Why do allergic edema occur? What are they?
This phenomenon is based on the body’s reaction to the allergen - an increase in the permeability of the vascular wall and the release of a large amount of fluid into the surrounding tissues. The speed of this process is directly related to the amount of allergen and the duration of contact with it, as well as to the sensitization of the body, that is, its sensitivity to the allergen.
Allergic edema can be acute or chronic.
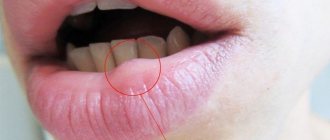
Acute edema is often manifested by Quincke's edema - a massive increase in volume of the face and neck, which threatens obstruction of the upper respiratory tract and may well cause respiratory arrest. Therefore, Quincke's edema is classified as an emergency. And in order to relieve such severe swelling, the allergy sufferer must be hospitalized as quickly as possible, and in the hospital, against the background of complex treatment, the swelling will subside. Sometimes acute swelling does not occupy the entire face, but some part of it. For example, in response to pollen, the nose becomes very swollen. Or your lips may react to a new lipstick, so much so that no hyaluronic acid is needed. Sometimes the upper and lower eyelids swell when an allergen gets into the eyes.
The second type of allergic edema is chronic edema. They appear gradually, over several hours, often in spring and at the beginning of the summer, during flowering. They are less dangerous, but no less noticeable.
Why do lips swell?
Mechanical reasons
Various mechanical impacts are one of the most common causes of lip swelling.
The symptom appears as a result of a fall or an accidental or intentional blow to the face. It is characterized by an asymmetry of location, the presence of hematomas and abrasions. Minor injuries with minor local swelling of one lip are the result of damage from a toothpick or dental floss. In some people, swelling occurs as a result of constant self-harm - the habit of biting the lip. Lip burns are usually superficial; in addition to swelling, hyperemia, pain, and sometimes peeling and crust formation are observed. Thermal burns are detected after ingestion of too hot liquids and food, or contact of lips with heated dishes. After prolonged exposure to the sun, sunburn is possible. Chemical burns are often severe and are caused by accidental or intentional use of aggressive substances.
In the summer, the lip may swell due to an insect bite. In women, the symptom often occurs as a result of cosmetic procedures: piercing, tattooing, contouring. Significant swelling of the lips is observed in the first days after plastic surgery: lipofilling, VY plastic surgery, lip shape correction.
Allergic reactions
Allergic cheilitis is most often observed when using lipstick. Other possible cosmetic allergens are contour pencils, lip creams, and toothpastes. Sometimes lip swelling is caused by dentures. Among food products, contact allergies are caused by citrus fruits, pineapples, and some berries.
Chemical industry workers and musicians who use mouthpieces when playing wind instruments may develop occupational allergic reactions. Swelling of the lips may be due to an allergy to an insect bite, which is different from the usual reaction caused by irritants entering the tissue.
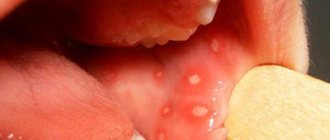
Allergic cheilitis is manifested by burning, itching, swelling, redness of the lips against the background of limited erythema at the site of contact with the allergen. Nearby tissues usually remain intact; in some cases, swelling is observed to spread to the oral mucosa and surrounding skin. A more severe form of allergy is considered to be Quincke's edema, in which swelling diffusely spreads to the face, lips, oral mucosa, tongue, pharynx, and larynx.
Atopic cheilitis, which is one of the signs of neurodermatitis, is characterized by a chronic course with seasonal exacerbations. Allergens include medications, pollen, household dust, food products, etc. The first manifestations are swelling and hyperemia, always limited to a red border. Then erythema, peeling, grooves and cracks appear.
Swelling of the lips
Other types of cheilitis
Inflammation of the red border of the lips is accompanied by swelling, redness, peeling, pain and burning. Sometimes complicated by the formation of bleeding ulcers and purulent crusts. Can be caused by the following forms of cheilitis:
- Exfoliative.
Develops against the background of neurotic disorders, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. Initially, superficial scales appear on swollen lips. Over time, rough, dense crusts form. - Glandular.
Caused by the proliferation of minor salivary glands due to congenital structural features or dental diseases. Swelling and dryness are complemented over time by the formation of deep cracks. - Meteorological.
Associated with increased sensitivity to cold, wind, and ultraviolet radiation. Against the background of swelling, itching, burning, erosions and crusts appear. With a long course, the development of precancerous diseases and lip cancer is possible. - Hypovitaminosis.
It is observed in people with a deficiency of B vitamins, especially -. Slight swelling and hyperemia affect the lips, mucous membranes of the mouth and tongue.
Dental diseases
In dental pathologies, swelling spreads to the lips from adjacent soft tissues and is localized mainly along their inner surface.
- Oral candidiasis.
Hyperemia, swelling and a white cheesy coating are detected on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, lips, palate, and back of the tongue. With the development of candidal cheilitis, maceration, superficial peeling, and the formation of grayish films and crusts are observed. - Stomatitis.
More often the lower lip swells. With catarrhal stomatitis, the swelling is insignificant; with aphthous, ulcerative, ulcerative-necrotic stomatitis, the swelling is more pronounced if the ulcers are located close to the lips, and may be asymmetrical. - Periostitis.
The swelling is one-sided, spreading to the lips from the cheek, accompanied by intense pain and limited jaw movements. - Salivary stone disease.
