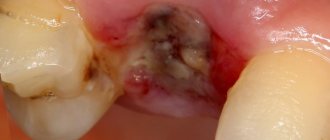
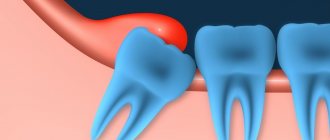
Fused teeth are one of the rarest anomalies in the development of the dental-jaw system, which consists in connecting the sides of the rudiments during the development of the embryo. It occurs in only 1% of Patients.
Most often, fused teeth are observed during a primary dentition; with a permanent dentition, such an anomaly is extremely rare.
The reasons for the formation of fused teeth can be:
- hereditary factor;
- too much pressure on the buds of neighboring teeth;
- jaw injuries;
- inflammatory and infectious diseases that cause metabolic disorders in the human body.
Often, the fusion of teeth is confused with their fusion, although these pathologies are completely different in nature. Teeth fusion occurs during the period after their growth and development, and fusion occurs during the formation of tooth buds.
What is ankylosis
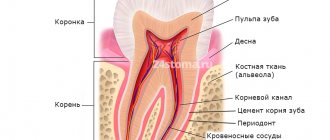
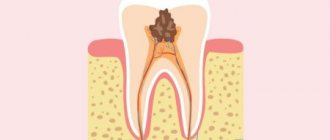
Tooth ankylosis is a pathology characterized by fusion of the cement of the tooth with the jaw bone. The tooth root is deprived of part of the ligamentous apparatus, which often leads to adhesion or germination of bone tissue. The aesthetics of the teeth are disrupted, they look shorter and change their angle. Ankylosis usually occurs during tooth eruption. Pathology can also form at a late stage in the formation of the dental arch.
It is important to know. The process is accompanied by periodontal necrosis and the incorporation of root cement into the alveolar bone.
Ankylosis of a primary tooth is caused by loss of the periodontal ligament. It is observed in cases where a primary molar does not fall out due to the absence of a permanent dental unit. Ankylosed teeth are different in size from their neighbors, so bite correction will be required.
Types of Teeth Fusion
In orthodontics, there are several types of dental fusion:
- first: supernumerary fusion. In this case, the second tooth is much smaller than the first. It is characterized by a spiky shape and a bumpy surface;
- second: non-gingival, observed only in the supragingival part involving a certain area of enamel;
- third type: root. Occurs in the root part at the level of cement and is characterized by deep damage to dentin. At the same time, both teeth have the same size;
- fourth: observed along the entire height of the tooth with damage to the crown and root parts.
Symptoms
Parents should be wary of the fact that their child’s baby teeth are not falling out. It is fused to the bone and cannot easily separate from the alveoli, as is normal. If the pathology is not detected and treated in a timely manner, the child’s jaw begins to develop incorrectly. The diseased tooth is located lower than the others, and the neighboring teeth are placed at an angle in relation to it. Problems with bite occur.
Another scenario is also possible. The baby tooth does not erupt completely and is delayed in its development. Because of this, the permanent tooth also cannot develop, and after the milk tooth falls out, it becomes fused with the jaw. This is how ankylosis of permanent teeth occurs. The final diagnosis is made after analyzing the results of a computed tomography scan.
Good to know. The service life of ankylosed teeth is completely different. They can last for decades or fall out, thinning out the dentition.
What are they?
Fused teeth are a rare pathology characterized by the fusion of the sides of the rudiments during the embryonic development of the fetus. This anomaly occurs in only 1% of the population.
Most often, this disease is observed during the period of primary occlusion . Permanent teeth are affected 5 times less often.
The reasons that provoke the development of pathology following :
- excessive pressure on the buds of adjacent teeth;
- injuries of various types;
- heredity;
- metabolic disorders caused by various inflammatory or infectious diseases.
In addition, the fusion can form in the presence of osteoporosis, dysplasia or hypoplasia.
Read how you can close diastemas in a new publication.
