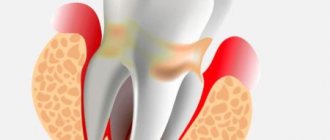
Periodontitis in children is an inflammatory process in the tissues surrounding the root of the tooth. This disease is considered one of the complications of caries, although other causes are possible. The periodontium is the area located between the jaw and the roots of the teeth. It develops synchronously with their growth and is constantly changing until the time when permanent teeth are formed.
Treatment of periodontitis in primary teeth in children can be done at CELT dentistry. We offer competitive prices and comfortable conditions for young patients. Our pediatric dentists have extensive experience. Parents can be sure that visits to us will not be a real test for their kids. Treatment of periodontitis in children without pain and tears? This is possible in our clinic!
Consultation with a pediatric dentist (pedodontist) - RUB 1,000.
Apexification with the application of a temporary filling (1 channel) - 1,500 rubles.
Filling the root canals of baby teeth - 4,000 rubles.
Installation of insulating gasket "VITRIBOND" - 800 rubles.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- Cost of consultation with a pediatric dentist (pedodontist) – 1,000
Make an appointment
Causes of periodontitis in children
Dental periodontitis in children can occur due to a number of reasons:
- as a complication of caries that was not treated;
- as a consequence of improper treatment of caries complicated by pulpitis;
- due to chemical damage to the periodontium using canal sterilization agents;
- due to injuries to soft tissues and teeth during falls or accidents.
Reviews from parents and impressions of children
Suvorova Anastasia
Periodontitis is a terrible diagnosis, and it came to us unexpectedly. Who knew that a simple fall would lead to such severe inflammation in the mouth. Misha just fell on the swing. And then a week later he began to cry, refuse to eat, and complain of tooth pain. The doctor from Aza&Buka made a diagnosis and suggested starting treatment immediately. In one go, the tooth was saved. The treatment was fun, with cartoons. With a creative and positive approach. Misha is happy, and the tooth no longer hurts.
I put Aza&Buka:
5
Misha
Alexander
Alice had to have her baby tooth removed due to periodontitis. At Aza&Buka they took an x-ray and saw that the new tooth was ready to grow. The patient removed it and after a few weeks a permanent one grew. Healthy! Thank you for your professional approach and for not needlessly tormenting the child with treatment.
I put Aza&Buka:
5
Alice
Veronica Stepanova
Pasha was diagnosed with periodontitis of a molar tooth. The reason is poor quality treatment of pulpitis in one of the clinics near Moscow. They were treated surgically under good anesthesia. Long enough, because carefully and scrupulously. They cleaned everything out of the affected cavity and scheduled an x-ray control in a month. It wasn't very expensive for such a service!
I put Aza&Buka:
5
Pasha
Symptoms of periodontitis
Periodontitis can occur in acute or chronic form. Acute periodontitis in children is characterized by an acute onset and severe, constant, increasing pain. The pain is especially strong when pressing on the diseased tooth and when chewing on it. Other pronounced symptoms:
- swelling of the gums around the tooth;
- fever, weakness and nausea;
- enlarged lymph nodes and their pain.
Chronic periodontitis in children during periods when there are no exacerbations is practically asymptomatic. Pain can only appear when pressure is applied to the tooth or when the tooth comes into contact with something hot or cold. But besides this, other manifestations are possible:
- exacerbations with symptoms characteristic of acute periodontitis of primary teeth in children;
- formation of fistulas on the gums in the granulating form of the disease;
- drowsiness, fatigue, general weakness.
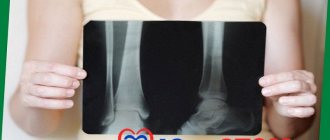
Diagnostics
It is very difficult to determine the presence of periodontitis in children. Since their dentofacial apparatus is still developing. This is also explained by difficulties in communication with a small patient. He is unable to describe his feelings in detail.
