From this article you will learn:
- why does the socket hurt after tooth extraction,
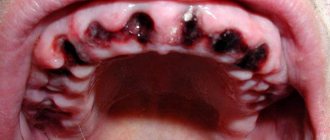
- what is alveolitis: photos and videos,
- How is alveolitis treated?
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
Alveolitis is a classic complication that occurs after tooth extraction and consists of the development of inflammation of the socket of the extracted tooth. Often alveolitis is also called “dry socket” (this is due to the fact that the alveolar bone in the depths of the socket is exposed due to the loss of a blood clot).
On average, alveolitis develops after tooth extraction in 3-5% of cases, but this applies to teeth of any location with the exception of wisdom teeth. When the latter are removed, alveolitis occurs in 25-30% of cases, which is associated with the greater complexity and traumatic nature of the removal process.
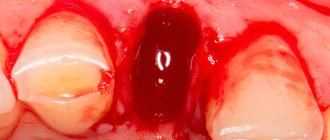
Dry socket after tooth extraction: photo
You can see what normal healing of a socket should look like (at different times from the moment of extraction) in the photo in the article: → “What a socket should look like after tooth extraction”
Reasons for appearance
In medicine, a hole in the gum is called a fistula. A fistula appears as a consequence of the activity of harmful microorganisms that are located in the area of the alveolar process. As a rule, the causative agents of pathology are coccus bacteria.
That is, the main reason for the formation of a fistula is a large amount of pathogenic microflora in the mouth. Lack of hygiene, the accumulation of soft plaque and the formation of tartar provoke the appearance of a fistula in the gums. Over time, tartar grows and begins to put pressure on the gums. In addition, soft dental deposits spoil the aesthetics of a smile; pigment spots may appear on the enamel.
Another reason for the appearance of a fistula near a tooth may be infectious inflammation. Diseases such as tonsillitis, ARVI, and whooping cough reduce immunity, creating all the conditions for the proliferation of bacteria.
Why you should entrust your treatment to the ENT Department of Dentistry
ENT dentistry combines two areas of medical services and treatment options - otolaryngology and dentistry . This is a modern format for the clinic’s work on comprehensive rehabilitation in the treatment of traumatic and inflammatory processes in the upper jaw, penetrating into the maxillary sinus or passing along its borders.
The Center for Private Dentistry “Doctor Levin” has been specializing in providing care to patients with combined ENT and dental pathology for many years. Medical and surgical treatment programs are carried out by candidates of medical sciences, maxillofacial surgeons with ENT training.
Statistics for the 20 years of work of the Center and for the last 10 years of work of the Department, unfortunately, are inexorable. The main providers of patients with complications are our colleagues who are caught in the dead end of an unsuccessful treatment plan. We are grateful to our colleagues who do not hesitate to send us patients with ENT complications, despite the reputational damage. It is always possible to avoid a dramatic outcome if you stop treatment in time.
Fistula in the soft periodontal tissues after tooth extraction
The formation of a hole after tooth extraction is normal. As a rule, the hole heals within one to two weeks. If the operation was performed on wisdom teeth, the tightening process may take several weeks. Impaired socket tightening can occur due to infection or in case of injury to the area where the tooth was removed.
In a situation where the hole has tightened and a gap has formed in the periodontium, it may indicate that the tooth was not completely removed. Small fragments of the tooth gradually begin to decompose, forming a fistula.
Forms of alveolitis
Depending on the course of the complication, three stages are distinguished:
- Serous.
It makes itself felt
2-3 days
after tooth extraction. At this stage, pain occurs when eating, headache. Lymph nodes increase in size. - Purulent.
This is the next form that occurs after the serous one, if timely treatment is not carried out. Diagnosed a week after the tooth was removed. The pain becomes unbearable and is also felt in the head or ear. The hole becomes covered with a purulent, dirty yellow coating. There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth. Swelling and lymph nodes enlarge and become painful. Opening your mouth and eating food is extremely difficult due to pain. - Hypertrophic.
