An oral burn is damage to the oral mucosa through exposure to high temperature, chemicals, electrical or light radiation. This condition is extremely painful, as there are a large number of nerve endings in the mouth. The mucous tissue becomes swollen and red. Later, the burnt epithelium peels off and painful areas appear.
Treatment for a burn will depend on the extent of tissue damage and the area of spread of the injury. First of all, it will be aimed at neutralizing the cause of the injury and relieving the pain syndrome. Further treatment is aimed at preventing infection of the affected area and speeding up its healing.
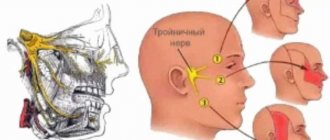
Types of burns of ENT organs
Like any others, they are divided according to severity - from the first with minor damage to the severe fourth, up to tissue necrosis. The nature of the injuries depends on the temperature and concentration of the substance, as well as the time of contact with it.
Depending on the injured area, damage can be external, internal or combined. In the first case, the skin of the outer ear and wings of the nose is affected. In case of internal lesions, the nasopharynx, trachea, throat and larynx, and auditory canal are affected.
Taking into account the source, thermal and chemical injuries are distinguished. In the first case, the cause is contact with open fire, boiling water, hot oil, hot metal, etc. Chemical burns are more common. They occur if you swallow an acid or alkali, or inhale their vapors. They occur upon contact with aggressive household chemicals, vinegar essence, and ammonia.
How to avoid complications?
In order not to aggravate the situation when treating gum burns, it is important to be attentive to yourself until the injury passes.
- For any type of gum burns, dentists do not recommend eating spicy, sour, or salty foods until the tissues are completely restored. Strong flavors irritate the affected tissues and can significantly prolong the healing process.
- You should not eat too hot foods - both during treatment and in the future, when the gums recover after the burn.
- All medicines, household chemicals, paints, solvents, and building materials must be stored in specially designated areas out of the reach of children.
If the pain from a burn becomes excruciating, we can take painkillers or use light anesthetic gels with analgin or benzocaine.
Complex gum burns, in which soft tissue dies, can only be treated surgically. The doctor in the hospital removes dead pieces of tissue and covers the damaged areas with donor parts. Such a “jewelry” operation often requires repetitions and additions. After treatment, the surgeon must prescribe antibiotics to the patient so that bacteria and microbes do not appear in the wounds and dangerous suppuration does not begin.
We hope that all of the above tips on caring for burnt gums will be for informational purposes only. Be careful and attentive to yourself, and accidents will bypass you.
Sources:
- The problem of treating inflammatory periodontal diseases in patients suffering from type 2 diabetes mellitus E.A. KHROMOVA* Ph.D., Associate Professor of the Department I.V. KULIK* Ph.D., Associate Professor of the Department N.A. UDALTSOVA**, ***candidate of medical sciences, associate professor of the department; Deputy Chief Physician for Organizational and Methodological Work A.K. IORDANISHVILI****,*****Dr.Med.Sci., Professor, Professor of the Department *Department of General Dentistry, North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikov" of the Ministry of Health of Russia; ** St. Petersburg State Budgetary Healthcare Institution “Dental Clinic No. 29”, Frunzensky District, St. Petersburg; ***Department of Maxillofacial Surgery and Surgical Dentistry of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "St. Petersburg State University" of the Government of Russia ****Department of Orthopedic Dentistry of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikov" of the Ministry of Health of Russia; *****Department of Maxillofacial Surgery and Surgical Dentistry of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "Military Medical Academy named after S.M. Kirov" of the Russian Ministry of Defense;
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- The role of hygiene products in the treatment of periodontal diseases (S.B. Ulitovsky Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Honored Dentist StAR Prof., Doctor of Medical Sciences, Department of Preventive Dentistry of Pavlov Pavlov State Medical University, St. Petersburg) S.B. Ulitovsky - Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Honored Dentist of StAR, Prof., Doctor of Medical Sciences; E.S. Alekseeva - associate professor, candidate of medical sciences; A.A. Vasyanina - associate professor, candidate of medical sciences; V.A. Grigoriev - Associate Professor, Ph.D.
What is the danger
- If the mucous membranes of the throat or nose are affected, there is a high probability of swelling. It spreads quickly and makes breathing difficult. Up to the point of suffocation.
