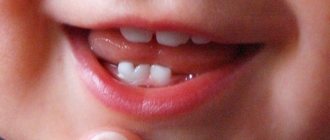
When the gums become inflamed, swollen and bleed, even if the symptoms are very mild, we can talk about a disease such as gingivitis .
Unfortunately, there is nothing special about such a diagnosis, since healthy periodontal tissue is found in only three percent of our fellow citizens. We are accustomed to ignoring minor manifestations of this disease, but it can lead to damage to deeper tissues, after which the process becomes irreversible. When gingivitis develops into periodontitis, doctors can only stop the disease for a while, but one day there comes a time when a person loses teeth. Therefore, it is very important to regularly check your gums for inflammation, and if gingivitis is detected, actively engage in treatment.
Patients often underestimate the seriousness of the situation and try to recover on their own. This is not the best move, because in the fight against gingivitis, reliable diagnosis and a properly designed course of treatment are important. And in order to be able to effectively fight the disease, you need to have a certain understanding of it.
How is the procedure performed?
In order to conduct a Schiller test, a gynecologist must insert a gynecological speculum into the vagina and perform the colposcopy procedure itself, that is, clean the cervix of mucus or discharge and treat its areas with iodine-containing preparations. Most often, doctors resort to using Lugol's solution. After a few minutes, the doctor cleans the sample site of the solution and dries the cervix. After this, he conducts a second examination under a microscope. The procedure takes no more than 5 minutes.
Schiller test in gynecology
Exocervicitis and vaginitis with Schiller's test
Exocervicitis is an inflammation of the ectocervix.
Vaginitis or colpitis is an inflammatory process of the vaginal mucosa.
These pathologies are very common.
They are also detected using advanced colposcopy.
Mottling during the Schiller test usually indicates an inflammatory lesion of the mucous membrane of the reproductive organs.
An indicator of inflammation is the appearance of light specks on a brown background.
As a rule, iodine-negative areas have a round shape.
But the Schiller test does not make it possible to determine the cause of inflammation.
This requires additional diagnostic procedures.
PCR or bacteriological culture allows you to identify the pathogen.
Nonspecific vaginitis and exocervicitis are most often caused by Escherichia coli, coccal flora, and corynebacteria.
Specific inflammatory processes are triggered by ureaplasmas, mycoplasmas, trichomonas, and chlamydia.
Schiller test: atrophic colpitis
In addition to bacteria, age-related hormonal changes cause inflammation.
Lack of estrogen leads to atrophic colpitis.
It is detected using the Schiller test.
After staining with 3% Lugol's solution on glycerin, weak and uneven staining of the mucous membrane of the vagina and ectocervix is noted.
Along with other studies, the Schiller test allows for differential diagnosis between infectious and atrophic inflammatory processes.
Their symptoms are often similar.
But if, during bacterial processes, multiple small foci of light color are observed, then with atrophic colpitis, a diffuse change in color is noted.
This is due to the fact that due to estrogen deficiency, there is a decrease in the number of mature epithelial cells containing large amounts of glycogen.
And when its content is low, cells are less stained with iodine.
This information shows the doctor in which direction to conduct further examination.
An accurate diagnosis is established after the appointment of additional diagnostic procedures:
- blood tests for hormones (estrogens deficiency);
- smear for oncocytology (atrophic type of smear);
- according to indications - a smear for infections (excludes STIs).
Cervical erosion with Schiller test
Cervical erosion is mechanical damage to the epithelium.
It looks the same as ectopia or false erosion (pseudo-erosion).
Extended colposcopy, including the Schiller test, helps to carry out differential diagnosis.
In the case of true erosion, it will be negative.
That is, the bottom of the damaged area of the ectocervix mucosa will turn brown in the same way as healthy tissue.
This suggests that no change in the structure of the epithelium occurred.
By origin, erosion can be:
- inflammatory;
- traumatic;
- burn;
- cancerous;
- trophic.
Damage to the epithelium of the vaginal part of the cervix heals on its own after eliminating the influence of the causative factor.
The goal of treatment should be to stimulate reparative processes and normalize the vaginal biocenosis.
Leukoplakia of the cervix with Schiller's test
Leukoplakia is excessive keratinization of the mucous membrane of the cervix.
The pathology is diagnosed quite often - it affects 1.1% of the female population.
Among patients with menstrual irregularities, leukoplakia is found in 12% of cases.
Leukoplakia is a precancerous condition.
Moreover, the risk of malignant degeneration is very high.