At this stage, it seems that the symptoms are subside: the condition is normalized, the temperature decreases. However, atrophied tissue grows, and when pressure is applied, pus is released from the inflamed wound.
If you notice any of the above symptoms, you should not self-medicate, but rather consult a dentist.
Fistula between tooth and gum
A hole between a tooth and periodontal tissue indicates the development of cervical caries or the complications it caused. Cervical caries can be located between the teeth and not be visible to the naked eye. Due to its inaccessible location, such caries often turns into pulpitis.
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the blood vessels and nerve endings located in the pulp chamber of the tooth. The chronic stage of the pathology may be accompanied by the formation of a purulent focus in the soft tissues. If pulpitis progresses to the next stage of periodontitis, several fistulas may appear at once.
Complicating factors
The extraction procedure itself is ordinary and highly predictable, given the level of modern dentistry and the technological equipment of clinics. Nevertheless, even such manipulation has complications, especially if you take it lightly. It is worth taking into account that each clinical case is individual: if in one case tooth extraction is not very difficult, then in another the dental surgeon has to apply all his skills and use advanced technologies and equipment in treatment. It is no coincidence that the price lists of clinics include the item “Complicated tooth extraction”: you have to pay more for this service. Experts identify several factors that can lead to complications, including fragments in the socket.
- Wisdom teeth.
Because of their remoteness, default eights are quite difficult to remove. They often grow incorrectly or do not fully erupt, which increases the risk of complications during removal. - Retention.
A tooth that has not fully erupted, when only part of the crown is visible above the gum or is completely hidden in the soft tissues. - Dystopia.
The tooth erupts at the wrong degree and abuts its neighbors. - The tooth is severely damaged due to trauma.
In such a situation, when removed, it may crumble, and some of the fragments will remain in the hole.
The appearance of a hole in the periodontium in a child
The formation of a hole in the gum near a tooth in a child can be due to reasons such as: periodontitis caused by complicated caries, or injury to the oral mucosa. With periodontitis, the lesion reaches the jaw bone. A cavity appears inside the periosteum, which is filled with pus. When there is an excess of pus, it breaks out through the fistulous tract, thereby bringing severe pain.
Frequent mechanical damage to the mucous membrane and gums causes infection to enter the oral cavity. Bacteria entering the periodontium cause inflammation and fistula formation.
Types of pain
The nature and type of pain depends on the type and surgical intervention, the duration of the operation, and the complexity of the clinical process. Clinicians distinguish the following types:
- Aching. It is felt immediately after the anesthesia wears off. Keeps for about 2-4 days. The jaw may ache when opening the mouth or chewing.
- Intense, enduring. Occurs during extraction of a complex tooth with drainage or opening of a purulent cavity.
- Phantom. Occurs after traumatic surgery and may be felt from time to time. Phantom pain occurs with weak immunity and a low pain threshold.
It is difficult to say how intense the pain will be in each specific case, which is why it is so important to follow medical recommendations to prevent complications.
Symptoms
Signs of fistula formation include:
- aching pain that increases in the evening;
- burning and itching of gums;
- swelling in the affected area;
- gum hyperemia;
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness, chills;
- increased irritability;
- apathy.
The appearance of symptoms of pathology is individual for everyone. Some may experience very severe pain and discomfort in the mouth, while for others the symptoms may be almost invisible.
Stages of healing
The process of tissue restoration consists of the following stages:
- During the first 24 hours after surgery, a blood clot forms in the socket. The formation closes the wound and protects against infection and food debris. Subsequently, the clot takes part in healing, so specialists urge not to touch or rinse the wound for the first day;
- After 3-4 days, the wound becomes covered with a white film, which indicates the formation of epithelial cells. The wound may have a yellow or grayish tint due to food pigments. If the wound is green, dark, or there is a putrid taste in the mouth, then you should visit a doctor;
- After 7-10 days, the gums become covered with a white coating, under which young granulation tissue is formed;
- On days 18-25, the wound heals and heals;
- Next, bone formation occurs, which can last 4-6 months.