- When ingested or inhaled vapors of acids and alkalis, damage to the nasopharynx and throat is usually combined with deeper damage to the trachea, esophagus and other internal organs. Necrosis of esophageal tissue and perforation are possible.
- External burns cause intoxication and take a long time to heal without proper treatment. The wound surface becomes infected.
- If the lesions are strong and extensive, a painful shock occurs.
Classification
We use the following classification of caustic injuries of the esophagus:
- 0 - no damage
- 1 - erythema and swelling
- 2 - ulceration is not circular
- 3 - circular ulceration
- 4 - perforation
There are also more detailed classifications:
- 1st degree - erythema and edema (damage is limited to the superficial layers of the mucosa, their rejection with subsequent epithelization without scar formation is possible).
- 2a degree - vulnerability, hemorrhages, erosions, exudate, blistering (mucosal, submucosal and muscular layers are involved).
- 2b degree - the same as 2a plus deep or circular ulcers.
- Grade 3a - deep ulcers, “gray or black esophagus” (transmural lesion).
- Grade 3 - extensive necrosis.
Related articles:
- Articles: ENDODIAGNOSTICS FOR ESOPHAGUS BURNS WITH ALKALI
- Articles: FEDERAL CLINICAL GUIDELINES “Toxic effect of corrosive substances”, “Toxic effect of soaps and detergents” 2014
- Articles: Zargar classification - assessment of damage to the esophagus when swallowing caustic (caustic) substances
CLASSIFICATIONS section
Alarming symptoms
If you have come into contact with a chemical or vapor, you should immediately contact a clinic. Otherwise, the condition will only get worse. There is a high probability of internal damage if:
- Severe, persistent pain appeared in the mouth, throat, and along the esophagus.
- When you swallow, the discomfort intensifies, and you can’t even drink the liquid.
- There is vomiting, especially with blood.
- Profuse salivation began.
- It became difficult to breathe.
- The temperature has risen (due to intoxication).
- Swelling of the mucous membrane.
- The victim is either drowsy or, on the contrary, restless.
- Severe burns of external tissues, blisters.
Clinical researches
Repeated clinical studies have proven that the two-component oral skewers ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component skewers - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Consumer Reviews
Natasha (vseotzyvy.ru)
“Mouth rinse Vertex JSC Asepta mouth rinse is sold in pharmacies, that’s why I bought it, it has more medicinal properties than just a cosmetic product, and indeed this rinse perfectly removes bad breath, disinfects gums, menthol gives freshness for almost a day perfectly helps smokers."
Dilya09 (otzovik.com)
“Hello to all readers of my review! I wanted to tell you my story about how I started using the Asepta oral brush.
It all started with the fact that I had an implant installed instead of an extracted tooth and was given strict instructions to rinse my mouth with chlogrexidine and, preferably, an oral scavenger. At the pharmacy, my choice fell on the Asepta drug, despite the price, because after the implantation procedure I had the feeling that now I would brush my teeth after every meal and rinse my mouth (it was just creepy). The price of this skimmer in pharmacies is above 160 rubles.
It doesn’t taste very nasty like some skimmers; after rinsing, it freshens your breath due to the “Lime” and “Mint” flavors. By the way, I don’t use it regularly anymore, I often forget to rinse my mouth, but, nevertheless, it is always present in the bathroom.
Of course, over the years, the memories of implantation have become dull, much has been forgotten, but Asepta and I are now friends. I take not only the skimmer, but also toothpaste. In general, not only is the skipper good, but the whole series is good. I recommend it to everyone who uses oral skewers.”
First aid for burns of the ears, nose, nasopharynx
If external damage of the first degree occurs, the skin is treated with a special product - ointment or foam. If necessary, you can take a pain reliever. If the damage to the integrity of the skin is more serious, you need to blot the surface with a weak solution of potassium permanganate and apply a dry sterile bandage. Next, seek medical help. The victim should drink more. Opening blisters is strictly prohibited - it will cause infection.
The degree of damage in internal burns is determined only by a doctor. Chemical injuries also require specialist supervision. If you know what caused it, then in the first minutes:
- The effect of alkali is neutralized with a weak solution of acid (1%) - citric, boric or acetic.
