A young mother tries to notice the first signs of any disease in her baby, so she closely looks at every fold and spot on the baby’s skin. Many parents have encountered such a phenomenon as a white coating on the tongue of a baby. In most cases, this is considered normal, but there are exceptions in which you need to consult a doctor. What factors need to be considered? Why does my baby have a white coating on his tongue? First of all, it is important to understand the baby’s nutrition: whether he drinks breast milk or is fed a special baby formula.
White coating on the tongue of a baby during breastfeeding
Mother's milk is not as rich as formula, so in the first months the baby may nurse almost every 30 minutes. Due to the constant presence of milk in the mouth, a baby may have a coating on his tongue throughout the day, and this is absolutely normal. Until approximately 3-4 months of life, the baby's salivary glands are underdeveloped and do not produce enough saliva. This is why a white coating forms on the baby’s tongue.
There is no need to clean off such a coating on a baby’s tongue; it does not bother the baby at all and does not cause discomfort, because it is ordinary mother’s milk, which does not have time to be washed off the tongue. When the baby’s condition is normal, he is cheerful, cheerful and actively suckles at the breast - there is no reason to worry.
White coating on the tongue of a bottle-fed baby
Formula-fed babies, like infants, eat very often in the first months of life and are thus constantly in contact with milk. Residues from such food may remain on the baby's tongue and cause plaque to form. However, in such children, the plaque should disappear 1-2 hours after feeding, since the intervals between meals are slightly longer than when breastfeeding.
The deposits from milk or formula are easily washed off with water, so you can do a little experiment. Invite your baby to drink water from a bottle or spoon (it should wash away most of the plaque), but if this does not happen, then you better contact your pediatrician. The doctor will be able to find out the cause of the white plaque in the baby and prescribe appropriate treatment. What else can cause deposits in a baby's mouth?
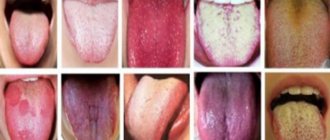
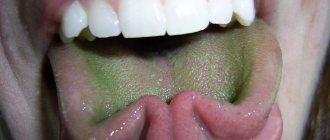
Natural color of the tongue in a healthy child
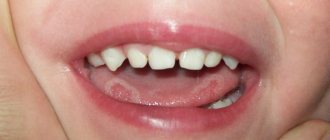
There are many cases when light-colored accumulations on the uvula do not require treatment. For example, during the examination in the morning, the mother may notice light deposits in a small amount. They are easy to clean off and are considered normal. At 1 year of age, such plaque is also diagnosed. These are often milk traces from mother's milk or its substitutes. Therefore, a thin light film is quite acceptable. But the natural shade of the surface of the tongue should be visible through it.
In healthy children, the color of the muscle organ is pale pink. At the same time, it must be mobile, all movements must be made unhindered and without difficulty. The condition of a child's tongue is significantly affected by humidity levels, as well as the temperature in the room where the baby is. For self-diagnosis, the mother needs to conduct visual examinations of her child’s oral cavity. Cleaning the baby's mouth is also necessary. First, this is done using special pharmaceutical wipes, and when the child grows up, a children's brush with a surface for treating the tongue is used.
Causes of white plaque on a child’s tongue
Let's find out the opinions of professionals. What does Dr. Komarovsky say about plaque on the tongue in infants? Like most doctors, he identifies the following reasons:
- dysbacteriosis and gastritis;
- stomatitis;
- intestinal dysfunction;
- other pathologies.
Every mother should arm herself with recommendations that will help her prevent a similar condition in her child. After plaque has already appeared, be sure to consult a doctor who can determine the exact cause of its appearance and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Self-medication precautions
When choosing methods for self-treatment of oral thrush in a baby, you need to understand that sometimes such procedures may not correct the situation, but on the contrary, harm the child.
For example, improper use of soda solution when treating the oral mucosa can cause additional injuries. Therefore, carefully prepare the soda solution, not exceeding its concentration more than 1-2%, because a stronger concentration leads to a burn to the mucous membrane.
You can complicate the situation with candidiasis by using a honey solution. After all, beekeeping products are one of the most powerful allergens, so when using them you need to be absolutely sure that there is no allergic reaction.
In addition, when using herbal infusions, do not use several herbs at the same time. In this case, if an allergy suddenly arises, you will know which plant caused it.
Similar folk recipes can be used when treating an older child, but it is better not to experiment with the baby’s health. If the situation is urgent and you cannot see a doctor today, it’s better to play it safe and call an ambulance. At your appointment at the clinic, your doctor will prescribe medications to combat the fungal infection. When treated with medications, you can avoid additional risks, and candidiasis will go away faster.
Maybe it's thrush?
