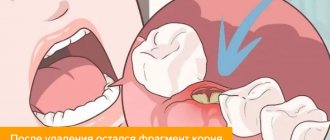
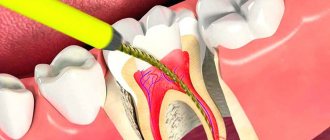
Author: Salatsky Dmitry Nikolaevich Chief physician, orthopedic dentist, gnathologist, maxillofacial prosthetist When treating most dental diseases, doctors do not limit themselves to simply removing the affected necrotic tissue, cleaning out the carious cavity. Very often, the dentist’s task becomes the need to remove the pulp, the neurovascular bundle located inside the tooth, and clean it with further filling of the tooth canals (endodontic treatment). In this case, the dentist must go through all the canals in the tooth without exception, since the anatomical space inside the dental unit remaining uncleaned and unsealed can lead to irreversible consequences due to which it will have to be removed.
Causes of obstruction of dental canals
The root canals of teeth can become obstructed for a variety of reasons. The most common include:
- features of the anatomical structure of the tooth - highly curved roots with small branches, flattened areas and transverse bridges;
- inflammatory processes in the neurovascular bundle - with dental injuries and chronic pulpitis with a subacute course, the root canals can become overgrown;
- age-related changes in tissues - over time, dentin deposits accumulate on the walls of the root canals, which lead to a narrowing of the lumen;
- dental procedures using phosphate cement - this material has a high density and cannot be destroyed by ultrasonic waves, instruments and solvents.
Before starting endodontic treatment, it is important to accurately determine whether the canals are patent.
How do root canals work?
An endodontist must perfectly know the anatomical and morphological structure of the tooth canals.
The tooth consists of three parts - crown, neck, root, and about 70% of the total volume falls on the root, around which the pulp chamber (cavity) is located, which passes into the root canals. A tooth can have one or several canals (the lateral group, as a rule, has more of them than the front). The exact number of canals can only be determined with the help of an x-ray examination, which also allows one to study the structure and characteristics of the canals in a particular patient. In modern endodontics, the most visual 3D images are used for these purposes.
It is important to know: the number of tooth roots may not coincide with the number of root canals.
Milk teeth are no different in structure from permanent teeth; their distinctive features are an enlarged apical foramen, thinner canal walls and low dentin mineralization. Treatment of pulpitis or periodontitis in patients with baby teeth is impossible without cleaning the root canals, and their mechanical treatment requires the doctor to be extremely careful and careful.
Diagnostics
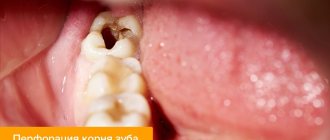
Treatment of impassable root canals begins with determining their length and anatomical features. The most informative diagnostic method is radiography. To obtain accurate data on the condition of the tissues, a photograph of the tooth root is taken with the instrument inserted into it. This allows you to see:
- length of root canals,
- the presence of curvatures and perforations,
- impassable areas.
The condition of the periodontium is also assessed. This allows you to determine further treatment tactics.
If your tooth hurts after root canal cleaning
Toothache is an acceptable consequence of endodontic treatment; provided that all doctor’s instructions are carefully followed, the pain should gradually go away within three days.
If the pain does not go away within three days (and even earlier, if the intensity of the pain increases), a repeat visit to the clinic is necessary. This is possible, for example, with periodontitis, when even high-quality canal treatment is not enough and further treatment is necessary.
Important! Only a doctor can prescribe adequate treatment (medical or surgical) after diagnosis; self-medication is extremely dangerous!
In conclusion, here are some tips for choosing a clinic for endodontic treatment. When choosing dental services, pay attention to the following points:
- Quality of the initial consultation: this should be a thorough examination of the oral cavity and the most detailed interview of the patient, who should be given the opportunity to learn about the state of health. Already at this stage, the doctor must demonstrate his ability to create a comfortable environment and win over the patient.
- The quality of the proposed diagnosis: the patient should be offered an X-ray examination; canal treatment should be preceded by a computed tomography scan, which allows one to accurately determine the number of canals to be treated in the tooth.
- Use of latex plates in practice (read about the purpose of rubber dam above).
Features of treatment
Various techniques are used to treat impassable root canals:
- devital amputation of the pulp followed by mummification,
- depophoresis.
A special approach is required if the root canal:
- strongly curved
- completely closed,
- narrowed,
- is located next to the neighboring root.
To make the canal passable along its entire length, modern dentistry uses:
- durable extractors - nickel-titanium files, which allow you to go through the canal without preliminary tooth preparation;
- drills - special instruments with spiral blades designed for quick and safe removal of gutta-percha, pastes, cements and other filling materials;
- solvents - necessary for unsealing previously sealed canals; they cope well with soft and plastic materials.
The treatment tactics for impassable root canals in each clinical case are determined by the doctor. The procedure is performed under anesthesia. Depending on the complexity, treatment is carried out in one or several stages. To obtain the desired result, 2-3 visits to the dentist may be required.
How channels are processed
The effectiveness and duration of endodontic treatment depends on the method of canal treatment chosen by the doctor, namely:
- Manual - cleaning using special tools; the process is lengthy and tedious not only for the patient, but also for the doctor.