Treatment
If you find a fistula on the gum, you should immediately go to see a dentist. Based on the diagnosis and identification of the causes of the disease, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Treatment can be carried out in two ways:
- drug treatment;
- surgical treatment.
If the cause of the formation of a fistula is a carious process or pulpitis, then the following treatment is carried out:
- destroyed dentin is removed;
- The cavity is processed and a filling is applied.
Then, to eliminate inflammation and remove pus, the following is prescribed:
- rinsing with antiseptics;
- antiseptic and analgesic gels and ointments;
- Antibiotics may be prescribed if necessary.
If the cause of the hole is periodontitis or an infection that has penetrated into the root of the tooth, surgical intervention is performed.
In the first case, the fistula is opened, the accumulated pus is removed through drainage, and the cleaned hole is treated with antiseptics and covered with a medicinal bandage.
When an infection occurs, not only the gums are opened, but also the alveolar process. After treatment of the tooth root, bone augmentation is performed. If the root is severely damaged and cannot be treated, the tooth must be removed.
Is it possible to return to a normal lifestyle?
It is important to pay attention not only to hygienic care of the hole, but also to habits in general. These, as well as lifestyle, can significantly affect healing. Therefore, out of a sense of caution and self-preservation, it is better to temporarily refrain from certain habits. The following points are worth noting:
- It is highly advisable to refrain from smoking and drinking alcohol on the day of surgery (or better yet, several days after). Tobacco dries out the mucous membranes and can cause dry socket syndrome. And alcohol and pills are generally incompatible.
- Do not touch the hole with your tongue or create a vacuum in your mouth. The latter is relevant for those who are used to sucking their lips. These actions can break up the blood clot.
- It is better to refrain from physical education and physical labor for a couple of days, and it is advisable to sleep on a high pillow.
- Ideally, you should avoid high temperatures (steam rooms, baths) and hot compresses, which can cause bleeding.
- After removal, you cannot eat for several hours. Then for at least a week you need to make sure that the food is soft, liquid, not cold and not hot. It is better not only not to chew on the healing side, but also to prevent food from getting there at all.
- You need to brush your teeth very carefully, especially near the wound. In the evening after removal, it is better to abandon the procedure.
Prognosis and possible complications
If the fistula is detected and treated in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. If you follow all the specialist’s recommendations, within a week the resulting wound will completely heal and heal.
If proper treatment is not carried out, the following consequences are possible:
- abscess formation;
- phlegmon;
- osteomyelitis;
- tooth loss.
Preventive measures
- regular teeth cleaning;
- carrying out professional hygiene in the dental office;
- preventive examinations by a dentist every six months;
- daily consumption of fruits and vegetables.
How long does it take for a dry socket to heal?
Many people are interested in the question of how long it takes for a dry socket to heal. In the absence of complications, the wound heals in 5 - 7 days, and within a month the hole is filled with epithelial tissue. If you have dry socket, the healing process may take longer than two weeks (with proper treatment, of course). As already mentioned, extensive inflammation may occur and even require surgical hospitalization of the patient: in this case, the healing of the dry socket may be very delayed.
Medicines prescribed by specialists
When the patient has visited the dental center and had a professional treatment of the hole, he must start taking medications to cure the alveolitis. Drugs that have proven their effectiveness include:
- Hexicon. This is an antiseptic drug that is taken topically. You can use it to rinse, make mouth baths, and applications;
- Corsodil. An antiseptic medicine that has a bactericidal effect. It is also used to disinfect the mouth. Corsodil can be used to create applications, irrigation, rinsing;
- Stomatidin. An antiseptic that prevents infection from spreading. You can make applications with it, as well as rinse your mouth;
- Chlorhexidine. Antiseptic, which is known for its wide spectrum of action. It is used to treat the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and treat purulent wounds;
- Eludril. It has an antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect.
IMPORTANT! Professional dentists prescribe their own medication to each patient in accordance with the clinical picture and characteristics of the body, therefore it is not recommended to self-medicate so as not to aggravate the condition.