you need to examine the oral cavity, feel the tummy, and put your hand to the head. The first reason for refusing to eat may be the presence of small wounds in the oral cavity. A disease such as stomatitis exhibits similar symptoms.
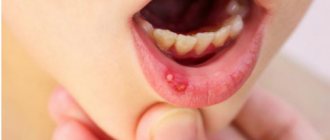
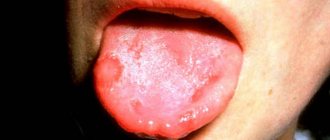
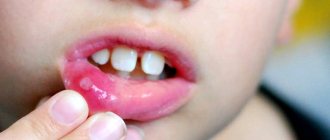
The first signs of the disease can be recognized even without medical education: the tongue becomes covered with a white coating, as does the entire oral cavity. The presence of sores on the inside of the cheeks, lips and palate can cause a rise in temperature. If you notice such symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor for help. A dentist can diagnose the disease and prescribe treatment. It is recommended to first consult with a pediatrician, who can indicate effective methods and methods of treatment.
In children, stomatitis can occur suddenly due to several reasons that contribute to the development of infection. When an inflammatory process appears in the oral cavity, the child will experience severe pain when trying to eat. The causative agents of this disease are different types of bacteria:
- Candida mushrooms;
- Allergic stomatitis;
- Herpes virus.
Diagnostics
If there is a suspicion of damage to the mucous membrane in the mouth, only a doctor, pediatrician or pediatric dentist should make a diagnosis and examine a child. It is important to identify the cause of the disease in order to prescribe effective treatment. Identifying the cause of the disease does not present any difficulties. This pathology is detected during examination due to the characteristic clinical picture, the presence of rashes, and signs of inflammation in the mouth. In addition to an examination to clarify the nature of the disease, the doctor prescribes a general blood and urine test. In severe cases, tissues of the affected mucous membrane are examined to identify the type of pathogen. For this purpose, washouts and scrapings from erosions and ulcers are taken.
The following methods are used to identify the type of virus:
- immunofluorescence method;
- PCR;
- RSK;
- ELISA.
In order to prescribe effective therapy, especially in severe cases, identification of the type of pathogen is required.
Inflammation of the oral cavity in a child: causes, treatment
Pathogenic bacteria do not select their hosts based on age; for them, the main factor is a beneficial environment. Children, as a rule, are more susceptible to this type of infection than adults, because... the body is weaker and does not have a strong enough immune system.
If a child has been infected with pathogenic bacteria, this does not mean that the parents are providing poor care; today, the risk zone for children is modern sweets, many of them may already contain strains of viruses, depending on where and by whom they are produced, and as a result, they can cause caries and other dangerous diseases. For example, as a result of an examination, a doctor can diagnose stomatitis.
We are talking not only about school-age children, but also about infants who feed on their mother’s breasts, since bacteria can also be transmitted through milk. Children aged from birth to three years old can suffer from candidal stomatitis. After three years, they may develop herpetic stomatitis. This occurs when a child is denied a pacifier and begins to suck dirty fingers, which leads to the spread of bacteria in the oral cavity and the formation of small ulcers in size and shape. In this case, stomatitis in children in the mouth can be dangerous and treatment must be carried out very quickly, since the child will not be able to eat food at all, which will negatively affect his general condition and activity, not to mention the terrible pain that the child will experience.
School-aged children may also be susceptible to oral inflammation. In them, the disease takes the form of allergenic or aphthozonal stomatitis. It should be noted that an unhealthy lifestyle, unsanitary conditions, dirty cutlery or lack thereof can lead to adults also getting stomatitis. When it comes to children, it is necessary to conduct preventive and educational conversations about the need to always take care of hygiene, because clean hands are a guarantee of protection against the occurrence of stomatitis and intestinal diseases.
Stomatitis is more common in children. This is explained by the fact that in babies the mucous membrane in the oral cavity is much more tender and thinner. This leads to its rapid injury and defeat. The child’s immune system cannot cope with a large number of bacteria, so wounds appear in the mouth, which are quite difficult to cure. At the initial stage, stomatitis in her child can be detected by the mother, who is always next to him. However, you should not experiment with treatment; it is important to identify the cause of the disease and undergo treatment. You can only take precautions by isolating the child in a separate room if there are other children in the family. The reason for isolation is simple: the disease is transmitted through airborne droplets.
