Causes of thrush in a newborn
There is only one reason that can provoke candidal stomatitis in babies in the first months of life - weak functioning of the immune system as a result of the influence of unfavorable factors.
Conventionally, unfavorable factors can be divided into two groups: internal, associated with the functioning of the body and the functioning of organs, and external.
Internal factors:
- deep prematurity (birth a month or more before the due date);
- low birth weight (less than 2500 g; and less than 1700 g for a child born during a multiple pregnancy);
- congenital defects and pathologies of the formation of internal organs;
- insufficient supply of nutrients and vitamins (occurs when the mother’s diet is poor, if the child is on breastfeeding);
- anemia (low hemoglobin levels as a result of iron deficiency);
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- rickets;
- history of infectious diseases.
External factors:
- Injury to the oral cavity . Abrasions and cracks in the oral mucosa are an excellent environment for fungi to settle and actively reproduce.
- Antibiotic therapy . It often happens that in the first days of a child’s life it is necessary to give him strong antibiotics (for example, when a child is born with pneumonia and is placed in the intensive care unit immediately after birth). Antibiotics of various groups have a detrimental effect not only on pathogenic bacteria, but also on beneficial microflora, destroying and destroying them. As a result, the newborn develops dysbiosis.
- Refusal of breastfeeding and transfer of the baby to artificial formula . Even the most expensive milk substitutes contain a lot of sugar, which is added to maximize the taste of the product. The acidity of the oral cavity increases and creates a breeding ground for fungal growth.
- Candidiasis in the mother in the last stages of pregnancy . If a woman does not have time to cure thrush before giving birth, the likelihood of infection of the child during passage through the birth canal becomes very high.
- Insufficient hygiene of the newborn. This includes any factors that can provoke the colonization of mucous membranes by harmful organisms: dirty rattles, unboiled nipples and bottles, poor skin care for the baby, etc.
Causes of thrush in a child
Because the child’s immunity is still too weak and this contributes to the development of favorable conditions for the development of candidiasis (candida fungi are the first of the microscopic fungi that a child encounters at birth).
In the first week of life, so-called thrush (damage to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity) may develop in the form of a cheesy white coating on the inner surface of the neck, tongue and gums. Basically, this process is temporary and goes away during the first month of life, and with a weakened immune system, thrush can be recurrent and difficult to treat. In addition, if the skin is damaged, the process can spread to natural folds and in the area of diaper rash. Healthy skin can resist the effects of fungi on its own, but damaged skin cannot do this, and a fungal infection can become more severe. Breastfeeding plays an important role because breast milk helps repopulate the sterile intestines with beneficial microorganisms. Therefore, the body of bottle-fed children is more susceptible to infection entering the body.
The process of fungal development is aggravated by wearing diapers, which create a “greenhouse effect” and due to the warm, humid environment, fungal infections multiply quickly. A healthy breastfed baby cannot develop candidiasis. If thrush appears again after treatment, this should be assessed as a signal that the immune system is weakened. In children, candidiasis can either be temporary or become a serious disease requiring treatment from a specialist.
Recurring oral thrush in infants can cause damage to the fingernails. This occurs in infants who prefer their finger to the pacifier. As a result of the lesion, the nail plate becomes deformed, thickens, the periungual fold turns red and a white mass is released from under it.
In girls, candidiasis can develop into candidal vulvitis, and in boys, balanoposthitis can occur (redness and a white cheesy coating appear in the area of the urethral opening). These phenomena may not bother the child, but are sometimes accompanied by itching, burning and pain.
In older children, Candida fungi can cause allergic diseases, which, in turn, affect the skin, mucous membranes and intestines. Therefore, children with allergic diseases should undergo a comprehensive examination, including for possible candidiasis.
How to determine if a newborn has candidiasis
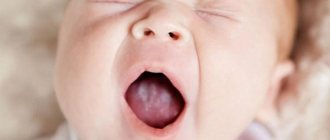
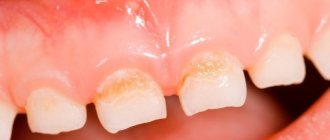
This will not be difficult, since the hallmark of thrush in the mouth is the appearance of a white coating that can cover the tongue, gums, inner surface of the cheeks, palate, tonsils, and tonsils.
Thrush spreads to the back of the pharynx in the absence of the necessary therapeutic measures. In very rare cases, the fungus can affect the baby's esophagus and even intestines.
