Symptoms Classification of periodontitis Causes Possible complications How is it diagnosed?
Treatment Options Home Treatment Is Periodontitis Contagious? Recovery from severe periodontitis Differences from periodontal disease Prevention Periodontitis is an inflammatory periodontal disease that, without appropriate treatment, leads to destruction of the periodontal junction and tooth loss. It begins with inflammation of the gums, which occurs as chronic gingivitis. Subsequently, the pathological process affects deeper tissues, leading to the destruction of the periodontium, dental alveoli (socket), and the adjacent jawbone.
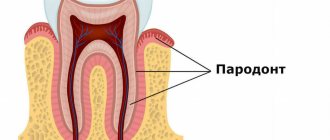
The tooth and periodontium are a single functionally and morphologically related system. The defeat of its individual elements disrupts the functionality of the dental unit, leads to disruption of the periodontal attachment, the formation of deep periodontal pockets, the formation of abscesses, fistulas on the gums, loosening, and tooth loss.
Symptoms
- Inflammation of the gums;
- hyperemia (redness) of the mucous membrane, swelling, reaction to temperature stimuli;
- sore gums;
- discomfort, bleeding gums when chewing, oral hygiene;
- detachment of the gum from the tooth wall;
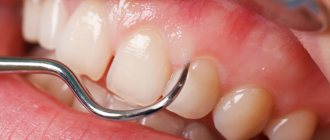
- formation of periodontal pockets;
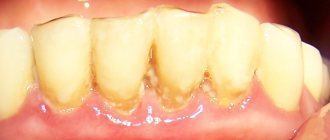
- abundant plaque and tartar around the tooth;
- pus from the gums;
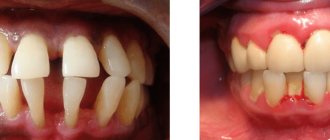
- loosening of the gum edge;
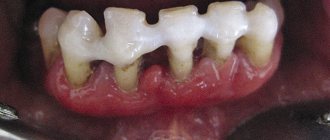
- exposure of tooth roots;
- tooth mobility;
- inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes
Symptoms of periodontitis vary depending on the extent of the inflammatory process. The more severe the stage of the disease, the more pronounced the symptoms. The disease does not occur suddenly; the early stage of periodontitis is catarrhal gingivitis - inflammation of the gums, not accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane.
What is gum periodontal disease?
It is possible to diagnose this disease independently only at a significant stage of development; initial periodontal disease does not show obvious signs. At the initial stage, the dentures of the teeth begin to become exposed and increased sensitivity is observed when eating hot and cold food. But for early diagnosis of the disease, X-ray studies should be carried out, and in the pictures you can see the size of the exposed tooth roots, on which the severity of the disease depends.
Due to the fact that obvious signs of periodontal disease do not appear immediately, its progression occurs unnoticed by the patient and leads to the destruction of bone tissue, and then to disruption of the functioning of the digestive system. In the most extreme stage, complete destruction, even tooth loss, is possible.
Classification
Periodontitis is classified according to location, nature of the course, and severity.
According to the nature of the flow
There are acute and chronic forms. In the first situation, the signs of periodontitis are pronounced, the gums are loose, bleed, and hurt. If the patient does not consult a doctor or ineffective treatment is prescribed, the disease takes a chronic course. In the chronic form, the symptoms are smoothed out, there are no acute signs of inflammation, but the consequences are more severe. Chronic pathology is characterized by periodic exacerbations, when the symptoms become pronounced.
By localization
According to the distribution of the pathological process, periodontitis is divided into:
- Localized
(focal) - occurs in a small area, in the area of 1 or several teeth. - Generalized
periodontitis is inflammation of all or most teeth in a row.
The symptoms of localized and generalized forms of the disease are no different, the only difference is in the number of teeth around which the pathological process has spread.
Degrees of periodontitis
- Mild
– fiber disintegration of the compact plate, reduction of the interalveolar septum to 1/3 of the length of the tooth root, signs of osteoporosis, slight tooth mobility, periodontal pockets of 2.5-3.5 mm. - Medium
– the depth of periodontal pockets increases to 5 mm, moderate tooth mobility is observed (grades I-II), bone atrophy around the teeth reaches 1/2 of the roots. Exposure of the necks and roots of the teeth or inflammatory growth of the gums occurs, abscesses (abscesses in the gums) can form. The teeth begin to “diverge” under chewing pressure, and the gingival margin becomes deformed. This is especially noticeable in the area of the front incisors. The gums bleed when chewing or brushing teeth, the necks of the teeth are exposed, and react painfully to temperature stimuli. - Severe
– symptoms increase, exacerbations of chronic periodontitis in adults are accompanied by the formation of abscesses, severe swelling of the gums, and pain. The depth of periodontal pockets reaches 6 mm, right up to the root apex. The interdental spaces increase, there is strong tooth mobility (II-III degrees), bone resorption, up to complete resorption of the alveolar septum.
Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, the disease progresses differently. Aggressive forms of periodontitis are characterized by rapid, almost rapid destruction of periodontal tissue, loosening of teeth, and their painless loss. In another part of patients, the disease progresses slowly, with occasional exacerbations, and long remission.
The most severe form is necrotizing periodontitis.
, in which the gum tissue stops receiving nutrition, blood circulation in them stops, and necrosis of the periodontium, periodontal ligaments, and alveolar bone occurs. This form of the disease occurs in patients with severe immunodeficiency conditions (AIDS, DiGeorge syndrome, SCID, etc.).
Antibiotics and antiseptics
Pathogenic microorganisms are not the main cause of periodontal disease, but their vital activity indirectly contributes to its development - it is no coincidence that a significant proportion of patients suffering from this disease exhibit one or another degree of decreased immunity. Accumulating in enlarged periodontal pockets and interdental spaces, the bacterial mass can cause inflammation, which in normal cases is not characteristic of this disease. That is why, in case of periodontal disease, it is often recommended to use various agents that can destroy pathogenic microflora and reduce the risk of secondary infection.
In the most severe cases, antibiotics in the form of capsules or tablets are used for this purpose, such as doxycycline and metronidazole, trichopolum, lincomycin. Broad-spectrum antibiotics effectively suppress the activity of microflora and contribute to the rapid elimination of inflammatory and infectious manifestations that complicate the course of the disease. However, long-term use of antibiotics is undesirable due to side effects and suppressive effects on the natural microflora of the body. They can only be used as prescribed by a doctor.
For a more gentle disinfecting effect, it is recommended to use rinses, gels, sprays and other external products containing antiseptics. In particular, the antibacterial rinse ASEPTA, which contains benzydamine and chlorhexidine. The adhesive balm ASEPTA, which contains metronidazole and chlorhexidine, thanks to its sticky base, is retained on the gums for a long time and has a long-term healing effect. Extracts of sage, witch hazel, chamomile, as well as xylitol, which are part of the ASEPTA Fresh mouthwash, also have a mild antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect.
Causes of periodontitis
A decisive role in the development of the disease is played by pathogenic microorganisms in dental plaque, which contribute to gum inflammation. The accumulating bacterial plaque hardens. Tartar builds up and penetrates deep into the gums, causing the mucous membrane to begin to peel off from the tooth, creating a free space that is gradually filled with pathogenic bacteria. Gingivitis develops, which without proper treatment quickly transforms into acute periodontitis.
Factors that provoke the development of periodontitis also include:
- regular injury to the gums due to incorrectly installed dentures and orthodontic systems;
- incorrect occlusion;
- accumulation of food particles and plaque under prosthetic and orthodontic structures;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- decreased immunity;
- physical trauma to teeth (impact);
- bruxism.
The development of chronic periodontitis can be influenced by problems with the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine disorders, blood diseases, vitamin deficiency, metabolic disorders, insufficient chewing load (the predominance of soft foods in the diet), autoimmune pathologies, and allergies to certain medications.
Possible complications
If you ignore the symptoms of periodontal disease for too long and do not take measures to solve this problem, the disease can lead to very disastrous consequences. Pathology leads not only to aesthetic problems, but also to the complete impossibility of carrying out hygienic procedures, and nutritional problems (due to pain that occurs when mechanical action is applied to exposed roots).
An advanced form of the disease can even lead to tooth loss. Atrophic processes and destruction of the ligamentous apparatus deprive the teeth of natural support. As a result, they become very loose and fall out. To prevent such an outcome, it is important to promptly seek professional help from a specialist.
Diagnostics
- Taking anamnesis;
- dental examination with measurement of the depth of periodontal pockets (periodontogram);
- orthopantomogram (OPTG), CT;
- rheoparodontography (assess the tone of blood vessels);
- Schiller-Pisarev test;
- microbiological studies (PCR);
- blood tests (general, sugar).
