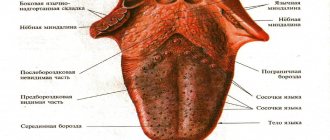
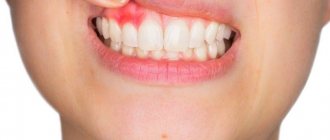
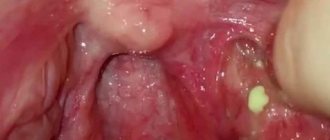
In the first months of a child’s life, every mother is especially sensitive and attentive to the baby’s health. The condition of the oral cavity is also a very important indicator.
Healthy gums in an infant should be smooth, without swelling and have a pale pink color. If any changes in their appearance appear, then this is a clear signal to show the child to the doctor. After all, there are many pathologies that can manifest themselves in the form of plaque, cracks or inflammation on the gums.
In this article we will look at why white plaque may appear on a baby’s gums and what to do in this case.
Plaque on the gums can be a symptom of various pathologies.
Why does white plaque appear?
Timely diagnosis allows you to quickly get rid of the problem.
White plaque on a child’s gums or on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity is a fairly common phenomenon and can occur in children of all ages, including newborns. There are quite a few reasons that provoke the appearance of white plaque on the gums.
Such a symptom can be a sign of both relatively harmless diseases and serious diseases, sometimes even having an oncological profile. Learn more about this in the video in this article.
But you shouldn’t worry too much about this, because most often, white plaque on the gums is easily treatable. The main thing is to notice the problem in a timely manner and show the baby to a specialist. The doctor will be able to quickly and accurately determine the nature of the pathology and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Important: Under no circumstances should you self-medicate if white plaque appears on your baby’s gums.
Stomatitis
Stomatitis can have a different nature.
If you notice a white coating on your baby's gums, one of the most common reasons for this is stomatitis. It is especially common in babies under one year of age, who, in order to explore the world with their own hands, pull into their mouths everything that comes their way.
Not all such objects are sterile; some of them may contain pathogenic bacteria, fungi or viruses, which can trigger the development of stomatitis.
Pathogenic microorganisms can be found on any object.
The incubation period of this disease is 4-8 days, after which the following symptoms are observed:
- weakness and drowsiness;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- increased body temperature;
- the appearance of a white or yellowish coating, white dots or spots.
If there is no treatment, plaque and white spots can degenerate into bleeding ulcers, which will cause particular discomfort.
The listed symptoms may manifest themselves to varying degrees, depending on the form of the disease:
| Type of stomatitis | Causes | Peculiarities |
| Most often caused by the herpes, measles, rubella virus. | First, bubbles form on the mucous membranes; after they burst, erosion appears, which is covered with plaque. |
| Contact with a sick person, caries, chronic diseases. | Redness of the area of the mucous membrane affected by bacteria, followed by ulcers. |
| Most often caused by fungi of the genus Candida. | It is characterized by white dots that grow and merge into a single white plaque. After its removal, bleeding erosions appear. |
| When there is local contact with an allergen, or when the allergen gets into the blood. | The mucous membrane becomes bright red, irritated and painful. |
| Caused by damage to the mucous membrane by high or low temperatures, chemicals, and various objects. | Redness, swelling and soreness of the mucous membrane in places of contact with the irritant. |
Stomatitis is not a dangerous disease, but it causes a lot of inconvenience and causes special discomfort. The child may become capricious and even refuse to eat completely. If stomatitis is not treated, ulcers appear, which cause severe pain to the baby. Therefore, at the first manifestations of such a pathology, you should immediately consult a doctor.
At the initial stage, it is not at all difficult to cope with this disease; the use of local anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antimicrobial drugs is sufficient. Medicines for stomatitis, which are most often used in infants, are presented in the photo.
Candidiasis
Candidiasis affects the gums, tongue and inner cheeks.