Prevention
It is not possible to completely prevent the development of this infection in a child. Most people are already infected with viruses at birth, but it is quite possible to reduce the incidence of the disease.
To do this, the following measures are used:
- if one of the adults is infected, they should not be allowed to contact the child;
- choose a group in kindergarten with a small number of children;
- If possible, do not attend mass events during epidemics;
- it is necessary to harden the child (walk barefoot at home, go to the pool);
- stop bad habits (sucking fingers, toys, other objects);
- thoroughly wash and treat the child’s toys and dishes;
- treatment of all surfaces in the apartment using antiseptics.
Infectious stomatitis in children is a rather unpleasant disease. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations and preventive measures, you can minimize the occurrence of this disease in your baby.
Treatment of stomatitis in children of different ages
Stomatitis in children is a kind of profuse inflammation of the oral mucosa. It is necessary to treat the baby immediately and avoid extensive lesions. The child needs to be provided with special hygiene products with which he can regularly rinse his mouth.
If the baby is still very small, then he should treat his mouth with special napkins, on which a special solution - an antiseptic - is applied. Children over one year old can easily learn to rinse their mouth after eating, clearing it of dirt. This rinse will allow the sores to gradually heal as all bacteria and infections are destroyed. If stomatitis is not treated promptly, ulcers can spread throughout the entire oral cavity. In the future, this will lead to diphtheria, which is much more serious than stomatitis.
If an infant gets stomatitis, it means that nipples and bottles need to be carefully treated. Also, before each feeding, the mother’s nipples need to be treated, since various infections can be transmitted through them. Everything must be clean and sterile. If the child eats independently, then you need to ensure that the temperature of the food is equal to body temperature. In this case, he will use it without whims and stubbornness. Sour foods or particularly spicy foods should be excluded from the diet. If it is too painful for your child to eat, you can offer him food through a straw. This can be broth or liquid puree.
If a child with stomatitis refuses to eat, it is possible that he experiences severe pain while eating. In this case, you can use special gels that reduce the sensitivity threshold, and the child can eat little by little. If stomatitis is detected in a child, treatment must be started immediately. Nowadays, childhood stomatitis can be successfully treated, and the treatment itself can be completed in just a few days if you regularly rinse the mouth and monitor hygiene.
Sometimes there are situations when stomatitis is accompanied by the appearance of another disease - periodontitis. Here, home treatment is not enough, since periodontitis in children is treated in a specialized dental clinic or hospital. These diseases can be treated by the staff of the Dent Prestige dental clinic. Experienced specialists will always come to the aid of children and their parents.
Treatment
Treatment of viral stomatitis in children is carried out under the mandatory supervision of a doctor. Mild forms can be treated at home; in severe cases, the baby is admitted to a hospital. Children are prescribed bed rest and a diet. Food should be pureed, warm, and not irritate the affected mucous membrane. The patient is advised to drink more fluids.
The disease requires complex therapy. For this disease, local and general treatment methods are used.
The following medications are indicated for the child:
- antiviral drugs (Panavir, Acyclovir) - taken strictly according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor; if you do not follow his instructions, a relapse of the disease is possible;
- antihistamines (Suprastin, Citrine, Loratadine) - reduce swelling and reduce pain;
- immunomodulators (Imunofan, Timalin) – strengthen the baby’s immune system;
- antipyretics (Panadol, Nurofen) are used at high temperatures.
Local remedies are used to treat infectious stomatitis. They relieve inflammation and swelling.
For this purpose the following are used:
- antiseptic solutions (Panavir, Miramistin) - the oral cavity is rinsed every hour with a soda solution or Furacilin, and then treated with antiseptics;
- dental gels (Kamistad, Dentinox), which have an anti-inflammatory, analgesic, disinfecting effect, are used thirty minutes before meals;
- antiviral ointments (Acyclovir, Oxolinic) - penetrate the virus and destroy it, the oral cavity is lubricated up to five times a day for two weeks.
Mouth rinses with herbal infusions are used. Herbs are used to relieve irritation and pain (chamomile, calendula, sage).
Physiotherapeutic methods are used: tube quartz, devices with infrared irradiation.
