Ear pain is a fairly common symptom. Painful sensations in this case give the patient a lot of unpleasant moments, and it is very difficult to simply “endure” such pain. It is noteworthy that pain in the ear is not always associated with diseases of the hearing organ. Such painful sensations can also be caused by other organs that radiate, that is, “giving off,” to the ear. A condition in which the ear hurts, but there is no inflammation in it, is called otalgia.
Otalgia can be caused by many reasons:
Temporal arteritis
The disease is an inflammation of the vessels of the temporal artery.
If the inflammatory process spreads to the ear artery, the patient will also experience pain in the ears. This disease is typical for older women. It causes blurred vision, headaches, pain in the temples, and increased fatigue. Make an appointment right now! Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
Along the branches of the vagus nerve, pain can radiate to the ear from the esophagus, thyroid gland, and organs of the cardiovascular system.
If you have ear pain, you should definitely consult with an otolaryngologist, since this condition may signal the presence of serious diseases in the body. If the ear is healthy, no abnormalities have been identified, and the pain does not go away, it is necessary to diagnose the nose, larynx, pharynx and, if necessary, other organs to identify the cause of otalgia. Further treatment will depend on the diagnosis.
Main causes of pain
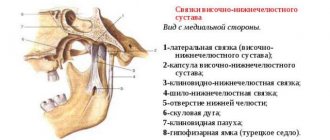
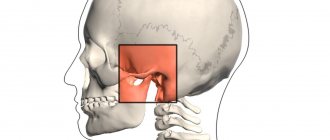
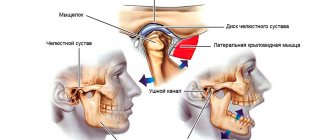
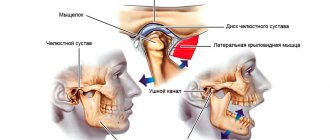
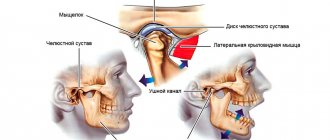
The human jaw is considered one of the most complex joints found in the human body. It represents the front part of the skull, consists of bones and nerve endings, and is involved in the process of chewing food, swallowing, and speaking. Therefore, when the jaw joint near the ear hurts, this can be a sign of a variety of pathologies.
There is a lymph node on both sides of the jaw; more precisely, they represent a paired symmetrical network, but it is in this area that the nodes responsible for the head and neck are located. If they increase in size and begin to hurt, you can suspect the development of an inflammatory process in the body.
Closer to the place where the upper and lower jaws meet, there is another organ - the ear. This organ is paired and is also penetrated by nerve endings and blood vessels. That is why, when the ear and jaw hurt on one side, this is not surprising.
The affected joint radiates pain into the auditory tube, and from there it is transmitted directly to the tissues of the jaw. In addition, pathologies of the teeth, trachea, internal organs, nasopharynx and larynx can cause discomfort. Being one of the most powerful and complex joints in the body, the jaw joint can become diseased due to degenerative changes in the osteochondral tissue (such changes are observed in osteoporosis).
Similar symptoms may be accompanied by inflammatory processes in the tissues of muscle fibers, which cause muscle spasms and pain when moving the head and jaw. There are many reasons why the jaw near the ear hurts, each of them requires its own treatment tactics.
Neuralgia and vascular diseases
Pain in the jaw joint, which is provoked by damage to the nerve plexuses, occurs for the following reasons:
Jaw displacement
- inflammation of the trigeminal nerve - accompanied by burning pain, mainly on the right side and radiating to the ear;
- damage to the superior laryngeal nerve - occurs with severe pain in the lower jaw;
- inflammation of the glossopharyngeal nerve - accompanied by a sharp pulsation throughout the lower part of the face, starting from the root of the tongue and ending with the jaw;
- pathology of the occipital nerve - this disease is characterized by the fact that the pain is deceptive, radiating to the jaw when chewing and to the back of the head, closer to the ear.
Pain in the ear area, accompanied by radiation to the neck and lower jaw, also occurs due to vascular disorders. This affects the carotid artery, neck and half of the face on the right or left side.