A specific coating, similar to semolina grains (in advanced cases, it can resemble particles of cottage cheese) is the primary sign of thrush.
There are also secondary symptoms that usually appear simultaneously with the main symptom of the disease:
- poor appetite (refusal to breastfeed or bottle);
- crying during feeding;
- sleep disturbance at night;
- general malaise;
- moodiness and irritability;
- redness of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, wounds and ulcers;
- an increase in temperature to 37-38 degrees (in cases where a bacterial infection is associated with a fungal infection).
The appearance of such symptoms is a reason to call your local pediatrician or consult with a pediatrician online.
Treatment plan
How to treat vulvar candidiasis (thrush) in children of school age, and not only?
Basically, treatment involves eliminating the pathogen and stopping its reproduction, which will therefore eliminate the symptoms. Only a good specialist can treat the disease correctly and effectively, who can prescribe:
- antifungal drugs and antiseptics (topically);
- antibiotics;
- ointments and medicinal baths;
- therapy to restore and strengthen the immune system;
- therapy to restore the microflora of the reproductive system.
Which course of treatment will be chosen and prescribed depends on the specific case and the reasons that led to vulvovaginal candidiasis in a teenage girl and a smaller child.
Repeated appointment
At the follow-up appointment, the doctor assesses the child’s condition and checks how effectively the chosen regimen works. If no positive dynamics are observed, then repeated diagnostics and selection of new methods for treating thrush in the child are prescribed.
Control reception
The control reception is an important point. The doctor prescribes it to see how the child recovers after a full course of treatment, to see if there are any relapses or suspicions of them. It is also possible to prescribe physiotherapy and rehabilitation (for example, if a long course of antibiotics has been prescribed). A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled after 21–30 days or later.
Treatment result
The disease can be cured, but the timing of treatment is individual and depends on the stage and causes of thrush in young children or teenage girls. All details of treatment are discussed individually at a doctor’s appointment. If there is a suspicion that the parents are infected, then both parents are treated.
Prevention
Thrush in children is a fairly common occurrence, especially under “favorable” conditions for the disease. To protect the child, it is necessary to take preventive measures:
- carry out proper personal hygiene of the child in accordance with age;
- wear the correct underwear;
- normalize nutrition (moderate or limited consumption of sweets, starchy foods and fast foods, more fruits, vegetables, etc.);
- Strengthen your immune system by taking vitamins and exercising.
Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene at home and in public places will also help avoid the occurrence of vulvar candidiasis and other unpleasant diseases in a teenage girl or young child.
How to distinguish thrush from the consequences of regurgitation
Some parents (especially if the child is the first-born) mistakenly mistake the plaque for the remains of curdled milk after the baby has burped. Indeed, it can be very difficult to visually determine the nature of the contents of the oral cavity.
To understand what exactly caused the symptom, you can do a small test. You need to moisten a piece of clean cloth with boiled water or chamomile decoction and try to remove the plaque.
If this is the remains of milk after regurgitation, then the baby’s mouth will be easily cleaned, and all the contents will end up on the tissue. If you have thrush, it is not so easy to remove plaque (after the procedure, irritated areas will remain at the site of inflammation).
Thrush in children: causes
In adolescents, the main cause of thrush is a hormonal imbalance, which occurs due to the growth and development of the child or due to disruption of the endocrine system.
Other causes that act as factors in the occurrence of childhood vulvar candidiasis:
- reduced immunity;
- antibiotic treatment (uncontrolled);
- poor or unhealthy diet (especially abuse of sweets, fast food, etc.);
- smoking and alcohol;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- improper hygiene or its complete absence;
- hypothermia;
- anatomical features of the reproductive system;
- infection from the inside (for example, from the intestines);
- after contact with household objects or in public places (swimming pool, etc.);
- during childbirth from the mother;
- excess weight (at the stage of obesity);
- anemia and other diseases;
- allergic reactions.
As you can see, there are a lot of answers to the question “Where does thrush come from in children?” Moreover, as a rule, a whole complex of problems leads to thrush. Another factor is age. In infants, thrush usually appears as a result of parental neglect, in teenage girls - as a result of changes in the hormonal system, etc.
If there is any suspicion of candidiasis or another infection, it is necessary to take the child to a doctor who will conduct an examination and prescribe a course of treatment and recovery, as well as give useful tips on how to prevent infection or relapses. The medical center employs specialists in pediatric gynecology and uses modern diagnostic equipment.