Symptoms of stomatitis in children
The first symptom of stomatitis in a child that can be seen by relatives is dry, flaky lips. A small white coating may form on the tongue, which over time can spread throughout the mouth. Infants may well become infected with fungal stomatitis, which manifests itself in the form of small white spots. By their nature, the spots resemble milk that has curdled on the tongue. Sometimes such stomatitis can occur as a result of long-term treatment with antibiotics. That is why doctors do not recommend long-term use of such drugs.
An increase in temperature is one of the primary symptoms, which may also indicate that the child is sick. Lack of appetite, lethargy, whims - these are the first symptoms that need to be responded to in terms of diagnosing the oral cavity in a child.
Causes of aphthous stomatitis
Not all causes of aphthous stomatitis are fully understood. The mechanism of aft formation is often associated with activation of the local immune system - immune cells begin to destroy the epithelium of the mucous membranes, which leads to ulcers.
Local reasons include the following:
- allergic reactions;
- pathogenic microorganisms;
- mechanical damage (biting mucous membranes, injury from sharp edges of fillings or orthopedic, orthodontic structures);
- temperature or chemical influences.
Systemic causes of aphthous stomatitis:
- menstruation, pregnancy in women;
- sudden cessation of smoking;
- enteropathy, celiac disease, malabsorption;
- blood diseases;
- diseases of the immune system;
- lack of vitamins;
- other systemic diseases (lupus erythematosus, Crohn's disease, HIV infection, etc.).
Treatment of stomatitis using traditional medicine
Medical staff at children's clinics say that when stomatitis is detected, it is best to consult with your doctor. Only a specialist can identify what stage the disease is at and prescribe treatment. However, there are situations when the clinic is not open (for example, evening hours and night time), and the child is very sick and does not feel well. If stomatitis is detected at first, you can resort to traditional medicine. There is no need to think that the disease will go away on its own. If the infection is not eradicated, the child will get even more sick.
In case of stomatitis, the oral cavity should be wiped with a bandage containing a soda solution. Plaque in the mouth is removed with a bandage or a piece of gauze, thereby eliminating the infection. Making a soda solution is very easy: add one teaspoon of soda to one glass of water and mix thoroughly. Before use, the liquid should be stirred so that the soda does not remain at the bottom of the glass. Using soda, you can thoroughly disinfect the oral cavity and mucous membrane, while removing plaque.
You can also try wiping the inside with slimy brilliant green. Procedurally, you need to do the same as with a soda solution. Then soak in brilliant green and thoroughly wipe the child’s mouth.
For older children, you can prepare herbal infusions and give them a mouth rinse after eating. In this case, food particles will be removed, and the mucous membrane will not burst. You can rinse with a chamomile solution, which quickly removes the inflammatory process. It is not uncommon for people to use strong green tea, which is also used as a mouth rinse. This procedure should be carried out several times, and it is not at all necessary to do it after meals.
It is sometimes quite difficult to persuade young children to rinse their mouths, especially if they experience pain there. In this case, they may like rose syrup, which also has a positive effect on eliminating infections in the mouth. You can make this syrup yourself using rose petals, sugar and water. You can easily prepare a decoction of oak bark at home. Herbs you can choose from are burdock, sage, and yarrow. You can prepare a mixture of these herbs and rinse your mouth with the tincture several times a day.
You can also use aloe, which you can simply chew. If a child cannot swallow such a plant, then holding it in his mouth will be enough. Aloe will taste good together with a little honey. However, we must remember that using large amounts of honey for stomatitis can only worsen the disease. When a child is ill, you should use only high-quality products without acid and harsh sensations, which will not cause allergies and irritation of the mucous membrane. It is advisable to limit yourself to a set of dishes that were pleasant to the child and did not cause him discomfort.
Aphthous stomatitis and how to deal with it
Well, the horror of the past five days is coming to an end. I want to share the nightmare that my sweet child had to endure, and my husband and I, of course.
