Dental periodontitis is an inflammation of an infectious nature that occurs at the membrane of the tooth root and affects the tissues of the oral cavity located next to it. Periodontitis is difficult to confuse with other dental diseases, because it has a clear symptom – severe and constantly increasing pain, which cannot be relieved by taking tablets from the pharmacy.
Treatment of periodontitis must be carried out urgently, because you risk not only losing a tooth, but also acquiring complications that are dangerous to the overall health of the body! How periodontitis occurs, what signs will help to identify the disease in a timely manner, how periodontitis is treated in dentistry, at what prices the service is offered in Moscow - we will talk about this in detail in this article.
Causes of dental periodontitis
Various reasons can lead to the appearance and development of dental periodontitis, but in the vast majority of cases the disease appears:
- Against the background of untreated dental caries and pulpitis;
- Due to poor quality treatment of tooth canals, or more precisely, mistakes made when filling the canals.
Less commonly, periodontitis occurs after injuries, incorrectly installed dental fillings, or violation of the dosage of dental medications.
Whatever the cause of periodontitis, its treatment cannot be delayed due to fear of dentists. It is important to understand that you will not stop the inflammation on your own, with pills or folk remedies, and the more it progresses, the less chance you have of saving the tooth. In addition, periodontitis can also affect neighboring healthy teeth.
How to identify periodontitis and not confuse it with caries or pulpitis? We already talked about the most striking symptom of the disease at the very beginning of the article, but the signs of periodontitis may vary depending on the form of the disease. Therefore, below we will consider the main types of dental periodontitis, as well as talk about their characteristic symptoms.
Take a short test and calculate the cost of treatment!
Take a short test
- Which teeth have caries?
- Visual assessment
- Reaction to stimuli
- Cost calculation
×
Manukyan Artavazd Genrikovich
Chief physician of the clinic
Features of the treatment of periodontitis in the acute stage
Exacerbation of periodontitis goes through two phases: intoxication and exudation (appearance of discharge). As the disease progresses, the patient first experiences aching and episodic pain, and then constant throbbing and tearing pain, so treatment cannot be delayed.
Acute periodontitis can be serous or purulent. In the second case, purulent exudate accumulates in the apical part of the tooth root, and the main task for the doctor is to remove it. Sometimes this is enough to clean the tooth cavity and treat the canals, but in severe cases it may be necessary to cut the periosteum for drainage.
Signs of acute periodontitis
Symptoms of acute periodontitis are always pronounced. Among them:
- Acute aching pain, the intensity of which is constantly increasing;
- Pain increases when trying to eat;
- If treatment for periodontitis was not started on time, attacks of pain will appear more and more often, and the intervals between them will become shorter and shorter;
Against the background of intense pain, a person cannot eat, speak, sleep, and may develop an elevated temperature. In the acute form of periodontitis, significant tumors and swelling often appear in the area of the diseased tooth. The cheek may also swell. This occurs due to the active accumulation of pus in the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Recommendations after treatment
After conservative or surgical treatment, you should not eat food for 2-3 hours due to the effects of anesthesia. Pain may be experienced for 7 days after surgery. It is recommended to rinse your mouth with antiseptics and a decoction of medicinal herbs. For severe pain, it is recommended to take painkillers. If pain persists and severe swelling is observed, contact your doctor immediately.
At the same time, the crown of the tooth changes its color, the presence of a carious cavity and tooth mobility are noted. Dentists at the CELT clinic successfully treat even the most advanced and severe forms of chronic periodontitis!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Symptoms of chronic periodontitis
Chronic periodontitis is a very insidious form of the disease, since it can develop completely asymptomatically. It is extremely rare for a person to feel a slight pain when trying to bite something on a sore tooth; sometimes unpleasant sensations appear when consuming hot food and drinks.
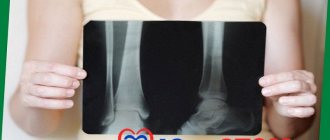
Chronic periodontitis of the tooth is diagnosed with an x-ray, which clearly shows the process of bone destruction at the apex of the tooth root. This form of the disease has its own classification, according to which there are: fibrous, granulating and granulomatous periodontitis. With fibrous periodontitis, there is almost no pain, which is why it is most often recognized either in the acute phase or during an examination by a dentist and x-rays.
Treatment of this form of periodontitis is quite simple and is carried out in 1-2 visits to the doctor. Granulomatous chronic periodontitis most often develops asymptomatically, but under the influence of certain external factors it easily turns into an acute form. The disease has its own characteristic symptom, manifested in the formation of granulomas - capsules with pus, which separate tissues affected by inflammation from healthy ones. The treatment process for granulomatous periodontitis is long and complex, it can last for several months and even require surgical intervention!
