We have repeatedly written that “sick teeth mean a sick body.” Many diseases have a close connection with dental health (see “Two scientific experiments that will make you go to the dentist”) and dental health is an indicator of the health of the body! Ignoring even simple hygiene rules and timely visits to the dentist is fraught with the possibility of the appearance of one or another disease.
In this article we want to talk about such an unpleasant disease as osteoporosis and, it would seem, what does the dentist have to do with it?
Osteoporosis (lat. osteoporosis) is a chronically progressive systemic disease of the skeleton or a clinical syndrome manifested in other diseases, characterized by a decrease in bone density, a violation of their microarchitecture and increased fragility due to impaired metabolism of bone tissue with a predominance of catabolism over the processes of bone formation, a decrease in bone strength and an increase risk of fractures. Wikipedia .
Medical observations show that a toothbrush can serve not only to prevent caries, but also that osteoporosis can be accidentally discovered with its help. Scientists have developed a unique program that can recognize decreasing bone density on an X-ray. Dental imaging may become a method for diagnosing osteoporosis in the future.
Research shows that plain radiographs are a simple and inexpensive method that can help identify patients with incipient osteoporosis. Such a place is the patient’s lower jaw – thinning of the bone can already be detected on an X-ray of the jaw.
What is periodontitis
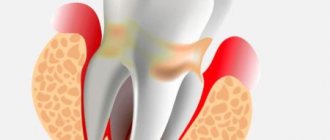
Periodontitis is an inflammatory process of the peri-root tissues of the tooth. Pathology develops regardless of a person’s age and gender. The disease is characterized by disruption of the periodontal ligament, destruction of osteocytes, formation of cysts, and loosening of the segment.
The periodontium is a layer of tissue penetrated by blood, lymphatic vessels, and nerve endings. It consists of the gum, alveolar bed and ligament. Due to this complex, each unit is held in its own hole.
The pathogenesis is based on the body's immune response to the inflammatory process. It manifests itself as a vegetative-vascular reaction. Blood flow to the affected area increases, stasis occurs in small vessels, and edema develops. The dentogingival connection is weakened, and under the influence of inflammatory mediators the bone begins to melt. This leads to expansion of the periodontal fissure.
Depending on the provoking factor that caused periodontitis, the following types are distinguished:
| Classification by cause of disease | Notes |
| Infectious | The most common. Periodontal infections are caused by plaque microorganisms. Under their influence, enamel and dentin are destroyed and caries develops. In the absence of medical intervention, microorganisms involve the pulp in inflammation, and pulpitis occurs. Further, along the root canal, the infection descends to the opening in the apex and enters the periapical tissue. In addition, an extra-dental route of infection entering the periodontium from surrounding tissues or hematogenously (periodontitis, osteomyelitis, tonsillitis, etc.) is possible. |
| Drug | Drug-induced periodontitis occurs when the dosage or exposure time of potent drugs during endodontic treatment is not observed. Medicinal substances exit through the root canal into the surrounding tissues, where they have a toxic effect. |
| Traumatic | It is provoked by mechanical impact on periodontal tissue (bruise, blow, improper root filling, etc.). |
The development of the disease is provoked by poor oral hygiene, diabetes, infections of the ENT organs, and metabolic disorders. There is an increased risk of inflammation in smokers and alcohol abusers.
Periodontitis can have a different course:
- acute form. Characterized by a vivid clinical picture. Based on the nature of the exudate, serous and purulent types of the disease are distinguished;
- Chronic periodontitis is a sluggish pathology with erased symptoms. There are fibrous, granulating and granulomatous periodontitis.
Chronic inflammation recurs from time to time. During exacerbation, the clinical picture corresponds to the acute form.
Depending on the location of the lesion, 2 types of dental periodontitis are classified:
- apical (near the root apex);
- marginal (the source of inflammation is located near the edge of the gum).
Implantation stages
Regardless of treatment protocols, the procedure is performed sequentially. The classic correction method takes a lot of time, and all manipulations using single-phase methods can take only a few days. This period includes diagnostics, surgery to install titanium roots, and prosthetics.
