Thrush is an inflammatory disease of the genitourinary system of a fungal nature. It most often occurs in women in the form of vaginal candidiasis. It manifests itself as cheesy or creamy white discharge from the vagina, burning, itching and redness in the genital area, pain during intimacy and during urination. Treatment includes local and systemic use of drugs with antimycotic effects, as well as correction of immunity.
Urogenital candidiasis is a common infectious disease. Thrush occurs mainly in women of reproductive age. In men who are sexual partners of such patients, candidiasis balanoposthitis may occur. A child becomes infected with a fungal infection from a sick mother during childbirth.
Causes
The disease is caused by microorganisms of the genus Candida.
They are part of the opportunistic microflora that constantly lives on the skin and mucous membranes of humans. However, with decreased immunity or hormonal imbalance, fungi begin to actively multiply, suppressing the growth of beneficial bacteria and causing an inflammatory response. The following factors can cause thrush:
- diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction);
- excess weight;
- diseases of the female reproductive system;
- disturbances in the state of the microflora of the mucous membrane of the external genital organs;
- taking antibiotics, hormonal drugs, drugs with cytostatic effects, immunosuppressants;
- radiation and chemotherapy;
- use of tight clothing, underwear made of synthetic fabrics;
- rare change of sanitary pads;
- intrauterine contraception - vaginal diaphragms, douching, spermicides;
- use of intimate deodorants, scented pads and tampons.
An exacerbation of the disease often occurs on the eve of menstruation and after significant stress. Diet is also important - consuming large amounts of carbohydrates contributes to the development of fungal infections.
Baking soda in the fight against thrush
Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate/bicarbonate, sodium bicarbonate) has many beneficial properties that are of particular importance in the fight against thrush.
- It does not cause disruption to the microflora in the mouth and has a gentle effect on the mucous membrane, which is especially important when treating newborns.
- Creates an environment that has a detrimental effect on yeast fungus. It needs a sweet and sour environment to develop. Sodium bicarbonate alkalizes the body and restores acid-base balance. As a result, all pathogenic microflora die.
- Dries out the mucous membrane. Due to its physicochemical properties, sodium bicarbonate gives a good drying effect. This helps to quickly relieve itching and other unpleasant sensations in the mouth. After soda treatment, a protective environment is formed on the surface of the mucous membrane, preventing the growth of infection.
- This is a natural, safe remedy. Pregnant and young mothers can safely use soda without fear of negative effects on the body. It is also safe for infants when treating the oral mucosa (subject to precautions).
Classification
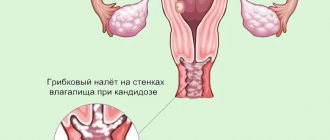
Vaginal candidiasis occurs in acute or chronic form.
In the latter case, the symptoms are less pronounced, but the disease has a long course and is more difficult to treat. Chronic thrush can be recurrent, with frequent exacerbations, and persistent, when episodes of deterioration are rare and associated solely with the provoking factor. The formulation of the diagnosis also specifies whether urogenital candidiasis is complicated or uncomplicated, depending on the number of exacerbations of the disease over 12 months and the severity of its manifestations. The congenital form of thrush is observed in children infected during childbirth from a sick mother. Candidiasis of newborns most often affects certain areas - eyes, mouth, respiratory tract, lungs, skin, but fungal sepsis cannot be excluded when a large amount of the pathogen enters the blood.
How to properly treat a baby’s tongue with soda
Attention! When preparing a soda solution for treating a child's tongue, it is extremely important to observe the proportions. Too concentrated a liquid can cause a burn to the baby’s delicate mucous membranes.
- Add 15–20 g (1 level teaspoon) of soda to a glass of boiled water, mix thoroughly and let it completely dissolve in the hot liquid (this is necessary so as not to harm delicate tissues).
- Wash your hands well with running water and soap. Dry.
- Wrap your index finger in gauze or wrap it in a cotton pad and soak it in the solution. Check that it is not too hot. Squeeze out excess.
- Using gentle progressive movements, remove plaque from the baby’s tongue.