Initial appointment
At the initial appointment, the doctor examines the child’s genital organs to assess the disease and state of health. The doctor also finds out the possible causes of thrush in a child, prescribes tests to understand how to treat, since the course is prescribed individually for each specific clinical case.
Diagnosis of the disease
In some cases, tests and examinations are required:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
; - blood and urine tests;
- taking smears and culture for fungi of the genus Candida;
- stool analysis for worms and intestinal dysbacteriosis
If children are suspected of having any diseases other than thrush, additional tests are prescribed. Also, if thrush has caused a nervous shock and affects the psychological and mental development of the child, then a consultation with a psychotherapist is prescribed.
Procedure and treatment regimens for vulvovaginal candidiasis in school-age children and teenage girls
The procedure and treatment regimen are determined individually and depend on the type and stage of development of the disease, the causes of infection and the presence of concomitant diseases. A visit plan is also assigned individually, since for one patient the first consultation and follow-up appointment will be enough, while for others several appointments will be needed.
Treatment
Some people mistakenly believe that candidiasis needs to be treated with antibiotics - this is not true at all. Antibiotics are effective only against bacterial organisms, and thrush is a fungal infection.
The disease is treated with local therapy aimed at destroying pathogens and producing a bactericidal and disinfectant effect.
Medication method
"Stomatidin" . Quickly copes with mushrooms that have a yeast-like structure. You need to use the product to treat the affected areas 2 times a day.
"Candide" (solution) . The active substance destroys the membrane of fungi, completely destroying them and suppressing the growth of pathogenic bacteria. The course of treatment is at least 10 days. It is important to continue therapy for the recommended period, even if visible signs of the disease have disappeared.
Doctor's advice
If you observe hygiene products for your child, you should use baby products – soap, foam, etc. Regular soap is too aggressive - it easily washes away representatives of normal microflora from the baby’s skin, and the resulting niche can be occupied by a fungus. It is easy to transfer it from the skin to the oral mucosa - any household item, the hands of mother and child, things can contribute to this. The child should not be sterile, so there is no need to get carried away with the excessive use of even children's cosmetics.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist
"Diflucan". The drug can be used in newborns starting from the 11th day of life. Until the age of 1 month, the product is used only for intravenous infusion. This measure is usually a last resort and is used only when necessary.
"Nystatin" . Destroys fungal infections, relieves inflammation and does not irritate the baby's mucous membranes. The duration of use of the medicine is 7-10 days (at a dosage of 1 drop on each side). The drug is applied to a cotton swab, after which the inner surface of the cheeks is treated.
Brilliant green (green) . The use of brilliant green is very effective in the treatment of thrush in infants. A small amount of brilliant green should be applied to a cotton pad and thoroughly treated the inflamed areas. Usually two procedures are enough to completely solve the problem.
If you cannot treat the oral cavity with cotton swabs, you can apply brilliant green to the pacifier or pacifier. To achieve a therapeutic effect, 1 minute of active sucking is enough.
The safest drug is chamomile. Treatment with chlorhexidine bigluconate solution 0.05% is possible. To do this, moisten the cotton wool, wring it out and carefully wipe the affected area. Make sure that the drug does not flow from the cotton wool into the child’s throat. You can process 2-3 times per day. If the place is hard to reach, then instead of the mucous membranes of the mouth, you can wipe the pacifier before giving it to the child. 2-3 times a day. Peroxide solution should not be used to avoid burns.
Victoria Druzhikina
Neurologist, Therapist
Traditional methods
The following folk remedies are effective in treating oral thrush:
- Soda . After feeding, treat the baby's mouth with a soda solution (if the baby is bottle-fed, do the same procedure with the nipples).
- Tincture of calendula. Suitable for slow douching or local surface treatment.
- Chamomile decoction . Use a moistened cotton swab to treat the oral cavity several times a day (5-6 times).
What to do if your child is not eating well due to oral thrush
Thrush in a child's mouth does not always cause pain and tears. And small white spots on the mucous membrane are easy to miss. Can thrush go away on its own or will it develop into something more serious, how to feed and treat a child with thrush, says allergist-immunologist Tatyana Nikolaevna Dzyaduk.
— Tatyana Nikolaevna, what is candidiasis in a child’s mouth?
— Candidiasis in an infant is a fungal disease of the oral cavity caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (candida). Of all age groups of children, it occurs most often in infants.
— How is thrush transmitted from mother to child?