Thrush, or candidiasis, is an infectious disease caused by fungi (Candida). Doctors often use the term “candidiasis” and claim that most children under one year of age suffer from this disease. The appearance of thrush most often manifests itself in the first 3 months of a child’s life, since during this period of life his oral cavity is not yet populated by healthy microorganisms, and the immune system, alas, is not strong enough.
What is the cause of plaque on the tongue of a baby at an older age? It happens that the immune system does not work properly and a fungal infection appears in the child's mouth or cheeks. Against the background of reduced immunity, for example after a respiratory viral infection, the risk of developing thrush increases.
Fungal infection
The development of thrush in the child’s mouth occurs as a result of the growth of Candida fungi. Intensive reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms occurs as a result of the influence of various factors.
Often babies become infected with thrush during childbirth, crossing the birth canal
These include:
- Weakened immune system.
- Dysfunctions of the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Hormonal disorders.
- Conducting antibacterial therapy.
- Excessive dryness of the oral mucosa.
Infection with Candida fungi occurs under the following conditions:
- In utero. Infection can occur through the placenta, umbilical cord and amniotic fluid.
- During childbirth. Often babies become infected with thrush during childbirth, crossing the birth canal. Therefore, it is important for women to exclude the development of thrush, especially in the last stages of pregnancy.
- Finding a child in a hospital and maternity hospital. Inappropriate and non-sterile care of the child contributes to the child becoming infected from health care workers.
- Poor sanitary conditions at home. Babies are born with a weakened immune system. Therefore, keeping a child in an unsterile home environment promotes the penetration of various microorganisms and bacteria into his body.
Diagnosis of candidal glossitis involves a complete collection of anamnesis data and conducting various types of comprehensive research.
Important! In most cases, when diagnosing thrush in a child, an instrumental examination is not performed.
For these purposes the following is carried out:
- Microscopic examination of the oral mucosa by taking a scraping from plaque and then examining it under a microscope. This allows you to determine the presence of Candida mycelium threads and yeast-like cells.
- Bacteriological research. Allows you to identify the type of Candida fungus and the number of its colonies. Sowing mushrooms on a nutrient medium helps install the most effective antifungal drug. This is necessary, since many medications have different effects on grown fungal colonies.
- Serological study. It is carried out if necessary to study antibodies that are concentrated in the blood serum.
The difference between thrush and milk plaque
How to determine the cause of plaque on the tongue of a baby? If a person does not have the opportunity to see a doctor or a frightened mother cannot wait to determine the nature of the plaque, then simply try to wash it off with water. If the situation has not cleared up, perhaps the child does not want to drink water (this happens to children in the first weeks of life), do not worry, there is another simple way to determine the cause of plaque. Try to gently remove the plaque from your baby's tongue with clean hands or a cloth. The fact is that plaque from thrush cannot be removed so easily, and in those places where you still manage to clean the child’s tongue, you may notice a bleeding surface. This sign is considered an undeniable symptom of thrush, and your child needs urgent treatment.
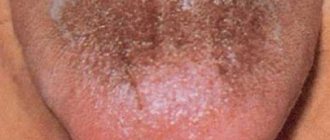
What does thrush look like in a child?
Any part of the oropharynx can be affected: tongue, lips, corners of the mouth, gums, mucous membranes of the cheeks, palate, pharynx, tonsils. White grains (spot coating) appear, reminiscent of curdled milk, or a film (solid coating) of a cheesy appearance. These elements are easily removed by scraping with a spatula, revealing a bright red base, sometimes with a bleeding surface. As a rule, the course of the infection is painless and has only local manifestations. General health is not affected.
The influence of thrush on the child’s condition
With candidiasis, the baby’s general condition worsens, he becomes capricious, lethargic and refuses to eat. Candida spots in the mouth cause severe discomfort to the baby; sucking the breast or bottle becomes painful for him, and because of this he constantly cries. In rare cases, there is an increase in body temperature, as with a cold, sometimes it reaches 39 degrees.
Candidiasis rarely affects only the tongue. Usually the entire oral cavity becomes covered with white spots, even the area around the mouth can be affected by the fungus. When the baby eats, the plaque peels off and disappears for a while, and the inflamed mucous membrane of the mouth is visible.
Treatment of spots, circles and dots on the tongue
When spots appear on a child’s tongue, consultation with a specialist is required, a full examination of the baby’s body, identification of the pathogen (if the disease is infectious), exclusion of dangerous pathologies: scarlet fever, neoplasms, as well as fungi and viruses. Therefore, all home therapy methods come down to alleviating symptoms:
- eliminating itching, burning and pain;
- temperature decrease above 38 °C;
- removing the initial plaque.
In this regard, antipyretic drugs, non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs and mild painkillers are good. If you suspect an allergic reaction, you need to give your baby antihistamines.
In addition to pharmaceutical products, before contacting a doctor, you can use a chamomile decoction (2 tsp per 200 ml of hot water) or a soda solution (2 tsp per 250 ml of water).
