Every parent worries about the health of their child and closely monitors the condition of his skin, mucous membranes, nails and hair. Quite often, adults may notice a yellow coating on the child’s tongue. It should be noted that most often the pathological sign in children is associated with improper oral hygiene. In 90% of cases, a high-quality cleaning of the surface of the tongue will be enough to get rid of the problem.
However, one should not exclude the fact that a yellow coating on a child’s tongue can be caused by internal disorders. A sign that appears on an ongoing basis should not be ignored. The child needs to be shown to a specialist for a full examination.
What kind of coating on the tongue indicates health problems?
If there is a thickening of the plaque, a change in its color and the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the mouth , this is already the result of the activity of bacteria and fungi. Of course, the body is not a sterile substance and microorganisms are always present in it, but the immunity of a healthy child controls their numbers. When immunity decreases or any disease occurs, there is a significant increase in pathogenic bacteria and fungi, which is accompanied by the formation of plaque on the child’s tongue.
What symptoms should parents be wary of?
Regurgitation may be a sign of a disease, and in this case, you cannot do without the help of a doctor. The child must be shown to a pediatric neurologist if he:
- regurgitates profusely (“gushing”), the intensity of regurgitation is 3 or more points;
- when regurgitating, he becomes capricious and cries;
- after regurgitation, he demands to be fed again, as he remains hungry;
- does not gain enough weight, sleeps poorly;
- has symptoms of respiratory diseases, suffered from pneumonia (especially in the first 6 months of life).
The presence of serious pathologies may be indicated by:
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- decreased frequency of urination (less than 8-10 times during the day);
- profuse vomiting of the stomach with an admixture of bile;
- lack of stool.
Regurgitation may indicate some problems in the body if they do not stop in a one-year-old baby.
Causes of plaque on the tongue
There are many reasons why various plaques may appear on the tongue: from the banal consumption of foods that can change the color of the tongue, to serious health problems that require immediate medical attention.
Read also: Computer anesthesia STA – dentistry WITHOUT PAIN!
The very first thing you need to do when you discover strange coatings on a child’s tongue is to remember what the baby ate in the last 24 hours. Very often, sweet carbonated drinks, caramels or other sweets contain active dyes that can give the oral mucosa the most exotic shades: crimson, purple, green, orange and others. Even natural berries and fruits can radically change the color of the tongue. Therefore, there is no need to panic right away. You should ask the child to brush his teeth and tongue, and then evaluate their condition and color. If the plaque has not changed or has reappeared without connection with food intake, then this is a reason to urgently visit your pediatrician.
How is the intensity of regurgitation determined?
A special five-point scale is used for assessment, where:
- 1 point - up to 5 regurgitations per day in a volume of up to 3 ml;
- 2 points - more than 5 regurgitations per day in a volume of over 3 ml;
- 3 points - the baby burps more than 5 times during the day up to 1/2 the volume of milk or formula (up to half of the feedings);
- 4 points - each feeding is accompanied by regurgitation of a small amount of formula or milk for half an hour or more;
- 5 points - at least half of the feedings end with regurgitation of from 1/2 to the entire volume of milk or formula.
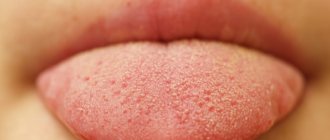
White coating on the tongue
White plaque can be found in the oral cavity of a baby most often.
This phenomenon also happens normally when, after a night’s sleep, a thin white coating without an unpleasant odor is found on the tongue, disappearing after hygiene procedures and not causing any discomfort or unpleasant sensations.
The appearance of a dense whitish plaque, which is extremely difficult to remove from the surface of the tongue and does not disappear after brushing your teeth, may indicate problems with the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, enteritis or dysbacteriosis). This phenomenon is often accompanied by bad breath. In addition, children may present complaints that may indicate gastrointestinal pathology:
- abdominal pain of various localizations;
- bloating;
- stool disorders;
- change in appetite
In order to get rid of such white plaque, it is necessary, first of all, to examine the digestive system and eliminate even the most minor disturbances in its functioning.
Read also: Drilling teeth? NO thanks, we use ICON!
In infants up to 2 months of life, thrush or oral candidiasis is a common occurrence in a nursing mother, especially after taking antibiotics or an error in diet. With this pathology, abundant cheesy white deposits appear on the tongue and cheeks, which are easily removed, and small ulcers are found underneath them. After starting treatment for thrush with antifungal agents and treating the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions, the tongue and other mucous membranes quickly cleanse and regain their previous appearance.
Treatment
Methods for eliminating yellow plaque depend on the cause of its occurrence .
If deposits appear after breastfeeding or formula feeding, you can remove the deposits using a small piece of sterile bandage soaked in a soda solution or plain water.
If the symptom was caused by various diseases, you will have to resort to drug treatment .
You should know! To eliminate plaque and treat the underlying disease, young patients are prescribed:
- hepatoprotectors that promote normal liver function;
- immunomodulators to restore the child’s immune system;
- anti-inflammatory drugs that eliminate pain, swelling and other symptomatic manifestations;
- antifungals for the treatment of oral candidiasis and thrush;
- enzyme preparations to restore intestinal microflora.
