22.11.2019
White plaque in the mouth is one of the signs of candidal stomatitis. This pathology is caused by the Candida fungus and most often affects young children. In addition to deposits, redness appears on the oral mucosa, which causes severe discomfort.
For what reasons does it appear?
White plaque in the mouth in adults occurs for the following reasons:
- development of endocrine pathologies;
- metabolic disorder;
- taking medications (antibiotics, hormonal drugs);
- vitamin deficiency;
- chronic infections of the nasopharynx and oral cavity;
- hepatitis (in particular hepatitis C).
Sometimes this symptom signals the development of cancer processes. In 10% of cases, intestinal cancer manifests itself this way.
What does it mean to have a whitish coating in your mouth in the morning?
In 80% of cases, this symptom is provoked by dry mucous membranes. This happens when a person sleeps with his mouth open - the appearance of deposits is due to a violation of natural hydration.
Another possible reason is impaired saliva production.
In women, this symptom occurs against the background of hormonal changes. Expectant mothers, as well as women in menopause, are at risk.
Appearance of yellowish deposits
A yellow coating appears in smokers, as well as in fans of black tea and coffee. If it is present in small quantities, there is no need to worry. If the deposits are poorly removed and are accompanied by additional symptoms, we may be talking about liver damage.
Possible reasons for the appearance of yellow deposits:
- gallstones;
- acute pancreatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- hepatitis.
A noticeable greenish tint may indicate stagnation of bile.
How does plaque form on teeth?
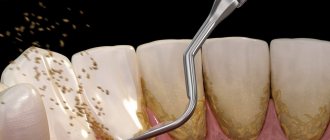
Plaque on teeth in adults can be soft or hard. The first is always present on the mucous membrane, and the second does not form immediately; dentists call hard plaque tartar.
1. On each tooth there is always a structureless semi-permeable film called pellicle. The thickness of this film is only 1 micron. The pellicle contains immunoglobulin proteins and enzymes. All metabolic processes between enamel and saliva are carried out through it.
2. Microbes in the mouth continuously secrete heteropolysaccharides, which are attached to the pellicle. The accumulation of microbes provokes the appearance of plaque on the teeth.
3. Without cleansing, bacteria, molecules, dead cells and other food elements settle on the teeth; saliva helps the plaque harden and thicken.
4. Soft plaque mineralizes and turns into hard plaque.
Then the stones begin to put pressure on the gums, irritating the tissues and interfering with the normal metabolism between saliva and tissues. As a result, tooth enamel is destroyed, gums become inflamed, plaque penetrates into the deep layers of the tooth, and caries appears.
Types of plaque in adults
Contrary to popular belief, plaque on teeth in adults can be more than just yellow. Let's look at their most common types.
Dark brown coating
Why it appears: Yes, dark stripes on the teeth do not always indicate caries. Most often, teeth acquire such pigment due to nicotine tar and colored foods. Such plaque can also appear due to disturbances in the metabolism of calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorus. Surprisingly, dark plaque is also common in children; a brown tint to the teeth indicates enamel hypoplasia and dysbacteriosis. The cause of a dark shade is often a lack of saliva.
How to get rid of it: Contact your dentist. Unfortunately, it is impossible to remove dark plaque on your teeth on your own. No active cleansing or application can cope with this shade: too careful self-care can cause the condition to worsen. If plaque is caused by smoking, ultrasonic teeth cleaning can deal with it, but if the cause of the dark shade of the crowns is dysbacteriosis, installation of veneers is recommended.
Black plaque
Why it appears : A terrifying black plaque on the teeth is most often a symptom of dysbacteriosis, helminthic infestation, fungi in the oral microflora and gastrointestinal diseases in adults. This plaque can also appear due to the abuse of cigarettes, coffee and alcohol.
Dentists consider the most common reasons for the appearance of black plaque on teeth in adults:
- taking antibiotics;
- severe diseases of the spleen, liver,
- viral infections;
- abscesses;
- drug use;
- presence of copper products in the mouth;
- allergic reactions;
- difficult working conditions;
- parasites.
Black plaque can also appear due to chemotherapy.
How to get rid of it: Black plaque can only be removed with the help of a dentist. No amount of whitening pastes, rinses or balms will help remove it. To restore your teeth to their former whiteness, the doctor can also clean them with ultrasound or install veneers.
Yellow plaque
Why it appears : Often teeth are distinguished by their natural yellow pigment. This, as a rule, indicates that the human body is oversaturated with minerals, so the enamel has become yellow and hard, and bleaching it is very dangerous. A soft yellow coating at the roots is often inherited.
The most common reasons for the appearance of yellow plaque, dentists include:
- sugar abuse;
- poor oral hygiene;
- wearing braces;
- varied diets;
- age;
How to get rid of it: Regular professional cleaning, oral care, visiting the dentist twice a year, proper nutrition are the basis for white and healthy teeth. If you follow these simple rules and give up bad habits, you can get rid of the unaesthetic yellow plaque forever.
Folk recipes can also help in the fight against yellowness. For example, fresh strawberries or wild strawberries are excellent for cleaning teeth from plaque. It is enough to eat a couple of berries before brushing your teeth: berry acid will soften plaque on your teeth, and then it can be easily removed with a brush.