— Candida fungi enter the baby’s body when passing through the birth canal, from the nipple of the mammary gland, or from the hands of the mother and staff. True, several cases of a child becoming infected with thrush in the womb have been described due to a violation of the integrity of the membranes. Unfortunately, the intrauterine process leads to stillbirth or miscarriage.
Candida in single quantities is a normal resident of the microflora of the skin and mucous membranes, including the oral mucosa. But when actively multiplying, it causes a disease, which in newborns and infants up to one year is due to the immaturity of the immune system.
— Why does candidiasis more often affect the oral mucosa in children?
— Candida fungi attach well to the epithelium of the oral and vaginal mucosa, which is why candidiasis occurs more often on these organs. The most common fungal infections in young children are oral candidiasis and skin candidiasis in the diaper area and skin folds (diaper rash).
— How is thrush in children related to intestinal infections and acute respiratory infections?
— You can talk about oral thrush after taking antibiotics - this is a risk factor for the disease, but not a necessary condition.
| Dysbacteriosis (changed ratio of bacteria and fungi on the skin and mucous membranes) will lead to thrush if you give your child antibiotics: they will only kill bacteria. Space will be freed up for mushrooms, and they will begin to reproduce more actively. | Regurgitation itself does not in any way affect the presence or absence of thrush. But if the cause of regurgitation is gastroesophageal reflux disease, then its treatment can lead to candidiasis esophagitis - this is a lesion of the esophagus, and not the oral cavity. | Intestinal infections and acute respiratory diseases do not affect the development of oral thrush unless treated with antibiotics. |
— Can formula or breast milk cause oral thrush in a newborn?
— According to statistics, formula-fed children suffer from thrush somewhat more often than breastfed children. This may be due to the fact that breast milk contains substances that inhibit the growth of fungus.
The fungus can enter the baby's body from the mother's breast. Therefore, laboratory detection of fungal cells in breast milk or culture of breast milk is pointless; this will not affect the treatment tactics or the outcome of the disease. But the mother needs to be checked for candidiasis of the nipples during breastfeeding and, if necessary, undergo external treatment, since the presence of candidiasis of the skin of the nipple increases the risk of oral candidiasis in the child.
Prevention of thrush in newborns
To prevent thrush from returning, as well as for preventive purposes, you should follow simple rules:
- boil bottles, nipples and pacifiers if the child eats formula after each feeding;
- cleanse your baby’s skin daily using hygiene procedures;
- wash your hands before playing or interacting with the child, before feeding;
- pay enough attention to mother’s breast hygiene if the newborn receives mother’s milk as food;
- after feeding, clean the mouth with water or special products sold in pharmacies or children's stores (foam, solutions, etc.);
- strengthen the child’s immunity (long-term breastfeeding, hardening procedures, daily walks, massage, etc.);
- Toys should be washed at least once a week;
- monitor the condition of the baby’s intestines.
Thrush is an unpleasant phenomenon, but it is quite treatable, provided that therapy is started on time and carried out after consulting a doctor. Complications after suffering from candidiasis almost never occur, so preventive measures and close attention to the hygiene and well-being of the baby are quite enough to avoid relapses and re-infection.
To learn how thrush manifests itself in infants and how to get rid of it, watch the video:
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. https://www.antibiotic.ru/cmac/pdf/6_2_168.pdf
Rate how useful this article was
4.4 7 people voted, average rating 4.4
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Candidiasis in children: consequences
Like any sexual disease, candidiasis in a girl is fraught with disruptions to the reproductive system, which begins during intrauterine development. Before puberty, girls have very delicate genital mucosa, so even a mild form of infection can lead to fusion (synechia) of the labia and vagina.
Thus, parents should carefully monitor the general health of the girl and her external genitalia, and later, when the child is able to take care of herself, explain how to take care of herself.
Thrush in children: symptoms and types
Symptoms depend on the form and type of candidiasis:
- candidiasis (without symptoms and harm to the health of the carrier);
- acute and chronic forms;
- recurrent and persistent (complicated) forms;
- secondary candidiasis, which develops with non-fungal lesions of the genital organs.
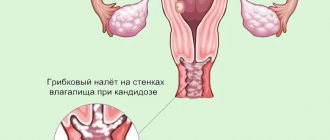
Vulvovaginal candidiasis (thrush, vulvar candidiasis) in children and adolescents is manifested by the following symptoms:
- itching and burning in the perineum (constant or worsening in warmth, in a hot bath, when walking and wearing the wrong underwear (too tight, synthetic, etc.);
- pain and burning when urinating.