Conservative treatment depends on the diagnosis made by the doctor:
- Stomatitis. The therapeutic course consists of a diet, rinsing the mouth with herbal decoctions, local treatment of the mucous membrane with healing, antiseptic agents, and drugs aimed at eliminating the pathogen: antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral.
- Herpes. Treatment of the affected mucosa with antiviral gels, ointments, diet, taking medications to strengthen the immune system.
- Candidiasis. Treatment of fungal-affected areas of the oral mucosa with antifungal drugs (Candide), rubbing and rinsing with soda, taking medications to increase immunity.
If the cause of the appearance of plaque, red, whitish or other spots on the child’s tongue is an internal disease, it is necessary to direct all efforts to eliminate it.
How to treat candidiasis in a baby?
Typically, your pediatrician should prescribe antifungal medications to treat oral thrush. Infants are given convenient dosage forms (syrup or solution) that should be used to lubricate the tongue and oral mucosa. The duration of treatment for plaque on the tongue of an infant depends on the degree of the disease, but is usually within 7-10 days. Feeling better occurs within 3-4 days.
The oral cavity is cleansed, and the child can begin to eat milk with renewed vigor, and then sleep peacefully. If it seems to you that the baby’s condition has returned to normal, this does not mean that you need to stop treatment. Candidiasis is a very persistent disease, and if you stop taking medications, the plaque and spots will definitely return. In this case, the fungus will become resistant to previously used drugs, and a new, most likely aggressive, treatment will have to be prescribed.
Treatment of candidiasis
The main method of treating the disease is the use of local antifungal and antibacterial agents, as well as antibiotics. Antimycotic (antifungal) drugs can not only eliminate the symptoms of the disease, but also destroy the fungus in the oral cavity, as well as in other organs and tissues. For this purpose, antibiotics of the polyene series (levorin, nystatin, etc.), as well as clotrimazole, econazole and other imidazoles, are used. Fluconazole, Diflucan, and Nizoral also have a pronounced antifungal effect.
A significant part of antibiotics has a number of side effects and has a negative impact on the immune system. Therefore, when treating children, antibiotics are used only in the most severe cases, as well as in cases where there is a risk of complications and generalization of the process. At the initial stages of the disease and with a mild course of the disease, preference is given to local remedies. We recommend using ASEPTA series rinses, which contain chlorhexidine and other active ingredients that have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. To remove plaque, you can use special ASEPTA Baby wipes. The individually packaged finger wipe is made of hypoallergenic materials and allows you to carefully clean the mucous membranes without the risk of damaging them or causing additional infection. It is also recommended to regularly treat the oral cavity with Lugol or silver solution. This procedure must be repeated every three hours.
For the prevention and treatment of candidiasis in children, diet and oral hygiene are also of great importance. It is recommended to exclude or strictly limit the amount of food containing simple carbohydrates - these are, first of all, confectionery and flour products. Make sure your child brushes his teeth regularly - it is best to use a special toothpaste for this, for example - ASEPTA Baby, Kids, Teens. The components contained in these pastes help prevent caries and, as a result, reduce the infectious load on the child’s immunity.
Prevention of tongue thrush in infants
Do not forget about preventive measures to prevent the formation of candidiasis in the baby’s mouth. It is important to regularly ventilate and humidify the air in the room. Do not forget about the importance of walks in the fresh air, after them the baby’s sleep normalizes and the immune system is strengthened.
If a child is fed artificially, then you need to thoroughly wash all the items necessary for feeding (bottle, pacifier), and even the pacifier. When breastfeeding, it is important for the mother to monitor her health and not eat a lot of sweets, which can provoke active reproduction of the Candida fungus. There is no need to wash or wipe your breasts with antiseptic agents. The Candida fungus is present in the body of every person, and the further development of the infection depends only on the state of immunity.
Frequent washing of the mother's breasts can dry out the skin, resulting in the formation of microcracks, which are the main factor contributing to the appearance of thrush in the baby. If you are not sure about the cause of thrush in your child, consult your doctor for help. A competent pediatrician will prescribe the optimal treatment specifically for your case. If you determine the cause of the white coating on your baby’s tongue in time and complete the prescribed course of treatment, the likelihood of complications will be minimized.
Treatment of thrush
The main task of effective therapy for white fungal plaque in infants is to identify and eliminate the main causes that provoke its formation. The use of local therapy, in the form of treating the oral cavity and lesions with antifungal agents, can be effective only at the initial stage of the development of pathology.
Traditional medicine, which can be safely used independently at home, is also considered effective in the fight against this disease.
Among them, the greatest therapeutic effect is exerted by:
- Bee Honey. It is mixed with water in a ratio of 1:2 and the resulting solution must be treated with the affected oral mucosa. To enhance the antibacterial effect, you can add 2 g of turmeric or flax seeds.