Swelling of the lower lip occurs when the salivary gland is blocked by a large stone and is a consequence of reactive inflammation.
Viral and bacterial infections
A common cause of asymmetrical limited swelling of the lip is the herpes virus. First, the patient feels a burning sensation, itching, and local swelling. Then a group of bubbles forms in the affected area, which after a few days subside to form a self-falling crust. The pathology is prone to a recurrent course; exacerbations are caused by acute infections, hypothermia, overheating, and decreased immunity.
Erysipelas occurs when infected with beta-hemolytic streptococcus, and is more often detected in patients suffering from caries, diseases of the oral cavity, and diseases of the ENT organs. Swelling is one of the first symptoms of erysipelas; it occurs on the lip, nearby mucous membranes or skin. Accompanied by severe symptoms of intoxication. Then erythema and regional lymphadenitis appear. Subsequent relapses are possible.
Tumors
Swelling is not typical for lip papillomas; it appears when the formations are traumatized. With keratoacanthoma, local swelling may be found around the central funnel filled with horny masses. Manganotti cheilitis at the initial stage is manifested by local edema, hyperemia of the lip, in the area of which an irregularly shaped erosion forms. Subsequently, swelling is absent or slightly expressed. In case of lip cancer, swelling is more often found in patients with an ulcerative form of the disease, when the tumor disintegrates.
Rare pathologies
Rare causes of the symptom include Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome, accompanied by recurrent swelling of the lips. During an exacerbation, the lips enlarge 2-3 times, become dense, bluish-elastic, and turn out, exposing the mucous membrane. Swelling of neighboring areas is possible: cheeks, eyelids, tongue. Other signs are facial neuritis and folded tongue.
Other reasons
Swelling of the lips and face can be observed in acute infectious diseases and other conditions accompanied by general hyperthermia. Another possible cause of swelling of diffuse swelling, including in the lip area, is somatic pathologies with fluid retention. Sometimes swelling is observed against the background of hypothermia or, conversely, exposure to high ambient temperatures.
What are the common treatments for allergic edema?
Edema, although located on the face or limbs, is a manifestation of a systemic disease - allergies. This means that you cannot do without medications that act systemically on the body (that is, tablets).
In case of massive acute edema, adrenaline, hormones, and antihistamines are administered intravenously to relieve them. Let's leave this work to emergency doctors.
Local acute as well as chronic edema require taking tableted antihistamines. Often this treatment is a course of treatment, covering the entire period of action of the allergen, for example, flowering. Or for the entire duration of the visit, a dusty room, for example, an old library or museum storeroom. I understand that among the readers there are those who do not like pills, but alas, without antihistamines it will not be possible to quickly relieve allergic edema.
Is it possible to quickly relieve allergic edema using topical agents?
Various external ointments containing hormones, mainly corticosteroids, are intended for this purpose. They are used as prescribed by a doctor, rubbing into the swollen area 2-3 times a day.
In addition, skin and nasal sprays and drops with a decongestant effect have recently appeared. To choose the right remedy and optimal dosage form, it is better to consult a doctor.
To quickly relieve allergic edema, there are many effective folk recipes. So, a mask made from fermented milk products (kefir, sour cream) helps to remove swelling from the face. It should be applied to the face for 15-20 minutes and then rinsed off with cool water. No less effective is applying an ice heating pad or directly massaging ice cubes made from freshly frozen black or green tea. Ice cubes are an excellent remedy for removing swelling from the lips. If your eyelids are swollen, an old cosmetologist - a cucumber - will come to the rescue. It is cut into rings, which are applied to the eyelids for 10-15 minutes.
Allergic reactions
Facial swelling is a manifestation of a local allergic reaction. This may be caused by:
- Insect bite.
- Food allergens.
- Plant pollen.
- Household chemicals.
- Decorative cosmetics.
As a rule, this causes a sore throat, sneezing, watery eyes, and photophobia. Allergies may be accompanied by nasal congestion, dry cough and other symptoms.
First of all, you should determine the source of irritation. If swelling begins to appear after a bee sting, you should carefully examine the wound and remove the sting.
Next, a cold compress is applied to the site of swelling. You need to keep it for at least 5 minutes. If necessary, after half an hour the manipulation can be repeated. At the same time, be sure to take any antiallergic drug that is at hand - Loratadine, Suprastin, Alerzin. For moderate allergic reactions, one tablet is enough for the swelling to go away in 20-40 minutes.
How to avoid the reappearance of allergic edema?
So that the surprise does not take you by surprise again, you need to consult with an allergist and try to figure out who was the source of the allergy. For this purpose, skin allergy tests, special blood tests, and provocative tests have been developed.
Knowing your allergen, you can realistically avoid contact in the future, or take preventive measures in a timely manner, starting to take antihistamines in advance if you cannot avoid unwanted contact.
Allergic edema is widespread, and its main problem is that many of us cannot figure out its allergic nature for a long time. They limit their fluid intake, refuse beer and tea, subscribe to “quick drying” channels on social networks, and buy expensive cosmetics. But everything is useless, the swelling persists, or even progresses. It is not surprising, because if the basis of edema is an allergic reaction, it is necessary first of all to act on the allergy systemically, taking antihistamines, and instead of using ordinary ointments, but hormonal ointments intended to relieve allergic edema.
If you still have questions, you can ask them to an allergist using the Doctis service.