In a separate article we will tell you which pathologies are characterized by spiky teeth.
Follow the link https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/okklyuzii/nepravilnyiy-prikus-zubov-kakie-mogut-byt-posledstvija.html let's talk about possible complications of malocclusion.
The main symptom of the anomaly is considered to be an overly large tooth, whose height is several times less than the length of the cutting surface . As a result, it often has an irregular shape and position.
Characterized by being rotated around its axis or located on adjacent ones.
The abnormal tooth has a longitudinal groove marking the fusion boundary. It starts from the gum line and can cross the entire height of the outer part, or only reach half of it.
What is the difference between fusion and fusion?
This anomaly is often confused with fusion, but in fact fusion and fusion are completely different pathologies :
- Fusion. It is a connection of two teeth in the area of cement, which is formed after the completion of their development and growth.
Most often it is provoked by crowding of the dentition or a violation of the integrity of the partitions of the alveolar ridge. Fusion can occur between both normal and supernumerary specimens.Typically, this pathology affects the molars of the upper jaw.
- Merger is formed at the rudimentary level. In this case, the area of connection is dentin, and in isolated cases, enamel.
The main area of localization is the incisors of the upper jaw. Most often, fusion leads to a decrease in the total number of teeth on the jaw arch.In rare cases, the anomaly combines regular and supernumerary teeth.
Possible consequences
Incorrect development of even one tooth can have very serious negative consequences , among which the following were most often noted:
- formation of malocclusion;
- dysfunction of biting and chewing food;
- with excessive increase, mouth breathing can form, which leads to frequent ENT inflammations;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, which develops as a result of increased load on them due to poorly chewed food;
- speech changes: lisp, unclear pronunciation of sounds, swallowing them;
- psychological trauma;
In addition, when removing the affected part of an abnormal tooth, there is a high risk of dislocation of a healthy one.
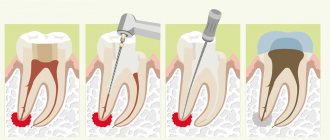
Treatment of ankylosis
Treatment of ankylosis with traditional orthodontic methods (braces) is impossible. The tooth grows into the bone and it is impossible to return it to its correct position. But restoring the functionality of the dentition is quite possible. In dental clinics, the method of treatment is selected individually in each individual case.
First of all, the patient is referred for a dental computed tomography scan. The dental surgeon studies panoramic images and draws up a treatment plan. Most often, surgical treatment methods are used: excess fibrous tissue is removed and joint mobility is restored. Crowns made of metal-ceramics, ceramics and zirconium dioxide are also used to treat dental ankylosis. With their help, the bite is corrected.
Correction methods
Several years ago, the only method of correcting fused teeth was to remove them. Modern orthodontics offers more advanced ways to eliminate this anomaly, allowing you to leave the tooth intact.
As a rule, treatment depends on the type of pathology:
- in the first type, correction is carried out by careful grinding of the adjacent part of the tooth and subsequent restoration;
- in the second type, hemiresection is performed - that is, detachment and removal of the adjacent part without traumatic effects on the periodontium;
- the third type requires hemisection - detachment of the gum tissue and incision of the root part;
- with the quarter type, hemisection is carried out along the entire length of the teeth.
Stages of treatment
Correction of teeth fusion is carried out in several stages:
- The first stage is the removal of the secondary part of the tooth. When cutting off the upper part, conduction anesthesia is used, and in case of complete dissection, general anesthesia is used. Hemiresection is carried out using a diamond disc, and a two-week bandage is applied to the wound. Hemisection is a more traumatic procedure performed with a scalpel. Sutures are placed on the dissected mucosal flaps, which are removed after a week, and the tooth is splinted for two weeks;
- the second stage - orthodontic, begins two weeks after the separation of the teeth. Its goal is to restore normal occlusion. Most often it is corrected with a braces system.