- Do this procedure up to 5 times a day, for at least 7-10 days.
For children under 2 years of age, this is the only safe and effective way to clean plaque from a child’s mouth. Mechanical cleaning is prohibited as it is too traumatic.
How to bury soda in the ears to remove wax plugs for children and adults.
Symptoms
The acute form of vaginal candidiasis has a clear clinical picture.
A woman is worried about intense itching, burning in the genital area and near the anus, pain when urinating, during intimacy, discharge from the genital tract of a white or yellowish color with a cheesy consistency and a sour odor. The latter can be abundant or adherent in moderate quantities on the mucous membrane of the vulva, in the posterior and lateral vaults of the vagina. Also in the affected area there is redness, swelling of the tissues, and possible cracks in the skin and mucous membranes. With persistent thrush, the symptoms are less pronounced. There may only be itching and discharge in small quantities, appearing, for example, only on the eve of menstruation. Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis may be accompanied by striking manifestations during exacerbations. They leave dryness, atrophy, and lichenification on the skin and mucous membranes.
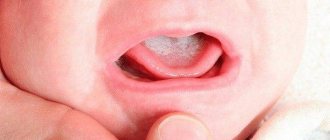
In newborns, thrush is often accompanied by damage to the oral cavity and tongue. A white coating appears on the mucous membrane; when you try to remove it, areas of redness and swelling are found underneath it. A child suffering from candidiasis from birth is capricious, and has sleep and appetite disturbances.
Thrush in men manifests itself in the form of candidal balanoposthitis and urethritis. The disease is accompanied by burning and itching, redness, and swelling in the area of the head of the penis. It may cause rashes, often covered with a white coating, and cracks. Just like in women, sexual intercourse and the process of urination become painful.
How to determine if a newborn has candidiasis
This will not be difficult, since the hallmark of thrush in the mouth is the appearance of a white coating that can cover the tongue, gums, inner surface of the cheeks, palate, tonsils, and tonsils.
Thrush spreads to the back of the pharynx in the absence of the necessary therapeutic measures. In very rare cases, the fungus can affect the baby's esophagus and even intestines.
A specific coating, similar to semolina grains (in advanced cases, it can resemble particles of cottage cheese) is the primary sign of thrush.
There are also secondary symptoms that usually appear simultaneously with the main symptom of the disease:
- poor appetite (refusal to breastfeed or bottle);
- crying during feeding;
- sleep disturbance at night;
- general malaise;
- moodiness and irritability;
- redness of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, wounds and ulcers;
- an increase in temperature to 37-38 degrees (in cases where a bacterial infection is associated with a fungal infection).
The appearance of such symptoms is a reason to call your local pediatrician or consult with a pediatrician online.
Diagnostics
A gynecologist diagnoses and treats thrush in women. If candidal balanoposthitis appears, you should seek help from an andrologist. During the patient’s initial visit, the doctor clarifies the nature of the complaints, the duration and frequency of appearance of signs of thrush, and conducts an external examination of the genital organs. Next, the patient is prescribed laboratory tests:
- a smear from the mucous membrane of the genital organs followed by a microscopic examination of the biomaterial;
- cultural seeding to determine the species of the fungus and its sensitivity to antimycotic drugs;
- detection of pathogen gene material by PCR.
In order to clarify the predisposing factors that contribute to decreased immunity and hormonal disorders, the following is carried out:
- clinical blood test;
- determination of antibodies to HIV;
- blood test for the content of important microelements and vitamins;
- analysis of blood glucose and carbohydrate metabolism metabolites.
For the purpose of differential diagnosis, it is possible to conduct other tests, and if necessary, consultations with other specialists are prescribed - a therapist, gastroenterologist, dentist, immunologist, endocrinologist, infectious disease specialist.
Artificial feeding, what measures to take
Attention! Infants who are bottle-fed are more susceptible to candidiasis than others. Therefore, they must be surrounded with special care. Parents should pay increased attention to caring for their baby's oral cavity.