Differential diagnosis of periodontitis is carried out with gingivitis, eosinophilic granuloma of the jaw, periodontal changes in Lefebvre-Papillon syndrome. What examination methods will be required depends on the form and severity of the disease.
Treatment and prevention of periodontal disease
Treatment of periodontal disease is a long process that requires the patient to strictly adhere to the recommendations and prescriptions of the doctor. Measures to get rid of periodontal disease can be different, it all depends on the stage and how far the damage to the gums and dental tissues has progressed.
The following methods are used in treatment:
- physiotherapy;
- surgical treatment (curettage of periodontal pockets);
- splinting (for loose teeth)
- anti-inflammatory treatment;
- preventive measures (aimed at preventing the development of periodontal disease and its more complex stages, and are also used to normalize the condition of dental tissue).
The main set of measures is aimed at restoring and improving gum blood flow, reducing pain, and inflammation of periodontal tissue. Correct and timely treatment restores the normal supply of tissues with oxygen and nutrients, and allows you to stimulate the formation of new cells.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment includes:
- ultrasonic treatment of the oral cavity;
- electrophoresis;
- KUF therapy.
Such treatment methods help improve the blood supply to the gum tissue and the general condition of the periodontium.
Treatment methods
Treatment includes a complex of local and general measures, prescribed individually, based on the results of the examination, according to the severity of the disease, the characteristics of its course, and general health. Effective comprehensive treatment of periodontitis is aimed at eliminating periodontal pockets, strengthening teeth and gums, and preventing the destruction of soft and hard tissues.
Hygienic cleaning
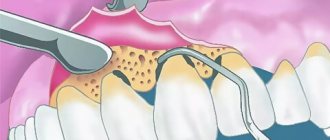
Regardless of the stage of the disease, the first stage of treatment is the removal of all dental plaque. For this purpose, special ultrasonic equipment is used, which allows you to carefully remove plaque and stone even in the most inaccessible places. After curettage (scraping) or ultrasonic cleaning performed using manual instruments, the gums are treated with an antiseptic, and medicinal dressings with an anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agent are applied.
Drug therapy
For mild cases of the disease, local medications for periodontitis are prescribed (gels, ointments, rinses) that have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and healing effects. In difficult cases, systemic antibiotic therapy, hormonal and antihistamine medications, and vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed. Conservative treatment is effective at an early stage of the disease.
Preparations for the treatment of gum periodontitis have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antiseptic effects. The therapeutic effect is provided by using the drug as rinsing solutions, applications to the gums, tablets for oral administration, injections into the gums (vitamins, FiBS, aloe preparations, etc.). Course of treatment – from 2 to 4 weeks
at intervals of several days.
Physiotherapy
For the speedy elimination of the infectious focus and active tissue regeneration, additional physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed - ultraphonophoresis, darsonvalization, ozone therapy, electrophoresis, gum massage, laser therapy. Localized periodontitis can be completely cured at an early stage without resorting to drastic measures. That’s why it’s so important to see a dentist at the first warning signs of illness.
Orthopedic treatment
During the treatment, orthopedic structures are corrected, parts of the fillings are removed from the interdental spaces, and crowns that have sunk deeply under the gum or are installed incorrectly are replaced. Splinting for periodontitis is indicated for degree II tooth mobility. Temporary splinting is carried out before curettage or immediately after it, permanent splinting is carried out a month after treatment.
Surgical methods
In severe cases of periodontitis, with deep periodontal pockets and defects of the gingival margin, in addition to conservative treatment, surgical treatment is required. Radical intervention involves cleaning the periodontal pockets with and without dissection of the gums, gingivectomy is an operation to remove inflamed, overgrown areas of the gums. The intervention involves reducing the volume of gum pockets and forming an aesthetic gingival margin. After the procedure, the natural process of tissue regeneration begins. When the alveolar septa are completely reabsorbed, excessively mobile, non-viable teeth are removed.
In case of significant destruction of the jawbone, when it cannot firmly hold the tooth in place, osteoplastic surgery is performed - directed bone regeneration. To do this, the area between the tooth and the bone is filled with a biocompatible osteoplastic material, which serves as a platform for the formation of new osteoblasts and restoration of bone volume.
Modern methods of treating periodontitis, such as laser and vector therapy, show impressive results. In just one procedure, gum pockets are reduced, swelling, pain, and bleeding disappear. Non-contact methods have a biostimulating effect and significantly accelerate tissue healing. Regardless of the severity of periodontitis, the correct occlusion is determined for all patients, and selective grinding of the teeth is carried out according to indications.