Stages and forms of the disease
Periodontitis is divided according to the general principle into chronic and acute. Chronic cannot be completely cured. It is only possible to eliminate local inflammation and stop further exacerbation of the disease. Chronic periodontitis is asymptomatic and does not bother the carrier, but in case of exacerbation of the disease, symptoms begin to appear. In a calm state, a small fistula may appear on the gum from time to time, and slight discomfort may occur when chewing food or mechanical impact on the area of inflammation. If left untreated for a long time, the risk of tooth loss is high.
Treatment of acute periodontitis has an end result. But even after complete recovery, control over the oral cavity is necessary to avoid re-inflammation. In acute periodontitis, all of the listed symptoms are characteristic, only 2-3 of them may appear, and this is already a signal to visit the dentist. Purulent periodontitis is especially pronounced. In this case, the pain is acute, body temperature rises, and gumboil formation is possible.
Forms of periodontitis:
- Fibrous. In this case, periodontal tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue. It is often asymptomatic and can be detected by external signs: changes in enamel color, bad breath, pulp death.
- Granulating. It leaks quickly and destroys bone tissue. It is characterized by painful sensations when pressing on the gums or chewing food. A pulling or bursting pain may be observed without mechanical impact on the tooth.
- Granulomatous. This is a dangerous type of disease because it is asymptomatic, while destructive processes take place inside the periodontium, which are accompanied by the appearance of cysts and granulomas. If left untreated, the tooth may simply fall out. An infection locked in a granuloma or cyst can “explode” under the influence of the slightest irritant: provoke inflammation (for example, sepsis).
- Apical. The simplest form, easy to treat. It occurs as a result of untreated pulpitis and is localized in one place near the root.
How does the acute phase of chronic periodontitis manifest?
When exacerbated, chronic periodontitis of the tooth expresses itself with the same symptoms as the acute form of the disease. That is, there is a strong, aching pain, swelling of the gums and swelling of the cheek. Typically, chronic periodontitis enters the acute phase when the immune system is weakened, the flu, ARVI, or simply severe hypothermia are present. If, during an exacerbation of the chronic form, a fistula appears in the gum area, pus will flow from the area of inflammation and the pain in the tooth will gradually subside.
But this does not mean that periodontitis has gone away on its own; the inflammatory process will continue to develop and will manifest itself again under favorable external factors, which we discussed just above. Based on the type of periodontitis, a treatment regimen is selected. The price of the service depends on the regimen chosen for treating the disease. We will tell you below about all the stages of treatment of dental periodontitis in different forms and prices for procedures. But no matter in what form periodontitis develops, its treatment always begins with diagnosis.
Diagnosis of periodontitis involves examination of the oral cavity, x-rays, and examination of patient complaints. All this together helps to accurately diagnose the form of periodontitis and prescribe adequate and effective treatment.
Why periodontitis is dangerous
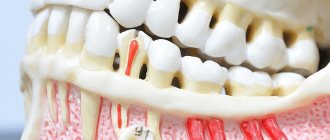
Periodontal inflammation is the stage following pulpitis in the spread of infection from a carious tooth.
Its focus is located at the apex of the root and is a small cavity filled with pus.
In the absence of therapy, the infectious-inflammatory process spreads to the periodontium - the intermediate tissues that separate the roots and neck of the tooth and the bone tissue of the gums.
Important! The periodontium surrounds the entire subgingival part of the tooth and plays the role of cement that fixes the tooth in the jaw. When it is damaged due to periodontitis, the likelihood of tooth loosening and loss increases many times over.
Most often, periodontitis is localized at the apical part of the root affected by pulpitis. If left untreated, the inflammation spreads further, covering the entire subgingival part of the tooth. As the disease develops, a purulent cavity forms around the roots, which sooner or later opens onto the mucous membranes of the oral cavity or onto the skin of the face. When it becomes chronic, periodontitis is accompanied by constant suppuration with the outflow of contents through a fistula - long-existing ducts, the walls of which do not grow together.
Permanent canal filling
Permanent canal filling in the treatment of periodontitis is performed during the third visit to the dental office. Before proceeding with any manipulations, the specialist sends the patient for a control x-ray. The image will help determine the effectiveness of periodontitis treatment. If the percentage of bone tissue destruction has decreased significantly, permanent filling of the canals is performed.
The procedure begins with the removal of the temporary filling from the crown of the tooth, and then the canals are freed from the previously placed composite. The doctor will carry out an antiseptic rinse and then fill them to the apical part of the root with a composite. Upon completion of the work, the patient is given another x-ray to monitor the quality of the filling performed. Gutta-percha must be tightly packed into the canals to the very apex of the root, otherwise there is a high risk of relapse of periodontitis.
A couple of days later, the patient comes to the doctor for the fourth time and during this visit the crown part of the tooth is restored with a permanent filling to restore its aesthetics and functionality.