You can suspect periodontitis in a baby based on characteristic clinical signs:
- in acute periodontitis, pain intensifies from heat;
- in the chronic form there is no reaction to temperature;
- upon probing, a pain is detected at the site of granulation growth; if they have not formed, then it does not exist.
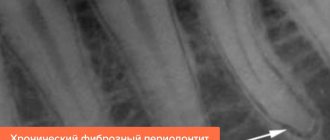
Radiography plays a leading role in the diagnosis of this disease.
It reveals:
- changes in the apical region of the root are detected (resolution of bone mass is noted);
- rarefaction of the substance of the root itself;
- granulomatous tissue is noted in the root;
- there are foci of destruction in the area of root separation and around them;
- destruction of the follicle of the permanent tooth is noted;
- the end part of the upper wall of the tooth germ is missing.
Thermal diagnostics and temperature tests are not carried out on children. The child cannot describe his feelings, so they are not informative.
Why is chronic periodontitis dangerous?
The acute form of periodontitis is characterized by pronounced pain, so parents immediately turn to the dentist. The chronic form of the disease occurs latently, and discomfort occurs mainly when eating. If you do not contact specialists in time, the inflammation may spread, and purulent bags will appear on the roots of the teeth. This can ultimately lead to tooth loss. Another unpleasant consequence is that the chronic form can re-exacerbate and lead to sinusitis or periostitis.
CELT pediatric dentists diagnose the chronic form of periodontitis with a preliminary X-ray examination. The selection of treatment is carried out taking into account the prevalence and severity of inflammatory processes, as well as the type of child’s teeth. If treatment is carried out on baby teeth, in order to carry out all the necessary manipulations in full, children are put to sleep using general anesthesia. In each individual case, the issue of pain relief is considered individually. We take into account not only the age of young patients, but also their health status, as well as the wishes of the parents.
Prevention
Like 99% of other dental pathologies, chronic periodontitis is easier to prevent than to treat. Enough:
- Maintain proper oral hygiene (brush your teeth twice a day, use floss, special rinses and irrigator).
- Stick to a proper diet. Less sweets, more fruits!
- Once every 3 months, go to the dentist for a preventive examination and professional hygiene.
- When the first complaints appear, do not delay your visit to the doctor and follow all recommendations.
The children's department of Megadent Clinic has excellent reviews. Each clinical case is considered individually. The little patient will be surrounded by care, found an approach and reassured. The treatment will take place without pain and tears. Call and sign up for a consultation!
Treatment of periodontitis in primary teeth
Treatment of periodontitis in primary teeth involves either their removal or the use of conservative techniques. The first is resorted to in extreme cases, since it can lead to such negative consequences as the development of malocclusions and slow development of the jaw. However, the affected tooth is a source of infection, which can affect the buds, and the consequences can be even more serious.
Treatment of periodontitis in children by removing the affected tooth is prescribed in the following cases:
- resorption of the diseased root by more than two-thirds of its length;
- severe mobility of the affected tooth;
- the process of changing to permanent teeth will begin in less than one year;
- conservative treatment does not give the desired result;
- development of sepsis;
- weakening of the child's body.
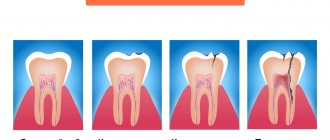
Forms and types of periodontitis disease
Periodontitis is the fourth stage from the onset of caries formation. The process looks like this:
- First, hard tissues are affected by caries;
- Further, in the absence of timely treatment, superficial caries turns into deep caries, the destruction becomes more extensive;
- After this, pulpitis develops - inflammation of the internal tissues (pulp);
- In the absence of qualified treatment for pulpitis, the pathology gradually turns into periodontitis, inflammation of the canals and periodontal tissues.