Without timely detection and treatment, every third patient will develop cervical cancer over the next 10 years.
The Schiller test helps identify leukoplakia in the ectocervix.
The area of hyperkeratosis is an iodine-negative zone.
It can have different sizes - from a pinpoint plaque to a large formation that occupies the entire vaginal part of the uterus.
Sometimes leukoplakia spreads to the vaginal vaults.
The Schiller test gives the doctor indicative information, but does not confirm the diagnosis.
This requires a targeted biopsy.
The Schiller test is also useful in that it allows you to select an area for collecting clinical material.
Histological examination makes it possible to establish the diagnosis of leukoplakia, identify malignant cells if present, and assess the risk of tumor development.
It allows you to determine the indications for surgical treatment.
Schiller test: cervical dysplasia
Dysplasia is a large group of cervical diseases that are considered precancerous.
Leukoplakia is one of them.
But this is far from the only type of dysplasia.
This concept also includes papillomavirus-associated lesions of the cervix, erythroplakia, and adenomatosis.
Any changes in the epithelium in the ectocervix area can be diagnosed by performing the Schiller test.
This study does not allow differential diagnosis.
However, the detection of areas of multilayer epithelium that are unevenly or weakly stained with Lugol's solution is the basis for a biopsy.
In addition, the procedure makes it possible to determine the optimal location for taking a section of tissue for histological examination.
The Schiller test helps in diagnosing:
- cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN);
- squamous intraepithelial lesions (SIP);
- cervical cancer.
You can perform extended colposcopy with the Schiller test in our clinic.
This study will help to identify inflammatory and precancerous diseases in a timely manner.
If the test result is positive, an experienced gynecologist will prescribe clarifying studies and determine the optimal therapeutic tactics.
To perform the Schiller test, contact the competent gynecologists of our medical center.
Indications for the procedure
Colposcopy is one of the generally accepted and recognized diagnostic methods in modern medicine in the field of gynecology. Using this study, the doctor can assess the position of the tissues of the vagina and cervix, as well as determine the presence of benign and malignant neoplasms.
This study should be carried out for women with:
- bloody discharge after sexual intercourse;
- the appearance of itching or uncharacteristic discharge;
- chronic infections;
- infection of the genital organs with the human papillomavirus;
- testing for cancer;
- vulvitis;
- ceresitis;
- colpitis;
- pregnancy planning;
- the presence of any neoplasms.
It is worth noting that in the initial stages of cervical disease there are no specific symptoms, so you cannot check yourself. In this case, it is better to trust the gynecologist.
After the test, the doctor will tell you what the results mean and prescribe the necessary treatment, if necessary.
Doctors advise not to neglect your own women's health and to conduct a Schiller test at least once a year for preventive purposes.
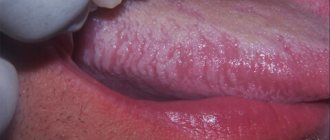
Symptoms of gingivitis
Despite the fact that there are many causes and types of gingivitis, dentists most often encounter catarrhal, usually chronic, gingivitis. Its very first symptoms are slightly swollen gums with redness, as well as discomfort on the teeth from hot and cold water.
The next manifestation is bleeding gums during hygiene procedures; this is already an average form of the disease. It is very important to start treating it immediately when a symptom is detected. And finally, if your gums bleed at night, then you have a severe form of gingivitis. It requires urgent professional intervention.
Less common symptoms are:
- yellow or red sores,
- gum overgrowth
- atrophy, pain.
Preparing for the study
In order to prepare yourself for the Schiller test and get accurate results, you must follow a number of certain rules. First of all, two days before the study, sexual intercourse is not advisable, in addition, there is no need to douche. The day before the test, doctors do not recommend using suppositories or tampons, various gels and ointments. While taking a shower, it is prohibited to use intimate hygiene products.
By following the simple instructions from the list, you can get reliable results. It is worth noting that the doctor will tell you about them directly when prescribing the procedure.
Causes
Gingivitis in most cases has several causes.
Firstly, rarely do any patients satisfactorily monitor oral hygiene, so first plaque and then tartar form on the teeth. Tartar hides a lot of pathogenic bacteria.
Secondly, many of us have gastrointestinal diseases, which also provoke gingivitis.
Thirdly, often in the oral cavity, or in general in the human body, immune defense is reduced. The reason for this is an unhealthy lifestyle, vitamin deficiency, bad habits, and chronic conditions such as stress.
More rare causes include burns of the mucous membrane, teething, heart disease, diabetes and others.
