Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
The human oral cavity has its own microflora and its own specific diseases arise. Let's talk about one of them - fibrous epulis of the gums: what kind of disease it is, what are the causes of its occurrence, how is the treatment carried out.
Growth on the gum: why it appears and how to treat
A growth has appeared on the gum: what is the cause
Infectious diseases
Non-communicable diseases
Types of growth
Gum cancer
Lump after crown installation
Growth on the gum: how to treat
Which doctor should I contact if a growth appears on the gum?
Normally, the gums have a smooth, pale pink texture. Any change, be it a thickening or a growth, signals problems in the body that cannot be ignored, as they pose a health hazard. Why lumps appear on the gums and how to treat them, we will tell you in the article.
Fibroma
Description
Benign tumor of epithelial cells. Initially, the bumps on the gums above the tooth are small in size and do not hurt. However, mechanical stress and other negative factors can lead to the transformation of fibroma into a malignant tumor.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out surgically. The doctor excises the tumor, applies stitches, and prescribes rinses. Further follow-up visits may be required to monitor the recovery process.
A growth has appeared on the gum: what is the reason?
A lump or growth is a compaction on the gum caused by damage to periodontal tissue, which may appear without any previous signs. Growths appear in people of any age, but mainly in young children, as they unknowingly introduce infection into their mouths. The first thing you need to do when you detect formations in your mouth is to determine the nature of their origin (only a doctor can do this). It comes in two types:
- Infectious. The appearance of cones is caused by the activity of bacteria.
- Non-infectious. Bumps and growths as a result of injury, mechanical or chemical damage.
If a lump has formed in your mouth, you should consult a doctor to rule out possible complications. The doctor will help diagnose the problem and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Rehabilitation after removal of exostosis
The wound heals completely in about 1 week. For better tissue healing and prevention of complications, it is necessary to comply with the doctor’s requirements.
During the recovery period, you should not exercise or overheat the body. It is prohibited to visit the bathhouse, sunbathe on the beach, or take a hot bath. Otherwise, bleeding from the wound may occur.
In order not to injure the damaged mucous membrane, you should not eat rough, spicy or sour foods. Food should be liquid or pureed, at a comfortable temperature. It is undesirable to smoke, as nicotine constricts blood vessels, which prevents rapid healing.
When brushing your teeth, you should avoid the operated area. The toothbrush should be soft. After eating, you should rinse your mouth with warm water. Daily rinsing with antiseptic solutions, for example, chlorhexidine, miramistin, is recommended. For these purposes, you can prepare decoctions of chamomile, sage, calendula, and oak bark.
In the first few days, pain and swelling of the tissues persist. To relieve acute pain, you can take analgesics. A cold compress will help relieve swelling. Ice or frozen product is wrapped in plastic wrap, cloth and applied to the cheek several times a day.
If the patient is in poor health or has chronic diseases, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
If you ignore the dentist’s requirements, complications may occur: infection and inflammation of the wound, bleeding, suture dehiscence.
Infectious diseases
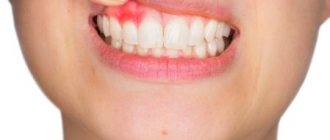
| Gingivitis and periodontitis Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum disease, often accompanied by the appearance of a red ball-shaped growth near the tooth. The next stage is periodontitis. With it, purulent discharge is observed, and the lump acquires a grayish or beige tint. |
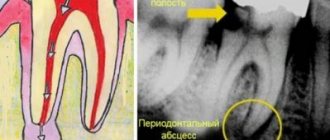
| Granuloma or cyst When pulpitis is advanced, the inflammatory process reaches the apex of the root, where a granuloma forms. Often this process goes unnoticed by the patient, so he is in no hurry to see a doctor. Over time, the pathology can develop into a fistula - a white formation on the gum. |
| Flux Purulent inflammation on the gums occurs against the background of advanced caries or pulpitis, a poorly treated root canal. At the first stage, minor pain appears; on the second - swelling and redness; on the third, the temperature may rise and the cheek may swell; on the fourth – the pain becomes sharp and throbbing, swelling increases. |
Preventive actions
Monitoring the condition of the teeth and oral cavity will reduce the likelihood of tumors.
