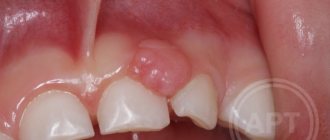
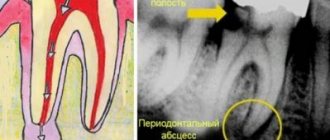
Visually, a fistula is a hole in the gum, directly connected to the source of inflammation located near the upper part of the root of any of the teeth. Typically, the fistula opening is located just above the diseased tooth, which is either filled or has a carious formation. Periodontitis is a disease characterized by the appearance of a fistula.
Development of a fistula on the gum
The process of fistula formation takes a fairly long period of time: for this to happen, inflammatory processes must occur in the tissues of the damaged tooth.
The stages that a tooth usually goes through before a fistula appears are as follows:
- caries is formed;
- the disease goes into a deep form;
- the development of caries leads to the formation of pulpitis;
- the last stage is periodontitis.
If you ignore periodontitis and do not take measures to treat it, the disease becomes chronic. At the moment of exacerbation, purulent masses come out through the fistulous tract formed in the gum.
Kinds
There is a large classification within which different types of fistulas are defined.
- Based on their origin, they are divided into congenital and acquired.
- Structure
– labiform, granulation and epithelialized. - By location - external and internal.
Fistulas help partially get rid of pus. Regardless of the cause and symptoms of the disease. However, it does not help cure the disease.
Main symptoms of fistula
Before the formation of a fistula, the tooth begins to hurt: when pressing on it and the surrounding area, painful sensations arise, it seems that the tooth is bursting from the inside.
Body temperature may rise and the gums may swell. When the pus comes out, the patient feels relief, thinking that the attack is over. However, this is a misconception: the disease continues to develop, although at this time the person feels much better. The tooth stops hurting, and pus no longer forms.
If no action is taken, the damage will affect the bone tissue, which will require more complex and lengthy treatment.
How a fistula is formed
The process of fistula formation looks like this. A small hole appears in the gum near the base of the tooth. Its color stands out a little against the background of healthy tissues - the color is rich pink or red. At the same time, the remaining teeth remain healthy and do not hurt.
At first, the fistula looks like a small swelling, then it grows and resembles a pimple or an abscess. The last stage - the seal opens, after which mucus or pus comes out of it. Then the wound becomes covered with a scar, but does not disappear. In the future, the development of the fistula can become chronic - it will open several times a year and exude pus. During exacerbations, mild pain will be felt.
How to treat a fistula on the gum: diagnosis of the disease
Any treatment is preceded by a diagnosis: the doctor needs to understand what to treat the patient for, as well as decide on the methods.
How to diagnose a fistula? First of all, the patient complains of pain. Often a person may find a small lump in the mouth from which fluid periodically leaks.
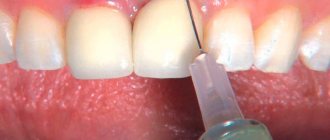
A more effective way to establish a fistula is a tomogram or x-ray. Gutta-percha is injected into the fistula tract under anesthesia. An image is taken to determine the location of the inflammatory process.
X-rays performed using modern equipment allow us to establish a complete picture of the disease, which makes it possible to use the necessary treatment methods.
Diagnostics
First of all, this is a visual inspection. An external fistula is visible to the naked eye. If the fistula in the jaw is hidden, an x-ray is taken. With the help of X-ray examination, the focus of inflammation and the depth of the pathological process of damage to the periosteum are accurately identified. It is important to distinguish a fistula from gum tissue, purulent tissue inflammation and other pathologies.
Self-medication of such a disease at home and self-diagnosis are unacceptable. Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor, which he prescribes based on the diagnostic results.
Fistula on the gum with untreated caries
A carious formation requires treatment as quickly as possible: if you delay contacting a doctor, the caries will develop into pulpitis, the infection from which, going beyond the boundaries of the tooth, will cause the formation of a purulent abscess.