Modern orthodontics makes it possible to treat fused teeth, restoring their normal appearance and preserving the pulp in 90% of cases.
Impacted supernumerary teeth
Often, supernumerary teeth stop growing and remain impacted, that is, unerupted. Such teeth may not appear for a long time; they are discovered by chance during an X-ray examination of the oral cavity. The presence of an impacted supernumerary tooth may be indicated by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of mobility of complete teeth;
- periodic aching pain in the area where the tooth is located;
- tissue compaction if the tooth is located close to the edge of the jaw.
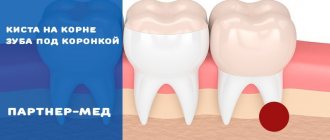
Cysts sometimes develop on the root of the tooth, which may not cause pain for some time; they are also detected during x-ray examination.
Removal of impacted teeth
Impacted teeth are those that did not erupt in time and remained in the thickness of the bone tissue, at different depths - in the dental arch or outside it.
Canines, premolars, incisors, unerupted and semi-erupted wisdom teeth may be impacted. They often do not have enough space in the dental arch; the gums around them can become inflamed and a pathological periodontal pocket can form. Impacted teeth are removed if they are associated with pain, discomfort, if they cause inflammation and orthodontic movement of them into the dental arch is impossible. Removing impacted teeth varies in complexity. Additional x-ray examination may be required before removal.
Primary and secondary edentulous teeth
Experts distinguish several types and subtypes of adentia. For greater convenience, below are tables showing the types of the disease, combined by certain characteristics.
Primary adentia
Caused by hereditary factors and diseases at the stage of fetal formation. With primary adentia, there is an absence of tooth germs.
Varies:
- partial primary adentia - the absence of one or more rudiments (for example, primary adentia of two incisors);
- complete primary adentia – absence of all tooth buds. It is extremely rare;
- true adentia – absence of tooth buds (without their destruction by diseases and infections);
- false edentia, when different teeth merge into one.
Secondary adentia
Secondary adentia occurs as a result of illness and injury during life.
Causes of edentia
The problem of missing teeth sooner or later arises in almost every person. However, the causes of edentia can be very different. It all depends on whether it is primary (lack of tooth germs as such) or secondary (loss of already formed teeth).
| Primary causes of edentulism | Causes of secondary adentia |
|
|
Classification of missing teeth according to the location of the disease
| By localization | Description |
| Missing upper teeth | The absence of teeth in the upper jaw can be either partial or complete, as well as single. |
| Missing lower teeth | A general designation for a disease indicating the absence of teeth in the lower jaw. |
| Lack of chewing teeth | May be referred to as missing lateral teeth. Lack or complete edentulism in the chewing region. In particular, we are talking about the absence of small molars (premolars) and molars. |
| Missing front teeth | Edentia of incisors or canines in the frontal zone. |
In addition to the classification described above, the type of teeth itself is also taken into account. Based on this, the absence of molars and edentulous primary teeth (not associated with the normal timing of their replacement) are distinguished.
Classification of edentulism by the number of missing teeth
| Number of missing teeth | Classes | general description |
| Partial edentia (ICD K00.00) | Partial primary adentia. Partial secondary adentia. | With partial edentia, from one to 5 teeth or their rudiments are missing on one jaw. Most often, three teeth are missing. |
| Multiple edentia | Multiple primary adentia. Multiple secondary adentia. | Many experts combine the concepts of partial and multiple edentulism. Criteria:
And so on up to 15 units on one jaw. |
| Complete edentia (ICD K00.01) | Complete primary adentia. Complete secondary edentia. | Complete absence of teeth or missing teeth |
Treatment of adentia
As has already become clear, the absence of teeth affects both functionality and aesthetics, as well as the overall quality of a person’s life. Treatment of adentia depends on the type, the presence of indications and contraindications for a particular prosthetic technique, as well as the financial capabilities of the patient.