- Mechanical - cleaning using nickel-titanium tools and an endomotor; Much faster and more efficient than manual cleaning, it allows you to clean even curved channels well.
- Ultrasonic – cleaning using an ultrasonic scaler; special endodontic attachments make it possible to easily remove remaining pulp and quickly expand narrow canals; with the help of such attachments, it will not be difficult to free the canal from old gutta-percha or remove a broken instrument.
Most experts agree that high-quality irrigation of dental canals can only be achieved by combining different methods.
Important! In our clinic, the endodontist has the opportunity to use mechanical and passive ultrasonic cleaning in his practice, which, in combination with competent medicinal treatment of the canal with special disinfectants, ensures a 100% result.
The main principle of qualified endodontic treatment is the use of a microscope, which allows, under multiple magnification, to achieve the necessary efficiency of treatment, thorough disinfection and sealing of canals.
To control the quality of the work done during treatment and after its completion, control images must be taken to exclude the possibility of complications.
Signs of canal infection
In some cases, patients can independently determine the presence of problems with a previously treated tooth. The main signs of canal infection are:
- pain that did not go away after treatment or occurred some time after it;
- a feeling of fullness in the gums, discomfort when pressing on the tooth;
- the presence of swelling, swelling on the gums, as well as the formation of a fistulous tract (cyst breakthrough);
- changing the shade of the dental crown from light to gray. This may indicate dentin destruction;
- persistent unpleasant odor.
If you have the above symptoms, you should not waste time by self-medicating. At the IMEZA clinic, the patient can count on a quick, accurate diagnosis and adequate treatment.
Microscope or X-ray
Currently, dentistry uses two types of control over the treatment process: x-ray and using a microscope. X-ray is inferior both in terms of diagnostic capabilities and from a safety point of view:
- Some types of pins and composite materials are not visible in the photographs, which blurs the objective picture of the condition of the dental canals;
- optical distortions and channel overlap are possible;
- if there is liquid in the cavity, then the x-ray will not show it;
- To diagnose and monitor the treatment of the canals, a series of images will be required, and this, although insignificant, is still radiation.
A dental microscope is capable of magnifying the image 30 times - the doctor will notice the smallest tissue defects. You can easily detect the mouths of additional canals, examine their most tortuous configurations, assess root damage and monitor the quality of cleaning.
The microscope allows for unsealing with ultrasound, thereby preserving a large volume of valuable healthy tissue. Optics has significantly expanded the possibilities of dentistry in terms of restoring teeth that were previously considered hopeless. Treatment under microscope control almost completely eliminates the development of recurrent inflammatory processes and ensures long-lasting results.
Patients of the IMEZA clinic can count on high-quality canal retreatment using high-precision optical equipment, technological instruments and modern materials. It is enough to make an appointment, during which experienced doctors will identify all potentially dangerous elements and determine the optimal therapeutic tactics.
Stages of canal retreatment
The procedure for re-treating the canals begins with providing access to them: removing the crown or removing (drilling out) the old filling, removing the stump inlays and pins. Then the canal cavities are freed from the filling material.
One of the stages that determines the quality of endodontic treatment is the correct measurement of the working depth of each canal. The most accurate result is obtained when using an apex locator - an electronic device connected via an electrode to a radiopaque K-file (a thin instrument immersed in the canal). As the K-file approaches the lowest point of the canal (apical constriction), the apex locator signal intensifies. An x-ray helps to clarify the readings of the device.
To ensure proper filling of the canal and adhesion (adhesion) of the filling material to its walls, preliminary mechanical treatment is necessary. Cleaning is done with hand instruments (high risk of breakage) or using an endodontic tip into which nickel-titanium profiles (thin drills) are inserted.
The intensity of rotation of the profiles is controlled by a micromotor, which triggers a reverse if the permissible pressure is exceeded. This method guarantees the absence of perforations, nicks and eliminates breakage of the instrument in the canal. Ultrasonic scalers and dentin softeners are used as auxiliary measures. This promotes maximum preservation of healthy tissue.
An important component of the canal revision process is their sterilization. The cavity is thoroughly washed and disinfected with antiseptics. In the presence of inflammatory formations, the following measures can be taken:
- opening the gums and excision of the root apex or complete removal of one of the roots (hemisection);
- laser removal of infected tissue;
- sanitation of channels through electrophoresis with calcium and copper ions.
After sterilization, filling material is placed. If the working length is incorrectly determined during machining, the top of the channel opens and the material flows beyond its limits. As a result, the patient will be bothered by prolonged pain, inflammation and neuralgia. At the IMEZA clinic, such errors in treatment are excluded.
The retreatment procedure is associated with additional damage to the coronal part, therefore, in some cases, its position is strengthened using an intracanal pin. Manipulation is possible if the layer of dentin surrounding the pin is at least 2 mm. Installation includes the following steps:
- preparing the bed using a calibration tool;
- adjusting the length of the pin;
- etching and drying the bed;
- applying adhesive material directly to the pin or into the cavity of the bed;
- installation of the rod, polymerization of the adhesive mass.
After completing the canal filling work, the dental cavity is closed with a temporary filling. At the next visit, the doctor begins to restore the upper part of the tooth using an artificial crown, inlays or volumetric restoration techniques.
After treatment, discomfort when biting on a tooth may persist for 3-5 days. If there are no complications, you should return for a routine examination in a year.