When a fistula appears, there is no pain or swelling, since pus can easily come out through the hole. Pain and swelling occur just before the fistula appears. Basically, the tooth in the projection of the fistula will either be affected by caries, or it will have a crown or filling. Quite often, the patient experiences severe pain when biting on the tooth that caused the inflammation.
With inflammation, accompanied by the formation of pus, at the apex of the root, the infection accumulates in the root canals. To eliminate it, it will be necessary to remove the pulp and high-quality filling of the canals. It is extremely important that the dentist seals the canal along its entire length, without leaving a single free millimeter, otherwise the inflammatory process may develop again after some time.
Complications and prognosis
With timely treatment and following the dentist’s recommendations, there is a high chance of saving the tooth. In advanced cases, complications arise:
- osteomyelitis;
- phlegmon;
- granulomas;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- sepsis.
The fistula does not go away on its own. Surgical and drug treatment is mandatory. When you contact the VIMONTALE clinic, you can be sure that you will receive professional assistance. The center's doctors use only the latest technologies and materials in their work.
Expert of the article you are reading:
Lozinskaya Alla Nikolaevna
Pediatric dentist, general dentist.
You may also be interested in:
Treatment of dental canals Dental treatment during pregnancy Dental consultation Treatment of dental cysts Increased sensitivity of teeth: causes and methods of treatment Filling of dental canals Treatment of pulpitis Treatment of flux (periostitis)
Show more
The appearance of a fistula due to unsatisfactory canal filling
Canal filling is a fairly common dental procedure indicated in the treatment of diseases such as periodontitis, pulpitis and in preparing teeth for subsequent prosthetics. However, in more than half of the cases, the canals are not filled as well as required by the rules. The most common mistake is filling not to the very top of the root.
Due to a mistake made by the doctor, an infection will form in the unsealed area of the canal over time, which sooner or later will go beyond the boundaries of the tooth and lead to inflammation. In addition to filling the entire length of the canal, the substance used to fill the canal during the procedure must be packed tightly: the appearance of voids and the formation of pores is unacceptable.
The main symptom indicating problems with the tooth is pain when biting. If you look carefully, in the immediate vicinity of the diseased tooth you can easily find a small hole through which pus will come out.
The appearance of a fistula on the gum, the treatment of which is not recommended to be delayed, indicates that the tooth will not stop hurting on its own. To treat it, the tooth is unfilled, an anti-inflammatory medicine is placed in the canals, which is removed after a certain period of time, and the canals are then filled again.
If a tooth has a crown or a pin, unfilling the canals becomes a real problem for the doctor. It is not always possible to remove the pin, and the crown will have to be re-installed after the procedure is completed, which is fraught with additional financial costs for the patient. Sometimes, if the canal is not sealed at its very end, the doctor decides to resort to a procedure for resection of the upper part of the root.
Resection is far from the most difficult operation: its duration is no more than an hour. The operation consists of several main stages:
- Preparation, during which the canals are carefully sealed a couple of days before the main procedure.
- Anesthesia. The operation is performed under local anesthesia: the patient does not feel pain during the doctor’s manipulations, but discomfort may occur later when the effect of the injection wears off.
- Gaining free access to the upper region of the root. To do this, the dentist cuts the gum, exposing the bone tissue, in which a hole is then cut using a drill.
- Through the resulting hole, the doctor cuts off the tip of the root, to which, as a rule, the cyst is attached, which causes inflammation.
- After removing part of the root, an empty cavity remains in the bone. The doctor can fill the space with synthetic tissue, which speeds up the growth process of natural bone.
- The final stage is suturing the gums. For intensive outflow of ichor, drainage can be installed for several days.
Treatment of gum abscess
After the examination, the dentist will choose a treatment method for the abscess. It’s better to see a dentist quickly to avoid unnecessary pain and spending on medications.