Types of prosthetics in the absence of a large number of teeth and a single defect
| Type of edentia | Prosthetic options |
| Partial | Fixed bridge prosthesis, removable plate prosthesis |
| Plural | If there are a large number of missing teeth, a removable plate or clasp denture with hooks, clasps or attachments is used |
| Completely edentulous jaw | Plate dentures that completely imitate one of the jaws. Edentia of the lower jaw is complicated by the fact that the tongue and cheeks can displace the prosthesis, so prosthetics of the lower jaw in the absence of all teeth is carried out if there is no alternative. The same can be said about edentulism of the upper jaw, because A schematic denture with complete absence of teeth often falls out and can cause discomfort when worn due to the bulky base. |
Note: prostheses in the absence of classical type front teeth (bridges and circuits) are significantly inferior in terms of aesthetics to implant-based structures, therefore traditional prosthetics in the absence of teeth in the aesthetic zone are highly not recommended.
Implantation for edentia
| Type of edentia | Implantation options |
| Partial | Single implantation or fixed bridge prosthesis on implants. |
| Plural | Single implantation or fixed bridge prosthesis on implants. |
| Completely edentulous jaw | Dental implantation for completely edentulous patients usually follows certain protocols (“All on 4”, “All on 6”); however, if funds and positive indications are available, it is possible to install the maximum number of implants. |
What are the dangers of fused tooth roots?
Most often, the roots of primary molars grow together. In such cases, treatment is usually not carried out. By the age of 5-6 years, the tissues dissolve. This process must be monitored to prevent displacement of the permanent rudiments and to avoid malocclusion.
Often, dentists identify fused roots of wisdom teeth. They may not bother a person, but more often they cause discomfort. With this disorder, the risk of inflammation, the development of periodontal disease, and the formation of a cyst or granuloma increases.
Lack of teeth in humans: what is it and what does it mean?
What is jaw edentia? If in some species of animals the dentition is renewed continuously or at least repeatedly (for example, in Indian elephants), then people have only two sets of teeth - milk and molars. Unfortunately, they can be lost during life, and with some types of anomalies and diseases, a person initially lacks one, several or even all tooth germs. Adentia is a situation where there is a lack of teeth on one or both jaws. In this case, the absence of eights is not taken into account, since they are a rudiment and may not appear in principle. Experts highlight the absence of primary and molar teeth. In the latter case, the loss is irreparable. Therefore, most often they talk about edentulous molars, taking into account the fact that all the most negative consequences of this disease are especially pronounced in adulthood.
What does missing teeth affect?
- Chewing dysfunction.
- Problems with the digestive system.
- Deterioration of aesthetics. The most noticeable consequence of edentia. A diagnosis of “missing teeth” is often a death sentence for a beautiful smile.
- Bone tissue atrophy. Without the load that the teeth bear, the bone tissue begins to dissolve. When there is a lack of teeth, over time the face seems to shrink in the lower part and those same senile sunken cheeks appear. This is a consequence of bone atrophy.
- Curvature of teeth. In the absence of teeth, the bite is disrupted and the dentition shifts. It also distorts a person's facial features.
- Problems with diction.
Unlike many dental diseases, signs of missing molars (as well as milk teeth) are very obvious. Diagnosis of edentia is usually carried out visually. However, to assess the condition of the bone tissue and the entire dentofacial apparatus as a whole, an x-ray examination is necessary. Now that it has become clear what jaw edentia is, it is necessary to talk about the causes and types of the disease.
Diagnostics
An erupted supernumerary tooth is detected during examination of the oral cavity; it is often dystopic, that is, abnormally located.
Diagnosis of unerupted (impacted) supernumerary teeth is carried out using x-ray examination. Often, X-ray diagnostics of supernumerary teeth is difficult due to the fact that in the image their contours overlap the contours of the complete teeth. For more accurate diagnosis, 3D computed tomography is used. The results of these studies make it possible to obtain comprehensive information about the relative position of erupted and impacted complete and supernumerary teeth.