- Timely sanitation of the oral cavity. Visiting the dentist for a preventive examination and professional hygiene twice a year will prevent the growth of caries, the appearance of defects in fillings and the formation of tartar, leading to gum injury and the appearance of epulis.
- Prevention of gum injury. If systematic injury to soft tissue occurs as a result of poorly fitted orthopedic or orthodontic structures, consult your doctor about this problem. He will adjust the crowns or dentures.
If these preventive measures are followed, the prognosis is favorable and epulis does not recur.
We hope that our article about epulis will be for informational purposes only. And if you want to soothe your gums, make them strong and strong, try the unique two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE.
This is the only rinse with a combination of chlorhexidine + benzydamine for the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases. The product has a combined effect: antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic. Instant anesthetic effect allows you to quickly reduce pain.
Non-communicable diseases
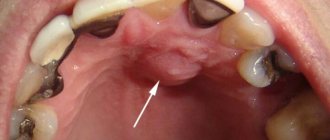
| Epulis This is a benign formation. It has a stem and a cap. Most often it occurs due to malocclusion, improper prosthetics, and hormonal changes. In the absence of adequate treatment, the tumor can develop into a malignant one. |
| Exostosis A bone growth that occurs against the background of a jaw abnormality - the bone extends beyond its usual boundaries, forming a lump. Most often, the reason lies in a genetic predisposition, less often - as a result of injury or complex tooth extraction. |
| Hematoma As a rule, it is formed as a result of an impact and goes away on its own over time. If there is damage to the tissue, then surgical intervention is necessary. |
If the causative tooth is permanent –
In this case, the tooth is not only possible, but also necessary to be saved.
If permanent teeth in children have already formed roots, then treatment of permanent teeth with periodontitis will be carried out as in adults. However, treating a permanent tooth with incomplete root formation will present some difficulty, because such teeth may have very wide root canals as well as gaping apical foramina (see photo below). And this poses a great difficulty for high-quality filling. Permanent tooth with incomplete root formation –
Currently, in pediatric therapeutic dentistry, there are 2 main approaches to the treatment of periodontitis in permanent teeth with incomplete root formation. The first method is based on temporary filling of root canals with materials based on calcium hydroxide or calcium oxide. This requires a long, months-long exposure of these materials in the root canals (with periodic replacement of the material with fresh portions). This will narrow the width of the apical foramen by creating an osteocement apical barrier, after which it will be possible to perform permanent filling of the root canals.
The duration of such treatment usually ranges from 0.5 to 1.5 years. If a water-based material with calcium hydroxide is used, then it needs to be changed in the root canals monthly, but if it is oil-based - only once every few months. The disadvantage of this method is the need for frequent repeat visits, and the effectiveness is only about 70-90%, because the emerging osteocement barrier has a loose porous structure and does not guarantee 100% reliable sealing of the root canal lumen.
The second method is a one-step technique for forming a barrier in the area of the apical foramen using materials from the MTA group (mineral trioxide aggregate). An example of such material is “Pro Root”. The method assumes that the apical part of the root canal for 3-4 mm will be permanently sealed with MTA. Thus, in this case, only 1 visit is required, but it is best to use this method only in the last stages of root formation (otherwise, it will be best to combine temporary filling with calcium hydroxide-based material for 1-2 months + subsequent permanent filling with MTA) .
Types of growth
New growths on the gums vary in shape, size, and method of formation.
- Angiomatous growth. A soft, bumpy, pink growth that grows very quickly. Often reappears after removal. This growth is diagnosed in children aged 10-12 years; as a rule, it does not occur in adults.
- A fibrous growth is a gum-colored lump. It grows slowly and does not cause pain, so patients are in no hurry to see a doctor.
- Giant cell growth. A rapidly growing neoplasm of red-blue color, from which serous fluid is secreted. The lump is easy to injure.