Damage to the facial artery occurs against the background of sharp pain in both jaw bones at once, it is localized in the areas of the wings of the nose, lips, ears
Arteries are responsible for a complete blood supply to brain tissue, for the supply of necessary microelements and nutrients there, so any vascular disease can provoke blood flow dysfunction. Pain in the jaw area, radiating into the tissues of the face and ears, but in some cases becomes a harbinger of an upcoming cerebral hemorrhage - a stroke.
Dental diseases and injuries
If it hurts a person to chew, the gum tissue is swollen, and discomfort radiates to the ears, the cause may be periodontal and molar diseases:
- carious process;
- inflammation of pulp tissue;
- periodontal abscess;
- wisdom tooth growth;
- atrophic and necrotic changes in the gums, which led to the development of a purulent process;
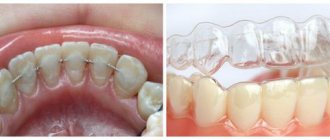
- adaptation period after installation of removable dentures, braces and other structures;
- poor-quality treatment, removal or prosthetics of teeth.
Sometimes simultaneous pain under the ear and when opening the mouth appears after mechanical trauma to the jaw joint, for example, after a blow, bruise, dislocation or fracture. Dislocation can be caused by opening the mouth too wide while yawning, laughing, coughing or vomiting.
If the lower jaw is dislocated on the left side, then pain will be transmitted to the entire left half of the face, and, conversely, if the joint on the right is affected, sharp discomfort will be felt on the opposite side.
The most common cause of dislocation is weakness of the ligamentous muscles of the jaw.
Muscle weakness occurs when there is a lack of calcium in the body and due to age-related changes in cartilage tissue. Osteomyelitis often occurs when the jaw joint is dislocated. After mechanical damage to the jaw, during purulent processes and the formation of phlegmon in the soft tissue, when the tissues of the face are strongly blown in the cold, pain often occurs, radiating to the ear.
Diseases of the ENT organs
What to do if your jaw hurts near your ear, and the discomfort is accompanied by an increase in temperature? First of all, you need to visit an otolaryngologist, since such symptoms are typical for sinusitis and sinusitis. In this case, pain occurs in the eye sockets, temples and forehead, photophobia, and discharge of mucopurulent contents from the nasal passages.
Also, in addition to dental diseases and sinusitis, ear pathologies can provoke intense pain in the jaw area. However, the symptoms here can be deceptive, for example, in a disease called erythrootalgia, or red ear syndrome, redness of the paired organs is caused not by an inflammatory process, but by a displacement of 3–4 cervical vertebrae.
Pain in the left corner of the jaw can be caused by angina pectoris or an impending heart attack, and in the right corner - by an infectious process in the throat or sinus cavity. In addition to the source of infection, such symptoms are characteristic of a tumor (osteogenic sarcoma) located inside the bone tissue.
In addition to other ENT diseases, pain in the ear and jaw can be caused by glossitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tongue), sialolithiasis (damage to the salivary glands), hypersensitivity of the tongue and neoplasms in the larynx
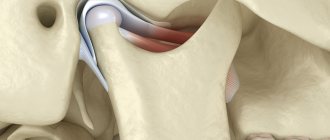
Joint pathologies
Pain in the temporomandibular region can also be caused by pathologies treated by an orthopedist - arthritis, arthrosis and osteoporosis. During a comprehensive diagnostic examination of the body, pathological changes in bone tissue will be recorded not only in the jaw, but also in the elbow and knee joints.
This fact will make it possible to differentiate pain in the jaw near the ear, caused by arthrosis and arthritis, from that caused by dental or neurological problems.
Arthritis is a pathology that develops when there are disturbances in the functioning of the immune system. Disease of the TMJ (temporomandibular joint) is usually of an inflammatory nature. But arthrosis occurs against the background of degenerative changes in osteochondral tissue.
These changes do not always occur due to age; sometimes the culprit is a serious pathological process of damage to the intervertebral discs and other joints. In this case, pain appears in the morning or during physical activity.