- If the cause is contact with acid, use alkali (2% baking soda solution).
- If there is no neutralizing agent, you can use ordinary boiled water for rinsing.
- When the cause is contact with quicklime, it is important to completely eliminate interaction with water. Use any vegetable oil.
- Medical assistance must be received within a maximum of six hours.
It's all the virus's fault!
The term "stomatitis" is derived from the merger of two Greek words: stoma (mouth) and itis (inflammation). There are a great variety of different types of disease - serous, aphthous, allergic, etc. The most dangerous is herpetic, or cold sore, stomatitis caused by a virus. Its main manifestations are painful ulcers covering the oral mucosa. The trigger mechanism of the disease is the activation of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. First of all, the disease threatens those who have a weakened immune system and, as a result, the body simply does not have the strength to give a worthy rebuff to viruses.
Treatment of burns of ENT organs
Even when it seems that the damage is minor, it is better to see an otolaryngologist. If the injury occurred due to contact with a complex chemical compound or an aggressive cleaning agent, then take the packaging with you. A specialist will study the composition of the substance.
For severe burns, antishock medications are indicated. If breathing is difficult, there is severe swelling, prednisolone or calcium chloride is used.
A tracheostomy is performed to restore breathing.
Medical appointments are conducted by ENT specialists with almost 10 years of experience. At your appointment, you will be treated with affected tissues and mucous membranes, and a pain reliever will be selected. If necessary, they will arrange a consultation with a surgeon or refer you to a hospital. The center is open all week, seven days a week.
Herpetic or aphthous?
It will be somewhat more difficult to distinguish between herpetic and aphthous stomatitis. The latter got its name from the Greek term “aftha”, which means “ulcer”.
If with herpetic stomatitis there are many ulcers, but they are small, then with aphthous stomatitis there are few of them, and the size can reach 7–8 mm.
The second important distinguishing feature is the absence of swelling of the gums with aphthous stomatitis.
If you are looking for differences between herpetic and aphthous stomatitis, then the third thing you should pay attention to is the localization of the rash. Aphthous is characterized by the appearance of ulcers in the oral cavity, while herpes infection can spread to the border of the lips.
Bacterial or viral?
In addition to viral origin, the disease can be caused by bacteria: streptococci and staphylococci are normally present in the microflora of the oral cavity and begin to multiply uncontrollably during the inflammatory process. The latter may be caused by caries or periodontitis (read more about the disease in the article).
How to distinguish viral stomatitis from bacterial one? It is extremely difficult to do this at home, so it is better to consult a doctor. The main differential feature is the localization of the rash. With viral herpetic stomatitis, vesicles with transparent contents first appear on the tongue (its tip, along the side surfaces and under it), and then can even spread to the pharynx and tonsils.
For bacterial stomatitis, the location of the rash on the gums and those areas where the skin borders the mucous membrane (for example, on the red border of the lips) is more common. Also, with a disease caused by streptococci, “jams” are often observed - pustules on the corners of the mouth, which quickly begin to bleed, become covered with a crust, crack and cause constant discomfort while eating and talking.
Types of diagnostics
An experienced doctor can identify herpetic stomatitis in adults during an initial examination, relying on only two methods.
- Clinical picture.
Based on the totality of the patient’s specific complaints and distinctive external signs, the dentist will not only assess the severity of the disease, but also differentiate it from ordinary stomatitis, candidiasis, etc. - Immunofluorescence.
Express microscopy method, the most accurate for diagnosing acute herpetic stomatitis.
Drug therapy
Rinse
To stop the spread of infection throughout the oral cavity, as well as to prevent the occurrence of sore throat, anti-inflammatory drugs such as Stomatidine and Miramistin are prescribed. The greatest effect is achieved by repeating the rinsing procedure every 3 hours, strictly adhering to the instructions for medicinal solutions.
Antiviral drugs
To suppress the reproduction of the herpes virus, the patient is advised to take “Immudon” and “Acyclovir” orally according to the scheme, and for external use - “Viferon” ointment or “Silicea” gel.
Vitamin therapy
Tablet vitamin complexes such as “Complivit” help improve immunity.
Attention!
Before use, consultation with a specialist is recommended!