Medical Internet conferences
Relevance. In recent years, thanks to the development of biophysics and electronics, the arsenal of physiotherapeutic treatment methods used in maxillofacial surgery has significantly expanded. The use of physiotherapy in combination with other treatment methods can reduce the severity of clinical manifestations and reduce the incidence of disease complications [1,2].
Purpose: to study the effect of physiotherapeutic devices on the healing of postoperative wounds in the maxillofacial area.
Tasks:
1) study the action:
· portable device for magnetic therapy – “MAG-30”;
· laser devices – “Optodan”, “Matrix”, “Milta”;
· ultrasound therapy devices – “UZT-1.3.01F”, “Sonopuls”;
· microwave therapy device – “Aquaton”;
· ultra-high-frequency therapy devices – “UHF60”, UHF with a special attachment – eddy current electrode (EVT);
· bioptron therapy device – “Bioptron”.
2) compare physiotherapeutic devices by duration of procedures and course of treatment.
Materials and methods. The effectiveness of physiotherapeutic devices in the treatment of patients with postoperative wounds of the maxillofacial area was studied. An analysis of literature and scientific articles was also carried out.
Results and discussion . Physiotherapy (physics-nature; therapia-treatment) is a science that studies the effects of natural and artificial physical factors on the human body for therapeutic and preventive purposes.
Features of physiotherapeutic methods:
· universality of their action, the same factor can be used for various diseases;
· physical factors in therapeutic dosages, as a rule, are not toxic, do not cause side effects and allergization of the body;
· long aftereffect - can range from several weeks to 4-6 months;
· good compatibility with other therapeutic agents, it is possible to combine physiotherapy methods [3].
Magnetotherapy is a set of methods of using constant and alternating low-frequency magnetic fields for therapeutic purposes.
Under the influence of an alternating magnetic field, low-frequency eddy currents are induced in tissues due to the movement of charged particles.
An external magnetic field contributes to:
Improve blood circulation and metabolism;
· acceleration of reparative processes.
The alternating magnetic field has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effects. When treating periodontal diseases, swelling, hyperemia, bleeding of the gums, and the release of exudate from periodontal pockets are reduced [3,4].
Laser therapy is the use of low-intensity laser radiation for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes. Laser radiation is electromagnetic radiation in the optical range, which has no analogues in nature. The laser beam has very small lateral divergences, which allows it to concentrate large amounts of energy and transfer it over significant distances. Optical quantum generators and lasers use the amplification of electromagnetic light oscillations on the principle of stimulated emission, which makes it possible to obtain powerful electromagnetic oscillations with the same frequency, phase and polarization as external radiation. The emission of atoms of the active medium occurs simultaneously. The essence of laser exposure is the interaction of a powerful monochromatic laser beam with intracellular formations. As a result, the course of biochemical reactions of the structure of molecules changes [5, 6].
Low-intensity laser radiation causes the following effects: activation of metabolism and functional activity of cells; stimulation of reparative and regenerative processes; anti-inflammatory effect; activation of blood microcirculation and trophic provision of tissues; analgesic and desensitizing effect; immunostimulating and adaptive effects; reflexogenic effect on the functional activity of various organs and systems [5, 8, 9].
Ultrasound therapy is the use of mechanical vibrations of ultrasonic frequency for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes. The physiological effect of ultrasound is based on mechanical and thermal factors, which determine physicochemical changes in the body. Ultrasound energy is transferred from particle to particle during oscillatory movements, which contributes to deep impact. An ultrasonic wave at the interface between media and tissue can be reflected, which creates conditions for interference. In this case, areas of increased sound pressure are formed due to the large difference in acoustic resistance in the region of the boundary layers.
Under its influence occurs:
· low heating of tissues;
· dilation of blood vessels and acceleration of blood flow;
· acceleration of metabolism;
· increased phagocytosis, permeability of tissue membranes, absorption of oxygen from the blood by tissues;
· improvement of regeneration processes;
· change in the function of the endocrine glands;
· normalization of neuromuscular excitability and vascular tone;
· activation of enzyme activity.