In addition, incorrectly installed veneers and braces, poorly made, old and decaying fillings can lead to increased gingivitis.
Process
The test is carried out using a solution consisting of iodine, potassium iodide and distilled water.
During the test, the doctor opens the woman's cervix using a speculum. Next, using a tampon, the cervix is cleared of any secretions and mucus present. Having finished this, Lugol's solution is administered.
This solution should be in such quantity that the cervix is completely immersed in it. In a number of situations, the area under study is lubricated with a swab, which is pre-wetted in a composition consisting of glycerin and Lugol's solution. Next, the solution is removed, and the treated area is dried using a cotton swab. The technique of the procedure ends with another examination of the condition of the cervix.
The result will be in just 5 minutes, the procedure itself is painless, so no anesthesia is used. But having the solution in the vagina can cause some discomfort.
There is no point in conducting a test at every visit to the gynecologist. It is enough to perform the Schiller test once a year. If a woman is diagnosed with some kind of disease, then it is considered necessary to carry out the procedure 2-3 times a year until the test is negative.
Colposcopy technique
Colposcopy with a smear for oncocytology is the main method for the prevention and diagnosis of precancerous diseases and cancer of the cervix, vagina and external genitalia.
The colposcope is a microscope adapted for this study, which allows one to examine pathological changes in the cervical mucosa under various magnifications.
Modern colposcopes are equipped with devices for receiving and storing photo and video information. This allows the doctor and patient to evaluate the results of treatment over time and consult with other specialists without repeating the study.
A doctor who has an idea of the symptoms of the disease and knows its colposcopic picture can make a preliminary diagnosis with an accuracy of 70-80%. In combination with cytological and histological examination, the material for which is taken during colposcopy, the accuracy of the diagnosis increases to 100%.
Colposcopy is routinely performed in the middle of the menstrual cycle, from 9 to 21 days.
The procedure is performed on a gynecological chair in a gynecologist's office, is short (5-10 minutes) and painless. With the help of a speculum, the walls of the vagina are moved apart, and the cervix becomes accessible for inspection.
First, a general examination is carried out and a smear is taken for atypical (cancerous) cells. At this stage, the doctor evaluates the shape of the cervix, identifies its deformations, ruptures, inflammatory processes and takes a smear for cancer cells for cytological examination.
Then tests are carried out, the purpose of which is to identify hidden lesions of the epithelium of the cervix, vagina and external genitalia, to clarify their size, location and nature. The test consists of examining the mucous membrane after treating it with a 3% solution of acetic acid and Lugol's solution (Schiller test).
Back to contents
Advantages and disadvantages
An important component of implantation at all stages is an accurate index assessment of the condition of peri-implant tissues, implants and supported prostheses. The Schiller-Pisarev test is quite effective and allows you to diagnose a wide range of conditions - gum inflammation, periodontal destruction, the amount of tartar, plaque, the need for certain therapeutic measures and their volume.
The relationship between the elements of the implant and adjacent tissues and its difference from a natural tooth may make complex periodontal studies impossible.
The Schiller-Pisarev test is quite accurate and objective and has two interpretation options. The first is visual, based on the nature of the gum staining, the second is numerical, that is, index. The main problem of the technique is that dental indices from 30-50 years ago do not meet the current needs of modern implantology.
That is, they can be used, but when interpreting the results, it will be necessary to take into account the full list of current changes and improvements in the field of prosthetics. At the same time, it is the Schiller-Pisarev test that is considered the most informative of all similar diagnostic methods and allows the results to be most successfully adapted to the conditions of endosseous implantation. However, the convention of numerical values still does not disappear anywhere, since diagnostics are carried out using markers, and not high-precision digital equipment. Modern researchers say that the Schiller-Miller test is still relevant, but should be used with certain modifications and clarifications.
What is the procedure
Colposcopy is a special procedure performed by a gynecologist to examine the condition of the vagina, vulva and cervix. A device used for the study is a colposcope. It is equipped with a special optical system, with which you can detect abnormalities in the genitals.
There are two types of gynecological colposcopy:
- Simple: a visual examination is performed with a colposcope without medications.
- Advanced: involves the use of tests to diagnose the cervix. In this case, the Schiller test is performed.
The Schiller test is a Lugol's solution test. It contains iodine, which causes healthy cells and tissues to turn brown, while the color of the affected areas remains unchanged. If they are detected, the patient is prescribed a biopsy for more accurate tests.