The fact is that the mixtures contain sugar, which promotes the growth of fungal colonies. In addition, the remains of baby food stick to the roof of the mouth, which causes a lot of unpleasant sensations with oral candidiasis.
Be sure to give your baby boiled water after each feeding. 2-3 tsp is enough. liquids to wash away food debris from the mucous membrane. This will stop further growth of the fungus.
Treatment
Since fungi of the genus Candida belong to the opportunistic flora, treatment is required only in cases of vaginal candidiasis or balanoposthitis proven in laboratory studies, which have characteristic symptoms.
In case of uncomplicated course of the disease and early contact with a gynecologist, it is possible to prescribe only topical medications - vaginal suppositories and tablets for thrush, antifungal ointments, creams. In case of their ineffectiveness, as well as in case of chronic urogenital candidiasis, systemic antimycotics are prescribed - fluconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole.
Drug therapy for thrush during pregnancy is limited to topical antimycotic drugs for intravaginal administration. Children are prescribed systemic antifungal agents for thrush in a dosage adjusted based on body weight.
Local and general drugs are also used to treat balanoposthitis. To achieve greater effect from the use of ointments and creams, the head of the penis is first washed with a weak soda solution. If a man has a regular sexual partner, she also needs to undergo an examination by a gynecologist and, if necessary, a course of antifungal therapy, since infection with thrush is possible during intimate intimacy.
Soda rinses for older children
When the child is old enough to rinse his mouth on his own (this usually happens at the age of 1.5–3 years), he can use the soda solution himself to fight thrush.
- Add 2 tsp to 1 glass of water at room temperature. soda and mix well.
- Your fidget should thoroughly rinse the mouth with the resulting solution, spitting out the liquid each time. One rinse should last at least 30 seconds.
- The procedure should be repeated 3-5 times a day.
Prevention
Prevention of thrush consists of maintaining immunity, eliminating factors that provoke its decline or hormonal imbalance.
It is important to use antibiotics reasonably and only as prescribed by a doctor, and after completing the course of treatment with such drugs, restore the microflora with pro- and prebiotics. The following measures will also help to avoid the development of fungal infections:
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- timely treatment of endocrine and urogenital pathologies;
- normalization of weight and nutrition;
- use of barrier contraceptives;
- having a permanent sexual partner;
- wearing underwear made from natural fabrics;
- refusal of scented personal hygiene products, intimate deodorants, and douches.
Stages of the disease
The disease begins at a mild stage, when reddish spots are barely visible on the mucous membrane, soon giving way to a cheesy white coating. At this stage, the child does not feel much discomfort, and the infection itself is easily treatable. If treatment is not carried out, then thrush enters the middle stage, when spots and plaque merge and form islands that fill almost the entire oral cavity. At this stage, when trying to clean the plaque, bleeding ulcers appear. The child becomes restless, especially during sucking. In the severe stage of thrush, bleeding increases and quite intense pain appears. Fever often develops and bowel movements are disrupted. It is advisable to treat this form of thrush in a hospital setting.
According to the course of the disease, acute and chronic forms are distinguished. The acute form is more common, and the chronic form is usually a companion to other diseases. In the acute form, the plaque is white, cheesy, with a tendency to expand the affected areas up to the corners of the mouth. In addition to discomfort, the child may experience increased temperature, enlarged and painful lymph nodes (usually submandibular). For diagnosis, the doctor will take a scraping of the plaque and, upon examination, will find in it epithelial cells, food debris, fibrin fibers and, of course, the pathogen itself.
In the chronic form, the coating is yellowish or brown and more dense. Touching the affected mucous membrane causes severe pain. There is swelling around the lesion, and nearby lymph nodes are also enlarged. As with the acute form, the child’s behavior changes - older children complain of pain when eating, and infants become whiny and restless. This form is difficult to treat, so it is important to prevent acute thrush from becoming chronic.
Complications from thrush are usually associated with disruption of the digestive tract and respiratory system, however, there is a risk of developing diseases of other organs. If adequate treatment is not carried out in time, thrush can develop into a chronic, recurrent form.