Ultrasound has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic, absorbable desensitizing, and tonic effect. Using ultrasound, drugs can be injected into tissues. This method is called “ultraphonophoresis”. Aqueous oil solutions are used for it. Most often, ultraphonophoresis with iodine, calcium, phosphorus, analgin, hydrocortisone, and galascorbine is used. Ultrasound is used in the diagnosis of diseases, is used to remove dental plaque, and its use in filling root canals is being studied [3, 10, 11].
Microwave therapy (microwave therapy) is the use for therapeutic purposes of alternating electromagnetic oscillations above high frequency (2.38 GHz) in the centimeter (SMV-12.4 cm) and decimeter (UHF-65 cm) ranges. Absorbed by tissues, electromagnetic vibrations evenly spread throughout them, causing the formation of endogenous heat. DMV are a milder tissue irritant compared to SMV. Body tissues absorb microwaves differently. The skin and subcutaneous fatty tissue absorb microwaves poorly and therefore heat up slightly. Tissues and environments rich in water (blood, lymph, mucous membranes) are heated more intensely, which is associated with the orientational rotation of dipole water molecules. With microwave therapy, thermal and non-thermal (oscillatory) effects are noted.
Microwave therapy causes:
· acceleration of blood and lymph circulation;
· increasing the permeability of the vascular wall, metabolism and protective reactions of the body;
· decreased sensitivity of nerve endings, i.e. analgesic effect.
Microwave therapy has an anti-inflammatory effect. These manifestations are observed in the affected area and symmetrical areas. Irritation of nerve receptors causes the formation of positive reflex reactions and secondary humoral effects [3,12].
UHF therapy is the use of an alternating electric field of ultra-high frequency (40 MHz) for therapeutic purposes. Under the influence of an electric field in tissues, ions vibrate and charged particles are oriented along lines of force. This causes the transition of electrical energy into thermal energy. In tissues with high resistance (nerves, bones, tendons), heat generation is most intense. The oscillatory effect leads to changes in the natural rhythms of biophysical and chemical processes. At the same time, new conditions are created for the occurrence of physiological reactions.
Electric field UHF:
· causes vasodilation, especially in deep tissues, activates blood and lymph circulation (at the same time, tissue nutrition improves, they can better withstand various influences);
· increases the permeability of vascular walls, the formation of leukocytes, phagocytosis, which contributes to faster resorption of exudates and reduction of tissue swelling;
· causes activation of metabolism and enzymatic activity;
· activates cellular, tissue and protective mechanisms.
The physiological response is largely dependent on the intensity of the applied electric field. Thus, a low-intensity field has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, a medium-intensity field stimulates metabolic processes well, and a high-intensity field promotes increased inflammation due to the breakdown of large protein molecules with the formation of amino acids. Therefore, when prescribing the UHF electric field, it is necessary to take into account the severity and stage of the pathological process.
The UHF electric field has an anti-inflammatory and antispastic effect, stimulates the regeneration of damaged tissues [3,4,13].
Currently, for portable UHF therapy devices, an inductor with a tuned circuit or a resonant inductor EVT-1 (eddy current electrode) has been created, which is used in dentistry. In tissues, under the influence of induced eddy currents or induction (Foucault currents), heat is generated, and tissues rich in liquid (blood, lymph, mucous membranes, muscles) are heated to a greater extent. Tissue heating is uniform, heat penetrates to a depth of 6-8 cm , while the vessels dilate, blood and lymph circulation accelerates, deep hyperemia occurs, which helps improve tissue trophism and metabolism. Under the influence of UHF, the phagocytic activity of leukocytes is enhanced, the vital activity of microorganisms is inhibited, and immunobiological processes are activated [3].
Light therapy (phototherapy) is a set of methods for the therapeutic and preventive effects of the energy of electromagnetic oscillations in the optical range: infrared, visible, ultraviolet. Treatment with the visible spectrum of light (chromotherapy, bioptron therapy, sunbathing, etc.) is a method of therapeutic exposure to natural and artificial light sources with a light wavelength from 400 to 760 nm. Polychromatic polarized light-bioptron therapy is used for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes. The Bioptron device is a source of rays with a wavelength of 400-2000 nm, i.e. generates visible and short-wave infrared radiation. Linearly polarized polychrome light penetrates to a depth of 2-3 cm. Biological effects are determined both by the direct influence of polarized polychrome light on photosensitive tissue structures (skin) and by reflexively formed reactions. In this case, immunostimulating, anti-inflammatory, trophic, decongestant and analgesic effects are observed [3,10,12].