Treatment of periodontitis in permanent teeth
Treatment of periodontitis in permanent teeth in children involves anti-inflammatory therapy. It requires an x-ray, the main purpose of which is to determine how well the child’s dental roots are formed. This is important because treatment of immature roots is much more difficult due to a number of anatomical features. They not only significantly complicate filling, but also increase the risk of medical errors. When applying a filling, calcium hydroxide is used. This material is the best for intra-root therapy for periodontitis. It has a pronounced bactericidal effect and creates a reliable barrier between the affected periodontal tissue and healthy tooth tissues.
Conservative treatment of periodontitis
CELT dentists widely use conservative methods for treating the symptoms of periodontitis in a child. If there is even the slightest opportunity to save a tooth without removing it, they do everything that depends on them. Endodontic treatment is carried out in a complex and involves the use of physiotherapy, which is an additional means to eliminate inflammatory processes. The procedures may be as follows:
- electrophoresis of antiseptic pharmacological drugs;
- laser therapy aimed at sterilizing tooth canals;
- phonophoresis of antiseptic agents using ultrasound.
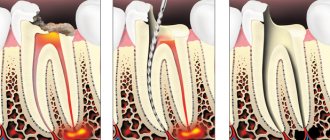
The main treatment requires two visits, the first of which:
- the carious cavity is cleaned and softened dentin is removed from it;
- in order to expand the mouth of the canals, a hand instrument is used, after which the necrotic nerve is removed;
- expand and thoroughly clean the canal, rinse it with an antiseptic;
- the apical foramen is opened, which allows for exudation;
- the canal is filled with calcium hydroxide-based paste (if the tooth is permanent) or oil-based paste (if the tooth is milky).
After 5 - 10 days, during which the small patient is prescribed rinsing the mouth with antiseptics, along with taking antibiotics, a second visit is required. It provides for the following activities:
- Cleaning the dental canal and removing medicinal paste;
- Using an antiseptic solution for rinsing;
- Canal filling with gutta-percha, tooth filling.
Service cost
| Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a dentist-therapist | 1,300 rub. |
| Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with a dentist-therapist | 500 rub. |
| Treatment of periodontitis of 1-canal tooth (mechanical and medicinal treatment of the canal for periodontitis, all visited) | 2,400 rub. |
| Treatment of periodontitis of a 2-canal tooth (filling 2 canals for periodontitis) | 4,800 rub. |
| Treatment of periodontitis of 2-canal teeth (mechanical and medicinal treatment of 2 canals for periodontitis, all visits) | 4,800 rub. |
| Treatment of periodontitis of a 3-canal tooth (mechanical and medicinal treatment of 3 canals for periodontitis, all visits) | 6,800 rub. |
| Additional or separate canal (canal filling due to canal unfilling) | 5,800 rub. |
| Temporary filling (1st canal with pastes during endodontic treatment for periodontitis) | 2,500 rub. |
Surgical treatment of periodontitis
Surgical treatment of chronic periodontitis in children may be required during periods of exacerbation or if the use of conservative methods does not produce the desired result. It is also used in cases of granuloma formation or canal obstruction. To do this, an operation is performed to resection the root apex. This is a complex surgical intervention that involves making an incision along the gum, peeling off the mucous membrane, and creating a small hole to gain access to the affected area. The dentist removes the root tip along with the granuloma, fills the free space with synthetic bone tissue and medicine, and sutures the wound. The technique is used only on permanent teeth; milk teeth are removed without preliminary manipulation.
Features of the pathological and clinical picture
Granulation tissue grows unevenly, and many cellular elements are formed. Partial osteoclastic resorption of bone tissue is observed. The cement and dentin of the affected teeth also dissolve.
The disease often occurs without pain. There may be complaints about the formation of a fistula and pus, and there is also a change in the color of the crown. A closed carious cavity with softened dentin appears in the tooth. This is explained by the fact that at this age, caries, as a rule, is acute, and the pulp does not sufficiently perform a protective function, so periodontal infection occurs very quickly.
The hard tissues of baby teeth differ from permanent ones. Their enamel and dentin are thinner, the degree of mineralization leaves much to be desired, and the dentinal tubules are shorter and wider.