Preparing for implant installation
At the initial appointment, the doctor collects anamnesis, examines the oral cavity, and conducts a computed tomography scan. The patient undergoes blood and urine tests to exclude general contraindications. You may need to seek permission from your physician.
If one or more implants are installed, professional hygienic cleaning of the oral cavity from dental plaque is carried out. When dental diseases (caries, gingivitis, etc.) are detected, appropriate treatment is first carried out.
After diagnosis, the dentist chooses a method of restoring the dentition, implantation systems. If complete edentia is treated with one-stage protocols, then 3D modeling of the result is carried out, and surgical templates are printed.
Performing implantation
The procedure is carried out in stages:
- pain relief with local anesthetics;
- preparing a bed for a titanium root;
- screwing the implant into the bone.
If the tooth is previously removed, the prosthesis is installed on the same day. In this case, special systems are used that can be installed directly into the hole.
The final stage is prosthetics
In the immediate loading protocol, temporary crowns are installed within three days. The permanent prosthesis is installed after at least six months. Some temporary orthotic systems can last up to several years.
With delayed loading, prosthetics are done after the implant has completely healed. In this case, a permanent crown is immediately placed.
Symptoms of periodontitis
A clear clinical picture is characteristic of the acute stage and periods of exacerbation in the chronic form:
- The pain in the initial stages is aching and intensifies when chewing food or pressing on the crown. As inflammation progresses, the intensity of the pain attack increases sharply. The sensations become unbearable, pulsating.
- A feeling of a tooth protruding from the gums. The causal segment becomes higher than other units in the series.
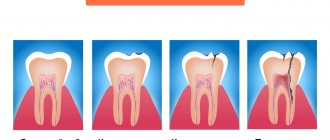
- Presence of deep caries.
- Previous treatment of pulpitis on the causative tooth.
- Swelling of the gums.
- The appearance of an inflammatory tubercle in the projection of the root apex on the gum.
- Formation of a fistula near the diseased segment, discharge of serous or purulent exudate from it.
- Loosening of the unit.
Chronic periodontitis during remission is asymptomatic or has mild symptoms.
Auxiliary techniques
The doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures. These are electro- and phonophoresis with antiseptic, anesthetic, vascular drugs, the use of therapeutic mud, paraffin baths, magnetic therapy, even quartz treatment. The latter is only dosed.
You should also pay attention to exercise therapy. The entire set of exercises is developed by a doctor who takes into account the patient’s age and the condition of his musculoskeletal system. It also determines how many exercises will be in the complex, as well as how often they should be repeated. Exercises should not tire the patient or give him unpleasant emotions. On the contrary, it will be good if they give him more strength and lift his spirits.
Exercise therapy is an equally effective method of treating periarticular osteoporosis
You can apply lotions of dimethyl sulfoxide (“Dimexide”), medical bile, and gently warm up the sore spot using warming and anti-inflammatory ointments.
When the patient is already reliably on the mend, doctors can recommend the following procedures:
- gentle painless massage with elements of light joint development;
- long-term use of chondroprotectors, for example, “Chondrolon” and/or “Teraflex”;
- courses of calcium supplements, including vitamins and antioxidants.
The complex treatment method also includes a change in diet. It should contain enough of the following products:
- dairy products;
- lean meat;
- fruits and vegetables;
- greenery;
- nutty.
In this case, the patient should eat fractionally, he should eat four to five small portions of food per day. At the same time, the following are strictly contraindicated:
- beer, vodka, wine and other alcoholic products;
- gas. beverages;
- everything is fried and fatty.
You can use it, but only a little:
- coffee;
- cocoa and products containing it (chocolate);
- sweet.
But he should consume as much kelp (seaweed) as possible, since there are a lot of microelements there.
What does periodontitis look like?
Forecast of treatment results
For a considerable number of people, the diagnosis of “periarticular osteoporosis” is associated with disability. But more than half the success of treatment is determined precisely by the attitude with which the patient takes up the matter and how much effort the patient himself puts in, and not by the doctor and medications. So this pathology should be diagnosed in time so that the joints do not have time to become overgrown with thorns and growths.
It is important to detect the disease in time to avoid dire consequences
As soon as the patient is prescribed medication and rehabilitation, he is obliged to follow each recommendation as clearly and patiently as possible. But if there is even a slight deviation from at least one, only then can a person really become disabled, unable to even get out of bed. The prognosis of treatment is determined by when the pathology is diagnosed and how it is treated.
