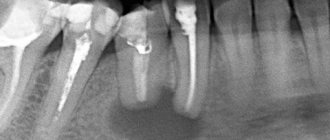
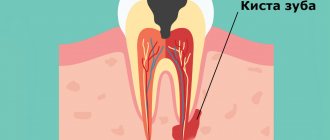
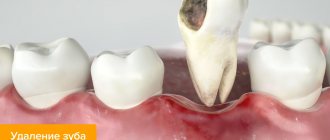
The Greek word "kystis", used to refer to a condition such as a dental cyst, is translated as "blister". This name most accurately reflects the essence of this disease. With it, a cavity is formed at the root of the tooth, which is filled with liquid (bacteria and dead cells), and the comparison with a bubble in this case is most appropriate.
The consequences of untimely treatment of a cyst in the gum of a tooth can be the most unpleasant - including tooth loss. The process may also involve neighboring teeth, which will also require professional dental treatment.
Resection of the root apex (frontal group) - 6,500 rubles.
Resection of the root apex (chewing group) - RUB 9,000.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- The cost of a dental consultation is 1,000
- The cost of an orthodontist consultation is 2,000
Make an appointment
Cyst symptoms
In the initial stages, the cyst is almost invisible. Unlike an abscess, it does not break out, but at the same time continues its development inside, affects healthy tissue of the jaw bone and leads to loosening of the tooth. As the inflammatory process develops, the following symptoms of a cyst in the tooth appear:
- pain in the affected area;
- swelling of the gums;
- increased body temperature;
- swollen and tender lymph nodes;
- flux.
The pathology quickly develops into a chronic stage and is asymptomatic for humans. During an exacerbation, attacks of pain may occur when eating solid foods. Gradually, the tooth enamel becomes gray or yellow, and the tooth shifts. As soon as the immune system fails due to acute respiratory viral infections or exacerbation of chronic diseases, the growth of the cyst accelerates, so the appearance of a fistula, swelling, acute pain, fever and migraine is observed.
Indications
- Bite abnormalities.
- Periodontitis.
- Installation of orthodontic systems.
- Severe deformation of the ligamentous apparatus (tooth loosening).
- Hyperdontia.
Contraindications
- ARVI and weak immunity.
- Chronic and acute forms of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Nervous and mental disorders.
- Cancerous tumors.
Treatment for retrochorial hematoma
It is recommended to treat retrochorial hematoma, mainly because only there it is possible to ensure truly complete physical rest and the absence of any stress. No promises to “lie down all the time” at home can be realized - there will always be a bunch of urgent household chores that you want to do - from cleaning to laundry. In addition, the hospital can provide emergency assistance at any time - intravenous administration of hemostatic agents, for example. If it is not possible to go to a hospital, then you should consider the option of a day visit to the clinic or staying with us for a couple of days.
Bed rest is recommended, and in order to restore the outflow of blood, it is advised to lie down with a cushion, for example made from a rolled blanket, under the pelvic area. To prevent congestion in the intestines, it is recommended to follow a diet: exclude legumes, spicy foods; products that strengthen stool or enhance intestinal motility (chocolate, coarse fiber). The intestines overflowing with gases put pressure on the pregnant uterus and increase the tone of the uterus, which increases the threat of miscarriage and increases the size of the hematoma. Also, to reduce the risk of increased uterine tone, you need to limit the consumption of strong tea and coffee.
Drug therapy consists of using drugs that improve blood clotting, due to which bleeding stops and the hematoma stops growing (tranexam, dicynon, vikasol). To relieve hypertonicity of the uterus, due to which the hematoma can grow, antispasmodics (no-spa, metacin, suppositories with papaverine) are used. In order to normalize hormonal regulation in the body, metabolic vitamin therapy is used. Progesterone preparations are used. In this case, the scheme and route of administration are selected individually by the doctor; these can be either drugs for intramuscular administration (oil solution of progesterone), or suppositories (Utrozhestan, Iprozhin), tablets (Duphaston) or gel (Crinone). It should be noted that when bloody discharge appears from the genital tract, utrozhestan continues to be administered intravaginally. Its effectiveness is not reduced!
Treatment usually lasts from 2 to 4 weeks, and, if indicated, is repeated at critical times (12–14, 20–24, 28–32, 36–38 weeks). Resorption of the hematoma usually occurs from 2 to 4-5 weeks.
Why does a cyst appear?
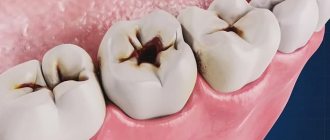
The causes of the appearance of a dental cyst, a photo of which can be seen in this article, are injuries due to mechanical stress or infection, which leads to the development of inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth. A tooth inside the gum can be injured under a variety of circumstances, for example, when the tooth is hit or when chewing nuts. As for infection, it can get into the root canal if dental treatment is performed incorrectly, in particular, if the dental canal is incompletely filled. A cyst that arose as a result of sinusitis or another infectious disease is relatively rare. In this case, pathogenic microorganisms enter the gums along with the blood flow.
How does the disease develop?
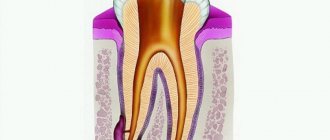
The process begins with periodontitis, when the tissue located between the jaw bone and the tooth root becomes inflamed. As a result, the tissues located around the root begin to grow abnormally. Initially, the size of the neoplasm does not exceed five millimeters (it is called a granuloma). Growing and enlarging, it becomes covered with a membrane and transforms into a cyst.
There are cases when the cyst grows so much that it eats away the bone around the tooth. With the next exacerbation of inflammation, it opens, forming a channel to the outside through the gum mucosa. Such a channel is called a fistula or fistula tract.