Result: index calculation, assessment of gum condition
For objectification purposes, the Schiller-Pisarev test is expressed in numbers (scores). The color of the papillae is rated at 2 points, the gingival margins at 4, and the gingival alveoli at 8 points. The total amount obtained is then divided by the number of teeth in the study area. That is, the calculation formula looks like this:
Iodine number = Sum of assessments for each tooth / Number of teeth examined.
The result is an iodine number in points. Evaluation of results by points:
- mild inflammation – up to 2.3 points;
- moderate inflammation – 2.67-5.0 points;
- severe inflammation – 5.33-8.0 points.
The peripheral circulation index (abbreviated as IPC) is also determined separately, taking into account the ratio of the time of resorption of hematomas that appeared under vacuum and the resistance of gingival capillaries. Test indicators are assessed in points, their ratio is expressed as a percentage. The index is calculated using the following formula:
- resistance of gum capillaries (scores);
- period of hematoma resorption (scores).
Based on index indicators, the functional state of the peripheral circulatory system is assessed. An IPC from 0.8 to 1.0 is considered normal, 0.6-0.7 is a good condition, 0.075-0.5 is a satisfactory condition, and from 0.01 to 0.074 is a decompensated state. You may be interested in learning how to strengthen teeth with periodontal disease.
Point system used to calculate the IPC (points are points)
| Resistance of gum capillaries | Period of resorption of vacuum hematomas |
| 1-10 seconds, 1 b. | 2.5 days, 10 b. |
| 11-20 seconds, 2 b. | 3 days, 20 b. |
| 21-30 seconds, 4 b. | 3.5 days, 40 b. |
| 31-40 seconds, 6 b. | 4 days, 60 b. |
| 41-50 seconds, 8 b. | 4.5 days, 80 b. |
| from 50 seconds, 10 b. | 5 days, 100 b. |
Benefits of the procedure
Diagnostic colposcopy with the Schiller test allows you to give an objective assessment of the condition of the vulva, vagina and mucous membrane of the cervix, identify pathologies of the epithelial zones, and establish the nature of the detected neoplasms. The procedure is a highly accurate diagnostic method. It is short-lasting, does not cause pain and has no side effects.
Indications
- Colposcopy of the vagina is prescribed if the presence of:
- cervical polyps;
- papillomas and conilomas;
- cercivita;
- cervical cancer;
- precancerous changes in the tissues of internal organs.
The basis for the procedure is also any deviation that was detected during the examination or when taking a smear. Colposcopy is indicated for all women of reproductive age and should be performed at least once a year. It is necessary to do a Schiller test twice a year for representatives of the fair sex who are at risk: patients during menopause, after a miscarriage and a sexually transmitted disease, surgical abortion, with a family history of various gynecological pathologies.
Reasons for visiting the clinic are also menstrual irregularities, vaginal discharge (unpleasant odor, pus, blood), pain and discharge during sexual intercourse, itching in the genital area.
Contraindications
Colposcopic examination has no contraindications.
Preparation
The reliability of the results of colposcopy with the Schiller test depends on preparation. Gynecologists recommend adhering to the following rules:
- Refrain from sexual intercourse 2-3 days before the procedure;
- Before visiting a gynecologist, do not use intimate gels, deodorants and other cosmetics, as they can affect the composition of the microflora;
- A few days before the analysis, avoid starchy and sweet foods, as well as foods that cause the formation of gases, alcohol and nicotine;
- A week before the procedure, stop taking hormonal medications and antibiotics.
Seasonality
The examination can be carried out at any time of the year.
Process
- Visual examination of the genitals;
- Insertion of a gynecological speculum into the vagina;
- Installation of a colposcope;
- Treatment of the area under study with 3% acetic acid;
- Performing the Schiller test.
Rehabilitation
During the procedure, the patient does not experience pain; after it, natural reactions sometimes appear (burning, tingling), which go away on their own after a few hours. After diagnosis, you can return to your normal lifestyle.
conclusions
- To diagnose periodontal diseases and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment, various methods are used, including periodontal indices.
- The essence of the Schiller-Pisarev technique is to stain the gums. Areas deeply affected by the inflammatory process will become stained. Based on the intensity of staining, the stage of the pathology can be determined. It also allows you to distinguish periodontal disease from other similar pathologies. For more information on how periodontitis differs from periodontal disease, see this material.
- The Schiller-Pisarev test involves two interpretation options - visual, based on the nature of gum staining, and numerical or index.
- To take Schiller-Pisarev samples, a solution of potassium iodide, crystalline iodine and distilled water is used.
- The main index indicators are the resistance of gum capillaries and the time of resorption of vacuum hematomas.