Another common cause of white plaque on the gums of babies is a disease such as thrush, or candidiasis. Its development is provoked by microscopic fungi of the genus Candida. These microorganisms are considered opportunistic.
This means that any healthy person has them, without causing any discomfort, and they exhibit their pathogenicity only under certain conditions:
- imbalance of normal microflora;
- stressful situations;
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- decreased immunity due to other diseases;
- infection through the birth canal of a sick mother.
Candidiasis can be either an independent disease or accompany other more serious diseases.
The causative agent of thrush is fungi of the genus Candida.
The main manifestation of thrush is a white coating on the child’s gums, as well as on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. This plaque consists of waste products of fungi and pseudomycelium. After removing the plaque, damaged mucous membranes are revealed, with bloody ulcers.
In addition to white plaque, candidiasis may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- burning;
- dryness;
- soreness;
- temperature increase;
- weakness.
Candidiasis is quickly treated with antifungal agents.
Thrush is easily treated with antifungal and antiseptic topical agents. Together with them, it is recommended to use drugs that help accelerate the healing of the mucous membrane.
It is important to understand that the earlier the disease is detected, the easier it is to get rid of it. The drugs that are most often used in infants to treat candidiasis are presented in the photo. But their independent use is unacceptable, since any drug has contraindications and side effects.
Important: The appearance of thrush or candidiasis in a baby is the reason for a thorough examination of the baby’s body for hidden causes of decreased immunity.
Calcium deficiency
A lack of calcium can lead to rickets.
Calcium is one of the most important microelements. Breastfed babies receive calcium from mother's milk, which is always adjusted in composition to the needs of each individual child, in accordance with his age.
But in some cases, the calcium in milk may not be enough, for example, if the mother is not eating well or has bad habits. In this case, the baby may develop hypocalcemia.
How does this pathology manifest itself:
- increased sweating;
- excessive hair rolling out;
- chin tremor;
- white plaque in the form of a film on the gums;
- flinching at sharp sounds.
Taking vitamin D3 is recommended by Rospotrebnadzor.
Important: Hypocalcemia can develop not only with insufficient calcium intake in the body, but also with a lack of vitamin D3, which is important for the absorption of calcium. Therefore, in the autumn-winter period, pediatricians often additionally prescribe this vitamin.
In the absence of timely corrective treatment, calcium deficiency can lead to very serious consequences that can no longer be completely cured. Therefore, it is very important to pay attention to the prevention of hypocalcemia and follow all doctor’s orders if this disorder is suspected.
Improper hygiene
It is important to observe the rules of oral hygiene from birth.
It is necessary to monitor the condition of the oral cavity from the very birth of the baby in order to prevent the development of pathological processes. Typically, in the first months after birth, when the baby is exclusively breastfed, no additional procedures are required to cleanse the oral cavity.
Wipes for cleaning the oral cavity.
But if parents notice a white coating on the child’s gums after eating or frequent regurgitation, then it is necessary to clean the oral cavity of such sediment daily to prevent the development of pathogenic microflora in it. To clean, you can use a gauze pad soaked in a weak soda solution, or purchase special baby wipes for the oral cavity.
The instructions for such hygiene products contain complete information on how to use them correctly. They are very convenient both for home use and on the road, and their price is quite affordable.
Other reasons
Sometimes plaque on the gums indicates diabetes.
The reasons listed above are among the most common pathologies accompanied by the appearance of white plaque on the gums.
But in rare cases, such a symptom may accompany more serious illnesses:
- HIV infection - transmitted from a sick mother to a child during childbirth, and it can also be acquired due to the negligence of doctors;
- Diabetes mellitus is very difficult to diagnose in children under one year of age; it is usually detected only when the level of glucose in the blood reaches critical levels. Therefore, it is important to know all the symptoms of diabetes in order to notice the problem at the initial stage;
- Gum cancer is more common in people over 40 years of age, but in very rare cases it can also appear in infants. In addition to white plaque, it manifests itself in bleeding and swelling of the gums.