It is worth noting once again the insidiousness of this disease, which not only negatively affects the condition of the roots of the teeth, but also affects the general condition of a person. At the initial stage, the pathology develops almost imperceptibly and can only be detected during a visit to the dentist. Pronounced symptoms appear in the later stages of the disease as a result of tumor growth and destruction of bone tissue.
The main danger of a cyst is the fact that, by corroding the bone, it deprives the patient of the opportunity to install an implant in place of a lost tooth without complex manipulations.
How to use an antibiotic for tooth inflammation with pus
At the first stage, while the pathological process is less active, rinses with an antibacterial effect are carried out as prescribed by the dentist.
Local medications act directly on the affected area and are less absorbed into the systemic circulation, which reduces the risk of side effects.
You need to crush the tablets of Lincomycin, Azithromycin or Tetracycline, combine them with lukewarm (not hot) boiled water, and rinse your mouth with the solution. The proportions of the components are selected by the dentist.
Active inflammatory process in the periosteum and gums after removal of the problem unit, with infection from the outside or hematogenously, flux is an indication for the prescription of antimicrobial compounds. It is important to prevent complications that develop when purulent masses accumulate or exudate exits into the oral cavity through the fistula. With the flow of blood and lymph, infectious agents penetrate into other parts of the body.
Periodontitis and periostitis in acute or chronic form are dangerous diseases. To heal the wound, the dental surgeon first cleans the affected area, removes a thick mass containing pathogens, particles of blood and mucus. The second stage is the prescription of antibacterial drugs. For purulent inflammation, penicillins show high effectiveness: Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav. Depending on the severity of the pathological process, antibiotics are taken orally or given injections.
If an odontogenic infection is detected, against which the gums fester, the use of the drugs Gentamicin, Grammidin C, Ciprofloxacin, Cifran is indicated.
What complications does a dental cyst lead to?
Untimely treatment or removal will lead to the following complications:
- Periostitis.
- Swelling.
- Abscess.
- Phlegmon.
- Temperature increase.
Usually the cyst does not make itself felt in any way, so complications may appear unexpectedly. To exclude serious consequences, you need to be examined by a dentist at least once every six months. The appearance of a capsule with pus can occur against the background of deep caries or severe inflammation of the gums, so do not delay a visit to a specialist.
The lack of results with conservative treatment leads to the fact that the cyst has to be removed along with the tooth.
Types of dental cyst
The type depends on the place of occurrence. A cyst forms in the maxillary sinus, gum, root or under the crown. To determine the type of capsule with pus, the specialist examines the medical history and assesses the client’s general health. There are 5 types of dental cysts:
- Follicular - formed when the tooth was unable to grow unhindered and most of it remained inside.
- Keratocyst - develops against the background of pathological processes during the growth of the body (the growth of the neoplasm is stimulated by the pharynx-forming tissue).
- Radicular - appears from a granuloma and is a serious complication of deep caries.
- Retention – is formed during the eruption of molars in children.
- Residual – appears due to complications and inflammatory processes after tooth extraction.
Types and regimens of prescribing antibacterial drugs during implantation
The patient does not need to know what antibiotics are prescribed for dental implantation. It is enough to follow the instructions of the dentist: purchase prescribed antibacterial drugs at the pharmacy and take them according to the prescribed regimen.
The name of the drug, frequency and duration of its administration depend on the type and complexity of the operation performed. In some cases, for example, the doctor may prescribe a single dose of the antibiotic amoxicillin 60 minutes before installing the implants. Others require an additional dose of the drug six hours after surgery. When performing complex traumatic procedures, the dentist may prescribe a stronger antibiotic (Augmentin, Tsipran, Tsiprolet) several times a day for three or five days.
In general, it is useful for the patient to know that before any dental surgery you can independently reduce the number of microorganisms in the mouth. This can be done by rinsing the mouth with a 0.2% chlorhexidine solution. If you don't have it, you can use plain water. Rinsing even with it alone removes about 60-70% of bacteria.
Cyst on the root of a tooth
This species grows in the alveolar area and can appear in any area of the gum. There are no symptoms except for tingling when eating or touching. Pain appears in later stages of development. A cyst on the root of a tooth is divided into 3 types:
- Peri-root - appears in the upper part of the root.
- Interroot – formed between the roots.
- Radical - appears near the root canal and over time can cause the growth of a malignant tumor of the jaw (if not properly treated).
Names of antibiotics used for inflammation of the dental nerve and root
The dentist prescribes medications to suppress infection based on the results of an examination of the problem area. When the nerve is inflamed, it is difficult to eat and drink; throbbing or aching pain accompanies a person throughout the day and intensifies at night.
Before starting therapy, the doctor conducts an allergy test and interviews the patient to identify contraindications.
Antibiotics help eliminate inflammation of the root and dental nerve:
- Ciprofloxacin.
- Azithromycin.
- Amoxiclav.
- Azithromycin.
- Ampiox.
- Doxycycline.
- Digital
Conservative and surgical treatment of cysts
In the early stages, in the absence of complications, a conservative method is acceptable. The root canal is drilled and cleaned. The capsule with pus is opened and cleaned, and a composition with an antibiotic is poured inside. Next, a bone tissue regeneration paste is applied and a filling is installed. A control check after 6 months demonstrates the absence of a cyst on an x-ray in 80% of cases
Surgical treatment is prescribed if there is no result. With the help of cystectomy, the affected part of the tooth and the capsule with pus are completely removed. Cystectomy is an operation that not all dental surgeons can do. Hemisection is often used, which gives a 100% result and is prescribed for severe root damage. All affected tissue is removed, and the appearance of the tooth is restored with a crown or composite composition.