On Monday evening, our temperature rose to 38, and there was no runny nose or cough, but Egor refused to eat and was whining all evening. I carefully drove away the thought that it could only be the flu. The temperature was brought down, the child slept all night quite calmly. On Tuesday morning, again 38.5 and a strong seizure on the left side of the mouth. They called a doctor - the diagnosis was aphthous stomatitis, it turns out there was something terrible going on in Yegor’s mouth - his entire tongue, gums and cheeks on the left side were burgundy in color and covered with whitish stomatitis ulcers :(((The first three days - continuous whining, dropping temperature, constant salivation , a wild squeal when trying to treat him and a complete refusal to eat. They had difficulty forcing him to drink, it was clear that he was in a lot of pain. His heart was breaking, they didn’t know how to help him... We took tests, everything was ok, there was no inflammation, and we were prescribed antibiotics did not. On the 4th day the temperature became lower, and for the next 2 days it stayed around 37.0-37.5. But this was already progress, my son at least became interested in toys-books, drawing and modeling. And he began to talk again, apparently it became a little easier in my mouth. Slowly I began to eat pureed soup, porridge and cottage cheese. God, what happiness it was. Today we already have a normal appetite, although the very process of eating still stresses him out, he eats with difficulty, but EATS! There is no temperature ! Started to get mischievous! YAAAAAAAAA! We overcame this nightmare!
This is what we treated ourselves with (for myself, so as not to forget, and I hope it will help someone else, although to be honest I wouldn’t wish such horror on anyone!): every 2-3 hours I washed my mouth with the Stomatofit rinse solution (since I still have to rinse my mouth we don’t know how, I took a baby syringe and poured it into my mouth over the bathtub), I screamed of course, but what to do... After this procedure - Hexoral spray in the area behind the cheeks and on the tongue, when I was moaning very much in pain - I smeared it with Cholisal gel, it numbs the pain for a while time. For every nap (daytime and nighttime) I smeared oxolinic ointment in my mouth (as an antiviral). In the corners of the lips, where there were jams, I first smeared it with Fukarcin, and now with just brilliant green. Well, of course, the temperature was brought down. Now that everything has begun to heal slowly, I lubricate it with vitamin E in oil, because... sponges crack and bleed.
I hope that in the coming days everything will heal completely and life will become wonderful again :))) I wish all the children and their mothers good health!
Features of treatment
The main goal of treating aphthous stomatitis is to completely get rid of the disease or at least reduce the frequency of relapses to a minimum. Therapy is aimed at relieving inflammation, relieving unpleasant symptoms, and accelerating the recovery processes of the mucous membrane.
For each specific case, the doctor will develop a set of measures. The main ones include local and systemic drug treatment.
Rinsing with antiseptics can be done using medications or mouth rinses that contain antibacterial components. An alternative to rinsing is to use a spray. Typically, the treatment regimen includes 2-3 sessions of 1-minute rinsing immediately after brushing your teeth.
Local treatment methods include the application of gels with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
Occlusive agents can reduce pain and speed up the healing of mucous membranes. They form an insoluble film on the ulcer, protecting the affected area from exposure to adverse factors.
Local glucocorticoid therapy is used against the background of immune diseases, as well as when standard measures are ineffective. They eliminate pain and quickly relieve inflammation, shortening the healing period. Such products are used only according to indications and are available with a prescription. In some cases, it is advisable to inject the drug under the base of the ulcer; this is done by a doctor.
Epithelialization drugs are used after acute inflammation has resolved. The specialist will prescribe a gel with an analgesic and healing effect, usually this occurs 5–6 days after the start of complex therapy.
Local laser therapy can relieve pain, speed up the healing process, and minimize the risk of relapse.
Systemic treatment of aphthous stomatitis in adults involves taking the following drugs:
- antihistamines (anti-allergic, anti-edematous effect);
- glucocorticoids (anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect);
- immunomodulators (to stimulate defenses and accelerate recovery).
And if antiallergic drugs can be recommended to any patient even in the absence of information about the exact causes of stomatitis, then other drugs are prescribed only according to indications: in case of acute severe course of the disease, frequent relapses, and the presence of severe systemic pathologies. An additional method of treatment is vitamin therapy - taking vitamins C, group B.
In addition to the main course of treatment, all patients without exception are recommended to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet, avoid taking too hot drinks and dishes, and spicy, irritating foods. It is better to give preference to toothpaste without sodium lauryl sulfate, this component can provoke the disease.
It is important to continue your oral hygiene, even if it is difficult. To make brushing your teeth easier, choose a soft toothbrush. If the disease recurs frequently, it is necessary to pay attention to the general state of health, promptly treat teeth and gums, replace fillings and dental structures.