Sometimes parents may mistake neonatal teeth for white plaque. They are extremely rare and most often doctors recommend removing them, because such teeth do not fully develop and will interfere with the eruption of baby teeth.
Treatment of gums in children
Medicines prescribed by a doctor have analgesic, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. They help restore the proper condition of the mucous membrane. Methods of using drugs are different, but the principle is the same: rinsing, irrigation.
For gum disease in infants, the dentist will prescribe special gels to relieve symptoms, namely itching and pain. Parents should pay special attention to cleaning their mouths from food debris.
Antibiotics are prescribed by a dentist in rare cases. Indications for the use of antibiotics is a form that reaches a complex (ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis) or chronic stage. Antibacterial or antifungal drugs are prescribed when the problem is caused by an infectious process, and the goal is to eliminate its causative agent.
Possible complications
The initial stage of the disease is easy to treat.
Most often, the initial stages of diseases accompanied by the appearance of white plaque on the gums proceed unnoticed. That is why there is a problem of early diagnosis of such a disease, which can sometimes be very serious.
In an advanced stage, this symptom causes severe pain in the child, and then even the most inattentive parent will notice the problem. But treating the disease at this stage is much more difficult and longer.
In addition, in the absence of timely and correct treatment, various complications may arise:
- dysbacteriosis;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- damage to internal organs;
- transition of the disease to a chronic form;
- diseases of ENT organs;
- development of sepsis, etc.
Such complications can arise not only due to lack of treatment due to late diagnosis, but also during attempts at self-medication, when parents may mistakenly believe that they are able to cope with the disease on their own, without the help of a doctor. But in the end, this only makes the situation worse.
Approximate timing of eruption of permanent teeth
The first of the molar permanent teeth to appear are molars (at the 6th year of life), located at the end of the dentition. But it is they who are most susceptible to caries, since there are deep depressions on their surface where bacteria accumulate due to poor cleaning and neglect of flossing.
The second molar appears 4-6 years later, when the child reaches 11-13 years of age. Incisors erupt at 6-8 years of a person’s life, canines - after 9 years of age.
Like newly emerged milk teeth, permanent teeth contain few minerals (a tenth of their amount in a mature adult). It is for this reason that it is important to teach a child proper hygiene. It wouldn’t hurt to treat your teeth with gels containing a large amount of fluoride once a quarter.
Prevention
To prevent oral diseases, regular examinations by a doctor are necessary.
It is important to understand that the fragile body of a newborn child is especially vulnerable. Therefore, you need to make enough efforts to prevent the occurrence of diseases, because then you will not have to deal with their treatment.
Oral health care includes, first of all, regular examinations of the baby's mouth for the presence of any formations, be it stains or plaque. If after eating a white coating appears on the child’s gums, then you need to try to gently clean it off with special means.
If you suspect the development of any disease, you should show the child to a doctor who will conduct an examination and establish an accurate diagnosis. After which he will be able to select the appropriate and most effective treatment.
Causes of gum inflammation in children
- Skipping or poor quality teeth brushing;
- Sucking dirty objects;
- Errors when installing seals;
- Pathologies of the dentition;
- Carious cavities with sharp edges;
- Bite correction;
- Breathing through the mouth;
- Abnormal structure of the oral cavity organs (attachment of the frenulum of the tongue and lips);
- Problems with the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Infectious diseases (ARVI, influenza);
- Hormonal abnormalities;
- Hereditary anomalies.
Questions for the doctor
Stomatitis during teething
My son is 10 months old. And from the very first tooth, which appeared at 7 months, before teething, all his gums are covered with a white coating. The child is in great pain, his temperature often rises, and he refuses to eat. Doctors prescribed a lot of things, but only Candide drops help. What else can you try to get rid of candidiasis once and for all?