- Baking soda. The solution for wiping the tongue is prepared using 250 ml of warm boiled water, in which 5 grams of the main raw material is dissolved. This composition must be treated (wipe) the oral cavity.
When removing plaque, you should strictly follow the basic rules of this manipulation and precautions:
- Only a sterile bandage is used, which is changed after each wipe.
- Control of the strength and intensity of pressure.
- Strict adherence to the concentration of the soda solution.
- Preliminary testing for allergies and tolerance to the main component.
- The frequency of manipulation is every 2 – 4 hours, but no more than 6 times per day.
- The duration of treatment should not exceed 5 days.
Cleaning your baby's tongue with a sterile bandage soaked in soda solution
At an advanced stage of development of candidiasis, drug therapy is required for both the child and the mother, especially if the child is breastfed.
In severe forms of the pathology, depending on the age of the child and the stage of thrush, the following are prescribed:
- Immunostimulants.
- Antifungal drugs.
- Vitamin complexes.
Important! Self-medication of thrush in infants is strictly prohibited. The intake of traditional medicine and medications should be carried out strictly as prescribed by the doctor, in compliance with the dosage and schedule. If the slightest side effects occur or there is no recovery dynamics, treatment adjustments are also carried out by the pediatrician.
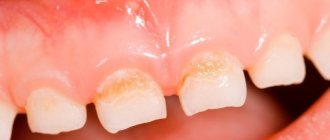
Causes of yellow coating on a child’s tongue
The appearance of a yellow coating on a baby's tongue can seriously frighten parents. If such plaque lasts for a long time and looks like a thick dense mass, and at the same time a sharp, unpleasant odor is felt from the baby’s mouth, then this is a sign of a serious illness. Do not forget that the tongue is one of the organs of the digestive system, and changes in its color may indicate diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (pancreatitis, hepatitis, colitis, cholecystitis, gastritis).
Pathological changes in the digestive system are accompanied by a decrease in the child’s appetite, stool disturbances, and the baby’s crying (due to abdominal pain). There are other reasons for the appearance of a yellow coating on the tongue in an older child:
- overeating (the child may have eaten too much fatty food, resulting in nausea, dry mouth and a yellow coating on the tongue);
- infectious disease (infection is accompanied by high temperature, which provokes the formation of a yellow-brown coating, you can also notice bleeding wounds on the tongue);
- poisoning (in this case, liver function is disrupted, the body becomes intoxicated and dehydrated, which leads to the appearance of plaque);
- jaundice (the tongue itself and the mucous membranes of the mouth become stained);
- local inflammatory processes in the child’s mouth (caries, sore throat, gingivitis, stomatitis, glossitis);
- somatic diseases (autoimmune processes, diabetes mellitus and kidney disease).
Causes of oral thrush in newborns
How can Candida fungi get into a baby’s body?
- infection can occur during the mother’s pregnancy if she suffers from genital candidiasis on the eve of childbirth: during the birth process, a fungal infection enters the placenta and amniotic fluid, and then into the newborn’s body;
- a baby can also become infected from a nursing mother if her nipples are affected by a fungal infection;
- when a child is bottle-fed or sucks on a pacifier, it, as well as bottles and nipples, must be treated in a sterilizer or boiled water before giving it to the newborn; unsterile nipples can cause bacteria to enter the oral cavity;
- the fungus can live not only on the mucous membrane, but also on the skin of the hands, from where it can easily migrate to the skin of the child if he is cared for by a person affected by thrush;
- The fungus can also be found in pet hair, dust, raw vegetables, meat or milk, so after contact with all these “transmitters” of bacteria, you must wash your hands thoroughly before touching the newborn;
- treatment with antibiotics can also disrupt the natural balance of the body's microflora; as a result of antibiotic therapy, candidiasis occurs in mother and baby who did not take medications containing “beneficial” bacteria along with antibiotics;
- candidiasis can occur if the mother has not learned how to properly attach the baby to the breast during feeding; the child may swallow too much air when sucking and, as a result, often burp; under such circumstances, most of the dairy food can remain in the child’s mouth, giving rise to fermentation processes and promoting the proliferation of fungi.
- thrush often develops in premature babies because their immune defenses are still too weak;
- candidiasis during artificial feeding can affect the baby due to the fact that he does not receive substances from mother’s milk that suppress the growth of fungal microflora;
- if the mucous membranes in the child’s mouth often dry out due to too dry air in the room or thirst, then such situations can contribute to the development of thrush;
- if the child’s immunity is reduced due to illness, poor sleep, lack of vitamins, then this can also cause fungi to multiply;
- candidiasis can also have a chronic form: in this case, it is often caused by serious illnesses in the child - diabetes, leukemia, HIV.