How to diagnose periodontitis
To determine periodontitis, you need to see a dentist. The doctor will collect anamnesis, conduct an examination using dental instruments, and prescribe additional diagnostics:
- Insertion of the probe into the cavity does not cause pain.
- There is no reaction to the thermal test.
- Percussion causes sharp pain.
- Electroodontodiagnostics. With periodontitis, teeth react to a current of 150 to 200 µA.
- Orthopantomography. In acute serous periodontitis, no radiological changes are observed. Later, the expansion of the periodontal fissure is determined. In an acute purulent condition, a limited abscess is detected. In case of chronic pathology in the apex area, the images show a focus of destruction surrounded by a zone of rarefaction of bone tissue.
Warning
It is easier to prevent any pathology than to treat it, and osteoporosis is no exception. Moreover, preventing the disease is most important for those with a hereditary tendency towards it.
To avoid osteoporosis, it is enough to follow the general rules of a healthy lifestyle:
- include in your menu the maximum number of healthy products listed above;
- regularly give yourself some physical activity;
- take a walk every day;
- exclude from the diet all carbonated, sweet and alcoholic drinks, as well as strong coffee;
- follow the daily routine.
What to do if you have periodontitis
If the diagnosis is confirmed, the disease must be treated. How dental periodontitis is treated depends on the form and stage of inflammation. The correction program may include therapeutic and surgical techniques.
Conservative therapy
Conservative methods are aimed at maximizing the preservation of the structure of the unit and restoring its functionality. The program includes elimination of the source of inflammation and endodontic treatment. All manipulations are performed under local anesthesia. Treatment regimen:
- Conducting anesthesia.
- Opening the crown, providing access to the root canals.
- Expansion of the cavity.
- Pulpectomy (if the segment has not been previously treated) or unfilling of the canals.
- Antiseptic, medicinal treatment of cavities.
- Temporary filling (for the period of anti-inflammatory treatment).
- Removal of temporary filling, filling of root canal.
- Restoration of the coronal part of the unit.
- Prescribing a course of antibiotic therapy.
Surgical intervention
Invasive methods are used when other methods are ineffective. The operation can be carried out using different protocols:
- Resection of the apex of the tooth root followed by filling the cavity with special bone-forming materials.
- Extraction of the diseased segment.
If periodontitis is not treated, complications are possible: odontogenic periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum), abscess, phlegmon, etc. The infectious process spreads to nearby lymph nodes, and lymphadenitis occurs. In severe cases, possible: tooth loss, osteomyelitis, sepsis.
The use of various drugs for periarticular osteoporosis
Conservative treatment of this pathology includes the use of drugs from different pharmacological groups. Treatment of symptoms involves reducing pain, as well as relieving inflammation. This effect is achieved by using the following medications:
- non-steroidal antiseptics, for example, Diclofenac and Movalis;
- analgesics - “Pentalgin” and/or “Baralgin”;
- glucocorticosteroid hormonal drugs, but only in an advanced stage, and for a very short time - “Prednisolone” and its derivatives.
In this case, to carry out blockades inside the diseased joint, the drug is injected directly into its cavity.
Risk factors
These are conditions that are not contraindications, but may reduce the effectiveness of the intervention, require parallel treatment, or for which implantation is considered as a method of intervention.
In these conditions, it is more difficult to achieve a positive result, additional efforts are required, the rehabilitation stage is longer, and the success rate is lower.
The list includes: dysfunction of the maxillary joint, periodontitis, periodontal disease. This also includes smoking and age.
Complications
According to statistics, osteoporosis is one of the leading causes of disability and mortality. The main complications of the pathology are fractures:
- femoral neck;
- radius bones;
- vertebrae
Bone fractures force patients to remain in bed for a long time.
As a result, the risk of bedsores and pneumonia increases. Severe stages of osteoporosis lead to external physical defects that contribute to impaired self-care. Therefore, it is important to diagnose the pathology in time and carry out correct treatment. If osteoporosis is detected, you must strictly follow your doctor's recommendations. Make an appointment