During teething, a significant decrease in local immunity occurs, which is why other pathological conditions often develop against the background of this process. In order to reduce the risk of recurrence of thrush in a child, you need to pay maximum attention to strengthening his immunity: good nutrition, frequent walks in the fresh air, drinking plenty of fluids and maintaining cool, moist indoor air.
White plaque during breastfeeding
Today I noticed a white coating on my child’s tongue. The baby is only 2 months old and is breastfed. The coating is only on the tongue, the palate, cheeks and gums are clean. I tried to clean off this deposit with gauze soaked in boiled water, and everything went away without a trace. How can you tell if it’s thrush or if you shouldn’t worry?
Most likely, your baby has plaque from breast milk. This is normal and does not require any treatment. If the plaque is easily and completely cleaned off, and the child behaves as usual and does not refuse food, then this is not candidiasis. Continue to monitor your child's oral health and take your child to your pediatrician if necessary.
Cholisal for a child up to one year old
My daughter is 9 months old and recently developed stomatitis. The doctor prescribed smearing the ulcers with Cholisal gel for pain relief, because they bother the child very much. But I read in the instructions that it should not be used on children under one year of age. What can replace this drug?
Cholisal gel has proven itself and is often used to alleviate stomatitis, including in children under one year of age. The instructions for this drug actually indicate that it can be used in children from 1 year of age. But as prescribed by a doctor and with caution, use in children under one year of age is also allowed. It is important not to use the drug in children of this age without a doctor’s prescription.
Treatment of children at RAIDEN
In the RAIDEN network of dental clinics, the treatment and prevention of oral diseases of young patients is treated with the utmost attention and reverence - the health of the younger generation is very important to us!
All medications used in our clinic meet the highest quality requirements. Before using them, we conduct a blood test of the baby to determine drug tolerance. The safety of your children, our little patients, is paramount to us.
Clinical manifestations of the disease
Each of the clinical forms has its own typical manifestations and features of the course of the disease.
The following symptoms of gingivitis in children are distinguished:
- Catarrhal - this form appears in babies at the time of teething (by 1 year) or their change. They experience swelling and soreness of the mucous membrane. They intensify when eating spicy and hot foods. There is also bleeding, itching of the mucous membranes, and bad breath. Upon examination, a loose, thickened mucous membrane is revealed, its color changes to purple with a bluish tint. Low-grade fever and general malaise are noted.
- Hypertrophic – refers to chronic forms. It is divided into edematous and fibrous. The edematous form is manifested by swelling, bleeding, itching, and pain. Fibrous tissue is characterized by a pronounced proliferation of gingival tissue. Upon examination, gum hypertrophy is revealed, it hangs over the crown, partially covering it. The mucous membrane is loose, edematous, and false gum pockets are formed. There is plaque in large quantities. This option is more common in teenagers.
- Ulcerative – is a complication of catarrhal gingivitis. It is characterized by ulcers on the mucous membrane, covered with a grayish-greenish coating. There is an increased viscosity of saliva. The patient's mouth has a putrid, unpleasant odor. There is a deterioration in the general condition, there are signs of general intoxication, decreased appetite, and disturbed sleep.
- Atrophic – its development is possible due to defects in orthodontic treatment, anomalies in the location of the frenulum. There are no signs of inflammation. Dystrophy of the gingival tissue progresses, and the necks of the teeth are exposed. There is an increase in reaction to temperature changes.
With all these forms, the baby is capricious and refuses to eat.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of gingivitis is established by a pediatric dentist or periodontist based on an examination of the oral cavity, due to the characteristic clinic. All forms of pathology have characteristic signs.
They are:
- the presence of soft deposits or tartar;
- the presence of gum inflammation;
- there are no gum pockets;
- dentogingival connections are preserved.
X-rays are performed to confirm the diagnosis. Changes in the jaws are not detected. Numerous concomitant diseases are detected (malocclusions, caries, abnormal attachment of the frenulum of the lips and tongue), filling defects. To find the causes of the pathology, consultations with a cardiologist, endocrinologist, or therapist are prescribed.