As a result of constantly appearing signs, the child may develop a fear of taking a bath or urinating, as well as before sexual intercourse (in sexually active adolescents), up to severe nervous disorders.
In the acute form of thrush in children, the following occurs:
- hyperemia and swelling of the external genitalia and vagina;
- discharge (cheesy or creamy) with a sharp sour odor;
- in some cases, a grayish-whitish coating is observed on the walls of the vagina.
In the chronic form of thrush in children, the following occurs:
- less pronounced symptoms (itching, burning, redness, etc.), which may intensify before menstruation (in menstruating girls);
- less intense swelling and mild or completely absent plaque;
- changes in the skin of the labia and around the vagina.
If you notice symptoms of thrush in your child, you should urgently consult a doctor to undergo a course of treatment and prevent it from becoming chronic or recurrent.
Treatment of white plaque on a child’s tongue
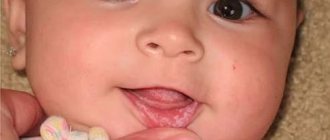
A white coating on a child’s tongue is most likely ordinary food debris. If it is not removed with a damp cloth and spreads to the mucous membrane of the cheeks, then this indicates the development of an infectious process.
Why does a white coating appear on the tongue of a baby during breastfeeding? As a rule, this is thrush - a fungal infection caused by yeast-like fungi belonging to the genus Candida. A white coating covers the baby's tongue and gums, the inside of the lips and cheeks. Thrush often occurs in children under one year of age. The reason is the immature immune system of infants. Thrush is a contagious disease, so to avoid it, bottles and pacifiers must be thoroughly sterilized. Older children also get thrush. Children with weakened immune systems and asthmatic children using inhaled corticosteroids are at risk. Treatment of white plaque on a child's tongue is carried out with local antifungal drugs. Important: medications should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor, since a similar picture may be a symptom of another condition in which antifungal drugs are not required. For example, diseases caused by the Coxsackie virus are often accompanied by the appearance of white “spots” on the tongue. In fact, these are painful ulcerations that disappear on their own within 3-5 days without any treatment. Therefore, if you find a white coating on your child’s tongue, you should consult a doctor and not self-medicate.
In infants, the surface of the tongue may be covered with a colored coating. How to treat a yellow coating on the tongue of a newborn depends on the condition that is accompanied by this symptom. For example, sometimes the tongue becomes coated with a colored coating from certain baby formulas. Just change your diet and your tongue will clear up. However, yellow plaque may also indicate problems with the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory infections. In these cases, treatment of the underlying disease is carried out.
Thrush in infants
Treatment of thrush in infants depends on the extent of the pathological process. In the early stages, with local damage, local therapy is indicated - irrigation of the oral cavity with anti-candidiasis (clotrimazole, nystatin), alkalizing (2% baking soda solution, 0.25% boric solution) and disinfectants (aniline dyes - Lugol's solution, methylene blue) agents. When breastfeeding, treatment of the mother's breast with a 2% soda solution and herbal infusions (oak, calendula and others) is indicated. Such treatment is carried out until the child recovers completely, but for a period of at least 14 days.
For moderate and severe forms, systemic therapy through oral or parenteral administration of antifungal drugs is recommended. When using anticandidal drugs orally, preference is given to powders for injection (fluconazole), since the prepared solution has not only a general, but also a local effect on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. In parallel, treatment of concomitant diseases and symptomatic therapy according to indications is carried out in full. According to modern recommendations, this approach should also be used for mild forms, since it allows reducing the treatment time to 3-6 days.
Forecast and prevention of thrush in infants
The prognosis for thrush in infants is favorable. With timely, rational therapy, complete recovery occurs within 7-10 days. Severe forms and the development of complications are observed only in the absence of antifungal treatment. Nonspecific prevention of candidal stomatitis consists of proper care of the child’s skin and mucous membranes, especially against the background of severe pathologies that reduce immunity. An important role is given to the rational use of antibacterial agents and the treatment of fungal diseases in the mother during the period of bearing a child.
Specific prevention of thrush in infants is necessary if there are indications, which include a complicated obstetric and gynecological history of the mother, prematurity and intrauterine malformations of the child, respiratory disorders, birth injuries of newborns, and pathologies of the central nervous system. Newborns included in this group undergo microscopy and bacteriology of samples of mucous membranes and feces during the first 7 days of life. For infants on antibacterial therapy, a prophylactic course of an antifungal drug, usually fluconazole, is prescribed.