An effective remedy against yellow plaque is baking soda. However, you need to remember that soda cannot be used regularly - the substance is unsafe for enamel. It is optimal to use baking soda once every 1-2 weeks and brush your teeth with it instead of toothpaste.
White (gray) coating
Why it appears: It’s hard to believe, but it is a soft white, not a yellow coating that is always present on the enamel in children and adults. With regular cleansing, these food particles, bacteria, and mucous membranes can be easily removed with a toothbrush.
If a person neglects oral hygiene, the plaque hardens, stones form on the teeth, which then provoke caries.
The main causes of white (gray) plaque on teeth include:
- lack of vitamins;
- unbalanced diet;
- the predominance of soft food in the diet;
How to get rid of: White plaque can be dealt with at home. The main thing is to notice its appearance in time and not neglect your teeth in the future.
If the white plaque cannot be dealt with using improvised means, it is recommended to visit a dentist.
Brown plaque
Why it appears: Smokers and coffee drinkers most often suffer from brown plaque. After eating these products, a film forms that is almost impossible to remove with a toothbrush.
In rare cases, brown plaque on the teeth provokes the production of brown salt, which is formed due to the production of secretions into saliva.
Causes of brown plaque on teeth also include:
- frequent mouth rinses with potassium permanganate;
- the effect of chlorinated water;
- vapors of iron, mercury, lead, manganese, iron;
- acid tissue necrosis;
- Rhesus conflict of a pregnant woman.
How to get rid of it: Unfortunately, it is impossible to remove brown plaque on teeth using improvised means. To prevent the unpleasant color from appearing again, it is important not only to hygienically brush your teeth, but also to determine and, most importantly, cure the cause of plaque formation.
Green, red and orange plaque
Why it appears: Most often, unusual green, red or orange plaque on the teeth of children and adults is caused by various types of fungi. For example, chlorophylls make green enamel, and chromogenic bacteria make orange enamel.
Red enamel can be a symptom of porphyria, a hereditary disease in which the pigmentation of soft tissues is disrupted. Teeth can also turn bright red as a result of bleeding injuries (pulp sac ruptures).
How to get rid of it: Only a dentist can eliminate unpleasant staining of enamel. If necessary, the doctor will refer the patient for tests and examinations from other specialists, help eliminate the cause of the plaque and, of course, clean the teeth.
If plaque of any kind is detected, it is worth remembering that dentists do not recommend cleaning it exclusively with home remedies, with the exception of Global White. Of course, whitening pastes and effective folk recipes can help to cope with the defect for a short time. But only an experienced dental therapist is able to assess the neglect of plaque and prescribe the most effective method of treating it, based on the condition of the oral cavity of a particular patient.
Main manifestations
White plaque on the palate of an adult is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- feeling of itching and burning in the mouth;
- the appearance of small ulcers on the mucous membrane;
- hypersensitivity to temperature stimuli;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- hypersensitivity to mechanical irritation.
Mouth ulcers are bright pink or red in color. If the wounds become infected, profuse purulent discharge appears.
Primary symptoms
One of the first symptoms of candidal stomatitis is the appearance of dry mouth and white plaque. Deposits appear in the form of ragged or neat small spots.
This symptom is accompanied by severe discomfort, which is expressed in burning and itching of the affected areas.
As the disease progresses, a white coating appears on the inside of the cheeks. Next, the gums and tonsils are affected.
At the initial stage of the pathology, plaque can be easily removed with a cotton swab. Beneath it, painful red lesions are found.
Secondary manifestations
Additional signs include:
- increased sensitivity of the mucous membrane. Eating salty, spicy and sour foods causes pain;
- decreased sense of taste;
- the appearance of a specific metallic taste;
- bleeding ulcers;
- the appearance of mycotic lesions (the skin in the corners of the mouth becomes red, then becomes covered with microscopic cracks. Then a white coating appears in the corners of the lips);
- the occurrence of pain when swallowing saliva;
- an increase in general temperature (this is due to the body’s response to the pathogenic activity of fungi);
- unmotivated weakness, drowsiness;
- the appearance of bad breath;
- slowing down the rate of speech;
- enlargement of taste buds on the tongue.
The “spotty” coating on the sky gradually merges into a continuous white film. Its structure becomes denser and it becomes more difficult to remove.
Causes of white plaque on the tongue
The reasons that cause a white coating on the tongue include:
- poor oral hygiene;
- medications (for example, long-term use of antibiotics);
- smoking;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- viral infections;
- diseases of the oral cavity (oral candidiasis (thrush), leukoplakia, lichen planus, geographic tongue (desquamative glossitis));
- chronic diseases (hypothyroidism, diabetes, syphilis);
- immunodeficiency conditions (HIV/AIDS);
- heat;
- improper use of an inhaler in the treatment of asthma, COPD;
- mechanical injuries to the oral mucosa caused by sharp edges of the teeth when damaged by caries or chips, dentures, piercings in the mouth;
- burns of the oral mucosa caused by too hot food or liquid;
- chemical injuries to the oral cavity;
- xerostomia (dry mouth);
- breathing through the mouth;
- a diet containing soft and pureed food, absence of coarse fibers in food;
- oral cancer, tongue cancer;
- radiation therapy of malignant neoplasms of the maxillofacial region.