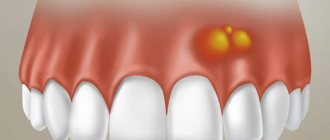
Ball in mouth - what is it?
When the inflammation begins to gradually progress, a blister appears on the gum. The main reason for the formation of a lump is poor oral hygiene and prevention. But the ball can also form under the influence of other factors: inflammation occurring in the roots of the teeth, gums, mucous membranes, and periosteum.
The problem is that the disease can be diagnosed in the later stages, with the development of a purulent process. This happens because the patient does not visit the dentist. For patients who experience fear while in a chair, the doctor can give sedative anesthesia, in which the receptors are turned off and the patient falls into a shallow sleep.
Attention! It is better to diagnose the disease early in order to prevent more dangerous consequences, including blood infection and inflammation of the entire jaw.
Gum cancer
This dangerous neoplasm is worth highlighting separately. Mutation cells begin to divide uncontrollably, which is why a red tumor forms on the gum. The disease progresses quickly and over time can develop into jaw cancer.
What are the symptoms?
- General weakness;
- increased body temperature (37 C°);
- loss of appetite;
- constant drowsiness.
The doctor makes an accurate diagnosis after a detailed examination. As a rule, treatment is long and painstaking. With timely medical intervention, the outcome is favorable.
Types of epulis
Depending on the nature of the pathological process, epulis on the gums is divided into three main types.
- Fibrous. The gum tumor differs in density. Its base is coarse fiber fabric. The tumor grows slowly and asymptomatically.
- Angiomatous. Epulis angiomatous consist of epithelial cells and a large number of blood vessels. The tumor is localized mainly in the molar area. Due to the many blood vessels, even with a slight impact on the tumor, bleeding occurs. On palpation, the lump is soft and painful.
- Giant cell. The tumor formation can be large. Giant cell epulis affects the position of teeth, displacing them. Pain is not typical for this species, but bleeding is possible due to mechanical damage.
The development of giant cell epulis on the gum poses the greatest risk, since the likelihood of the tumor becoming malignant is much higher than with other forms of the disease.
Growth on the gum: how to treat
The treatment plan is developed by the doctor based on the nature of the growth, so in no case should you self-medicate. It is important to understand that if you do not contact a specialist in a timely manner, serious complications can arise.
If the cause is an infection, then it must be removed. In case of periodontal inflammation, professional oral hygiene is performed. If the cause is periodontitis and complicated pulpitis, then first the lump is opened and pus is pumped out of it, and then conservative or surgical treatment is carried out.
If there is no pain, for example, with epulis or ecostosis, then the decision about surgical intervention is made together with the patient.
Clinical researches
Repeated clinical studies have proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
Classification
There are several types of epulis. Each of them has its own number in ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision).
Fibrous (K06.82 - benign neoplasms):
Location area: vestibular side of the gum;
- Round or oval shape;
- Slow growth;
- Surface smooth/lumpy surface;
- Doesn't bleed;
- Wide base;
- Thick consistency;
- Light pink (to match the gum color).
Angiomatous:
- Location area: neck of the tooth;
Giant cell (K06.81 - other specified changes in the gums):
- Location area: alveolar part;
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on examination by a specialist and histological examination. A differential diagnostic method is used to exclude the presence of hypertrophic gingivitis in the patient. It has similar symptoms to epulis. An x-ray is also used for diagnosis, where, with epulide, rarefaction and destruction of bone tissue due to inflammation are observed.
Cyst
Description
A hard, bone-like compaction of gums under a tooth, up to 1 cm in diameter. Occurs in people with weakened immunity, genetic predisposition, as well as due to acute infectious diseases, mechanical damage to the soft tissue of the oral cavity.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out in the same way as for fibroma - by excision. After surgery, mouth rinses and baths are necessary, as well as repeated visits to the doctor to monitor recovery.
Causes: why does a tumor form?
Epulis occurs under the influence of the following factors:
- Injury to the gums through: an overhanging filling;
- edges of a decayed tooth;
- tartar;
- burn;
- bruise;
- poor quality prosthesis.