How to remove wax plugs for ear pain
Earwax is difficult to remove painlessly if you have a sore ear. But there are options.
To remove the cork, instill almond oil, onion juice, and a decoction of birch tar. They instill it overnight, and in the morning the sulfur flows out on its own.
To make it easier to remove wax plugs, use vegetable oil or a soda solution. You can wash the ear plug with furatsilin solution using a regular bulb or syringe.
To do this, fill a full syringe or bulb with a warm solution and forcefully inject it into the tilted ear. You just need to wait a little and the sulfur will flow out. Then close the ear with a cotton swab.
Diagnostics
The cause of pain in the cheekbone is determined by the maxillofacial surgeon. According to indications, the patient is referred to an otolaryngologist, neurologist, and other specialists. During the survey, the time and circumstances of the onset of the symptom, the dynamics of its development, and the presence of other manifestations indicating the nature and localization of the pathological process are established. During the dental examination, dental diseases are excluded.
When determining the etiology of neuropathic pain, an important role is played by the study of trigger points and special tests (for example, with dicaine and adrenaline for ganglionitis of the pterygopalatine ganglion). To clarify the diagnosis, the following procedures are prescribed:
- Radiography.
X-ray examination of the zygomatic bone, orbit or maxillary sinus is used for injuries, osteomyelitis, sinusitis, and pansinusitis. Allows you to establish the type and severity of the pathology, determine the need to prescribe additional techniques or treatment tactics. - Other imaging techniques
. They are used at the final stage of the examination when X-ray data are ambiguous. Provide detailed information about the location, characteristics and extent of the pathological focus. - Otolaryngological examination
. Indicated for ENT diseases. May include anterior rhinoscopy, diagnostic puncture and probing of the maxillary sinus. - Lab tests
. Inflammation is characterized by leukocytosis with a shift to the left and an increase in ESR. In purulent processes, based on the results of inoculating the material on nutrient media, the pathogen is determined and antibiotic sensitivity is established.
Dental treatment
Treatment
Conservative therapy
Analgesics are used to eliminate intense pain. The list of other therapeutic measures is determined depending on the characteristics of the pathological process:
- Traumatic injuries
. Patients with a fresh fracture of the zygomatic bone without displacement are prescribed a protective regimen, gentle nutrition, and physical therapy. If there is displacement, reposition is performed, then management is carried out in the same way as in the previous case. - Osteomyelitis
. The basis of treatment is antibiotic therapy, taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen. Antibiotics are administered intramuscularly, or intraosseously during surgery. They or nitrofurans are used to wash the surgical wound. - Neuralgia
. Patients with damage to the trigeminal nerve are prescribed anticonvulsants; antispasmodics, antihistamines, and medications to improve microcirculation are used as auxiliary agents. For ganglionitis, the nasal cavity is lubricated with dicaine, and ganglion blockers are sometimes used. Along with general remedies for neuropathic pain, therapeutic blockades are effective. - Dental diseases
. Taking into account the nature of the pathology, the tooth socket is washed or the tooth cavity is treated, followed by the application of anti-inflammatory and regenerating pastes. The list of general agents includes sulfonamides and antibiotics. - Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses
. Patients are recommended antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, detoxifying and antihistamine drugs, immunocorrectors. Punctures are performed and a YAMIK catheter is installed.
Possible complications
If an unpleasant symptom occurs, you should immediately contact your dentist. You should not postpone your visit, since the problem itself will not disappear, but may only get worse. Only a specialist can tell you what to do. In order to make an accurate diagnosis, a computed tomography scan is prescribed. If the doctor excludes the presence of dental problems, the patient will be referred to another specialist (neurologist, oncologist, phlebologist, etc.). Lack of help for muscle tension can lead to the following problems:
- the appearance of back pain;
- dizziness;
- sleep disorders;
- blurred vision, pain in the eyes;
- increased sensitivity to light;
- depressive state.
If the discomfort is accompanied by congestion in the ear, there is a risk of partially or completely losing hearing. When the jaw does not open completely, it shifts. It becomes painful to chew. After some time, problems with teeth arise, enamel wears off, and sensitivity increases.