Conclusions:
1) As a result of the study, we studied the effect of various physiotherapeutic devices used in maxillofacial surgery. Based on this, one can judge the effectiveness of therapeutic measures, including magnetic therapy, laser and ultrasound therapy, microwave and UHF therapy, as well as bioptron therapy. Carrying out all of the above procedures can significantly reduce the number of complications (pain, severe swelling, neuropathy, hematomas, suture dehiscence, inflammatory complications) in the early postoperative period, and reduce the likelihood of late complications compared to traditional treatment methods by 1.5 times.
2) as a result of the comparative characteristics of physiotherapeutic devices, it was found that the most optimal choice for the treatment of postoperative wounds is the Optodan laser device, because The duration of the procedure takes only 2-5 minutes, and the course of treatment is 5-7 procedures.
Is it possible to treat at home?
Decoctions of medicinal herbs (tricolor violet, calendula, lingonberry leaf, calamus, oak bark) will help relieve symptoms of acute inflammation. But no amount of rinsing will get rid of supragingival, and especially subgingival dental plaque. Only professional hygienic cleaning at the dentist's office can handle this. Folk remedies in the form of formulations of hydrogen peroxide, soda and lemon will only aggravate the situation. But maintaining the condition of your gums after treatment at home is not only possible, but also necessary. The dentist will give you all the necessary recommendations on how to treat periodontitis at home.
How to restore teeth with severe periodontitis
In severe cases of the disease, the risk of losing a tooth or an entire row of teeth is very high. Tooth extraction for periodontitis is indicated in cases of excessive mobility, when the unit is barely held in the bone and moves in all directions around its axis. If it is impossible to save the tooth, orthopedic treatment is carried out - prosthetics supported by natural teeth or implants.
For single defects or restoration of a tooth segment, two-stage implantation with delayed loading is used. Implants are implanted after a course of gum treatment and restoration of bone volume. Bone parameters are restored through osteoplastic surgery. After new bone tissue is formed (after 6 months), implants are implanted, the prosthetic system is fixed after they have fused with the jaw bone ( after 3-6 months
). Treatment may take about a year.
In case of complete edentia, one-stage implantation methods with immediate loading demonstrate high efficiency. The ability to install implants in deep bone layers that are not subject to inflammation allows you to avoid osteoplasty and sinus lifting. Treatment will take no more than a week.
Injections into the gums for periodontal disease
In addition to drug treatment, injections for periodontal disease are also used. These are injections of aloe extract, which is an effective biogenic stimulant. Typically, the course of treatment consists of 20 - 25 injections with a break per day. What injections for periodontal disease are prescribed if the disease has become severe? In the presence of an inflammatory process in the later stages of the disease, dental periodontal disease can be treated with injections with synthetic tissue regeneration stimulators according to the same scheme.
Differences between periodontitis and periodontal disease
| Periodontal disease | Periodontitis | |
| Pathogenesis | Systemic dystrophic periodontal disease | Infectious and inflammatory periodontal disease |
| Character of the course | Develops slowly, asymptomatically | Develops quickly, often recurs, symptoms clearly manifest themselves in the acute period |
| Causes | Mainly systemic pathologies of the body, hereditary predisposition | Poor hygiene, excessive bacterial plaque, tartar, malocclusion, jaw injuries |
| Prevalence | A segment of teeth or the entire dentition is affected | Inflammation is localized in the area of one, several teeth or affects the entire jaw |
| Inflammation and bleeding gums | Absent | Main features |
| Tooth mobility | Occurs when gum recession extends more than 1/2 the length of the tooth root | It is observed in the acute period of the disease, against the background of looseness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums. Disappears after treatment |
| Forecast | Requires constant, maintenance therapy. In moderate and severe forms, the process only needs to be stabilized. The overall prognosis is poor (tooth loss) | With timely treatment, complete recovery |
Forecasting. Can periodontal disease be cured?
Yes, if you received qualified and emergency care at the initial stage of the disease. And no, if moderate or severe forms of periodontal disease are diagnosed. At these stages, it is only possible to stabilize destructive processes and slow down the progression of periodontal disease.
It is impossible to ignore such an important aspect as prevention. Dental and oral hygiene is very important. At the slightest sign of gum problems, you need to contact a specialist - early detection of the disease is the key to success. For prevention, you can do a hygienic massage of the gums, use herbal infusions and decoctions to rinse the mouth, eat solid vegetables and fruits (additional massage of the gums), and to strengthen bones (including jaw bones) eat foods containing calcium and vitamins.