Establishing a diagnosis
If a plaque is detected on the palate of an adult’s mouth, the doctor undertakes:
- Listen to the patient's complaints.
- Collect anamnesis.
- Inspect the mucous membrane and skin.
- Make a microscopy of a scraping from the oral cavity.
Additionally, the patient may be referred for consultation:
- to a dermatologist - in order to identify fungal infections of other systems and organs;
- endocrinologist - to detect endocrine pathologies;
- an allergist - in order to determine the body’s sensitization to the materials from which dentures are made.
After clarification of the diagnosis, treatment is prescribed.
Features of therapy
Treatment involves the use of topical drugs and internal medication.
To treat the oral cavity in adults, with very high sensitivity of the mucous membrane, it is allowed to use a diluted Lugol's solution (2 tsp per 200 ml of warm water from a kettle).
You can also lubricate the oral cavity with baking soda diluted in water (1/2 tsp per 150 ml of warm boiled water). The procedure should be carried out 2-3 times a day.
Drug therapy involves the use of antifungal and painkillers. Antihistamines are additionally used as prescribed by an allergist.
Use of antifungal agents
The main antifungal drugs are presented in the table:
| A drug | Description | Mode of application | How to use |
| Ketocanazole, 200 mg | The main effects are antiandrogenic, antifungal, fungicidal, fungistatic. The drug helps inhibit the synthesis of ergosterol, triglycerides and phospholipids. Against this background, fungi lose their ability to form colonies and threads. | Oral | The daily norm is 1-2 tablets for 14 days. Then, after the disappearance of acute symptoms - 1 tablet 24 hours - until the white deposits and ulcers completely disappear. |
| Fluconazole, 50 mg | The main effect is antifungal. Has a highly specific effect. | Oral | 50-100 mg/24 hours, for 1-2 weeks, until the sensation of plaque in the mouth completely disappears. |
| Nystatin, 1% | Effects – antifungal, fungistatic. The presence of double bonds in the composition helps ensure high tropism of the antibacterial drug to the sterols of the fungal cell membrane. | Local impact | The oral cavity should be treated 2 times/24 hours until the white plaque and other symptoms disappear. The approximate duration of the course is 10 days. |
| Clotrimazole, 1% | The product belongs to the group of imidazole derivatives. Effects: antibacterial, antiprotozoal, trichomonacid, broad-spectrum antifungal. | Local impact | The oral cavity is treated 2 times/24 hours until the white plaque disappears. The average course duration is 7 days. |
| Chlorhexidine bigluconate, 0.05% | The main effect is antiseptic. | Local impact | Intended for the treatment of mouth ulcers. 3 times/24 hours, 7 days. |
How to prevent plaque formation?
As you know, the best treatment for diseases is their prevention. To prevent unaesthetic plaque on your teeth from bothering you and making you suffer in the dentist’s chair, remember a few rules that will help keep your teeth white, strong and smooth:
- Give up bad habits. No matter how trivial it may sound, it is smoking and alcohol abuse that are the strongest enemies of enamel. Put out the cigarette once and for all, minimize the consumption of wine, beer, vodka and other strong drinks, and within a couple of months you will notice that the condition of your teeth has noticeably improved.
- Review your diet . Coffee, soda, sweet juice and black tea are not at all safe for your teeth, even if you drink them through a straw. And caramels, toffees, cakes and chocolates not only leave an unpleasant coating on the enamel, but also provoke tooth decay. Include more fresh fruits, vegetables, and herbs in your diet - these are the foods that allow you to cleanse crowns naturally; in addition, plants strengthen the body.
- Don't write off sugar-free candies and chewing gum . These products activate salivation.
- Remember the rules of personal hygiene . Brushing your teeth twice a day is the key to healthy enamel, crowns, gums and nerves. Choose your toothpaste carefully, brush every square millimeter, be mindful of the space between your teeth, and be sure to remove the film from your tongue.
Effective and safe teeth whitening and cleansing of surface enamel stains is provided by Asepta Plus gentle whitening toothpaste. This paste has a unique multi-stage teeth cleaning system that guarantees whitening for 4 weeks without damaging the tooth enamel. Hydroxyapatite and potassium citrate, which are part of the paste, mineralize weakened tooth enamel, prevent the occurrence of increased tooth sensitivity, and calamus and eleutherococcus extracts strengthen the gums and accelerate the regeneration processes of the oral mucosa.
Use of painkillers
The table shows the most effective analgesics. They are prescribed only according to indications.
| A drug | Description | Mode of application | How to use |
| Lidocaine hydrochloride, 1% | A potent local anesthetic. Effects: antiarrhythmic, local anesthetic. | Local impact | Prescribed against the background of hypersensitivity to amide anesthetics. Used for applications, before meals. |
| Procaine, 5 mg/ml, 0.5% | Local anesthetic. | Local impact | In the form of applications before meals and treating the mouth with antifungal drugs. |