Treatment of periodontitis at home
Periodontitis cannot be cured at home, since the disease is caused by bacteria that colonize the dental canals. The only way to get rid of them is to carry out antiseptic treatment and sealing of the canals, and this can only be done by a doctor, but by waiting for a visit to the clinic, you can alleviate the symptoms and reduce pain.
Disinfectants that do not irritate the mucous membranes can be used for rinsing 4 - 5 times a day. Doctors also recommend rinsing with a solution of salt and soda, including after treatment, to relieve swelling and reduce inflammation. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are suitable for pain relief. All this will help relieve symptoms, but is not a cure.
You may experience pain after periodontitis treatment. Normally, they last 3–5 days and gradually fade away. If the pain does not subside or returns with renewed vigor, re-therapy is necessary.
Indications for treatment
The following indications exist for conservative treatment:
- Periodontitis of acute and chronic forms of single-rooted teeth, when the periapical tissues have not undergone large-scale changes.
- Periodontitis of acute and chronic forms of multi-rooted teeth, subject to patency of the canals and the absence of an irreversible process in the periapical tissues.
How is periodontitis eliminated? Treatment of the disease at the chronic stage
Regardless of the form, the root cause must be addressed first. To do this, the doctor works in the main root canal and its branches, as well as in the periodontium itself. If exudate is present, it must be quickly released. At the end of treatment, the gap between the periodontium and the root canals is carefully sealed.
Methods for diagnosing periodontitis
Acute periodontitis is usually diagnosed during examination by a dentist based on the clinical picture and patient complaints.
The difficulty of diagnosing chronic periodontitis is due, first of all, to the fact that the patient does not have sufficient motivation to see a doctor. A fairly typical situation is when the tooth initially hurt (in the stage of pulpitis), and then the pain disappeared. But the inflammatory process continues. And the longer treatment is delayed, the less opportunity there is to save the tooth. To avoid negative consequences, Family Doctor dentists recommend undergoing a dental examination at least once a year.
Orthopantomogram
As part of your annual dental examination, your doctor may recommend an orthopantomogram, a panoramic photograph of your teeth taken using a special X-ray machine (orthopantomograph). X-rays will help identify chronic periodontitis and determine the choice of treatment method.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Contraindications to treatment
Absolute contraindications for this type of treatment include:
- Severe changes in periapical tissues (cyst, cystogranuloma) with the presence of focally caused ailments.
- Obstruction of the canals at the acute stage.
- Tooth mobility of 1I-IV degrees, when the alveolar arch at the level of the diseased tooth has atrophied.
- Cysts of peri-root teeth with root penetration into the pathological process.
- Irreversibility of the course of the disease and the impossibility of performing post-apical therapy.
- Perforation of a cavity or tooth root.
Temporary filling
During a second visit to a dentist-therapist during the course of treatment of chronic periodontitis, the area of manipulation is examined. The specialist will also clarify whether the patient has any complaints of pain, swelling in the gum area or other discomfort. If such negative phenomena are not observed, temporary filling of the dental canals is performed.
For this purpose, the temporary filling is initially removed, as well as the antiseptic placed in the tooth canals. The canal openings are thoroughly washed with an antiseptic and then filled with a special type of composite material used for temporary filling. This composite contains calcium hydroxide, a substance that destroys pathogenic microflora and also catalyzes the process of bone tissue regeneration in the area of the upper zone of the tooth root. Temporary filling of canal cavities is done for a fairly long period - from two to three months. The dentist then places a temporary filling in the crown of the tooth.
How to prevent the development of the disease? Prevention
The main preventative point is the treatment of caries immediately after the onset of dental problems. The infection enters the periodontium through the carious area. To prevent marginal or marginal types of disease, in which the infection passes through the deep periodontal areas, it is important to monitor the condition of the gums. Periodontal treatment immediately after its appearance, as well as timely removal of tartar, is of great importance.
Acute forms of the disease are eliminated using an integrated approach to treatment in order to prevent the anomaly from moving to the chronic stage. This rule fully depends on the qualifications of the doctor and the availability of high-quality equipment in the clinic.
Third visit
In addition to a visual examination, the doctor will need an x-ray to examine the quality of the therapy and make sure that the abscess is not growing. Having seen a positive result with traces of bone restoration, the doctor either proceeds to install permanent fillings or decides to continue treatment.
If the outcome is favorable, the dentist cleans the tubules from the substrate that temporarily fills them, rinses, disinfects and carefully seals with gutta-percha to the very top.
Finally, an x-ray is taken to show how well the tooth canals are filled. If the filling material extends beyond the apex or does not reach it, the doctor's work was in vain. The channels will have to be redone. In the opposite case, periodontitis recurs with the same force.
A temporary filling is placed for the third time.