All medications should be used only as prescribed by a doctor..
Self-medication in this situation can lead to disastrous consequences.
Need to know! In order to prevent the reappearance of yellow plaque in the future or to prevent its formation, it is recommended to carry out simple but effective preventive measures:
- Regardless of the child’s age, establish proper nutrition . Do not give babies artificially colored foods or drinks.
- Promptly treat any infectious and non-infectious diseases.
- Regularly clean the child’s mouth from plaque and dirt using a special silicone fingertip.
- Nursing mothers should monitor their diet and follow a strict diet in the first months of the baby’s life.
- For newborns transferred to artificial feeding, select suitable formulas that do not cause allergies.
Gray coating on the tongue
A gray coating on the tongue can be a sign of some infectious diseases.
For example, with scarlet fever, on the very first day the mucous membranes become covered with a dirty gray coating, which, starting from the tip of the tongue, gradually disappears and reveals a “raspberry tongue” - enlarged papillae on a bright red background, which is very reminiscent of raspberries.
With diphtheria, gray filmy deposits can be found on the root of the tongue, which are difficult to separate. Such plaques spread to the mucous membranes of the throat, palatine arches and are accompanied by coughing and attacks of suffocation.
Treatment of such infectious diseases is carried out only in a hospital setting. After healing, all plaque on the tongue disappears.
Dehydration in a child can also lead to the formation of a gray coating on the surface of the tongue. At the same time, the mucous membranes look dry and dull. Replenishing the required volume of fluid quickly eliminates this symptom.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are widely used for rinsing the mouth and throat. In addition, they are required to normalize the digestive system. Among the most effective means are:
- anti-inflammatory infusion;
- antimicrobial agent;
- antiseptic decoction.
To prepare an anti-inflammatory infusion, you need to mix mint, oregano, St. John's wort, and lemon balm in equal proportions. Then you need to take 1 tbsp. l. vegetable raw materials, pour 500 ml of boiling water and leave to infuse for 2 hours. Then filter and consume 1 glass of the medicine 2 times a day a quarter of an hour before eating. This healing infusion has a good complex effect on the digestive organs, while eliminating the inflammatory process. The course of therapy is 10 days.
To prepare an antiseptic decoction, you need to take sage and chamomile in equal proportions. Then 2 tbsp. l. The resulting mixture needs to be poured with 400 ml of water and boiled for 15 minutes. Then leave the product to sit for 1 hour and filter. The medicine should be used to rinse the mouth and throat 4 times a day after eating food for 2-3 weeks. The decoction is good for inflammatory throat diseases.
To prepare an antimicrobial infusion you need 1 tbsp. l. oak bark pour 300 ml of boiling water. Leave to infuse for 2 hours, then filter and rinse the mouth 3 times a day, after consuming food for 2 weeks. You need to prepare a new rinse every day.
To eliminate pathogens present in the oral cavity during various inflammatory processes, propolis should be used. You need to chew it every time after eating food for 5-7 minutes.
If you have a yellow-orange coating on your tongue, flax seeds are a good remedy. A decoction of them helps normalize the functioning of the digestive system. It is recommended to take this remedy in the morning on an empty stomach.
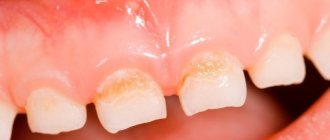
Yellow coating on the tongue
A dense yellow coating on the tongue indicates pathology of the liver or biliary tract.
Often in children, diseases of the biliary system occur without a clear clinical picture, and the presence of bile stagnation can only be suspected by a change in the color of deposits on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
If a child has a yellow coating on the tongue , it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor and have an examination of the internal organs and the biochemical composition of the blood.
Read also: Medication sleep - WHAT? For what? HOW?
Diagnostics
If a child has noticed a change in the color of the mucous membrane on the tongue, it is necessary to first exclude everyday incidents that led to this effect.
If a child has noticed a change in the color of the mucous membrane on the tongue, it is necessary to first exclude everyday incidents that led to such an effect.
It is impossible to eliminate dangerous situations on your own, so it is recommended to contact your local pediatrician.
After the examination, you may need to consult a dentist or gastroenterologist.
If severe somatic pathologies are detected, the child is referred to a specialized specialist (endocrinologist, hepatologist, nephrologist, hematologist).
To confirm or refute a preliminary diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a number of studies:
- blood, stool and urine tests;
- a detailed biochemical blood test (for the level of glucose, bilirubin, ALT, AST, creatinine, urea, etc.);
- Ultrasound of organs involved in the functioning of the digestive system, and, if necessary, the abdominal cavity;
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
Vegetables and fruits that are yellow can cause your tongue to turn yellow.
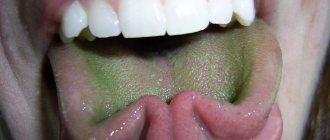
Green coating on the tongue
The appearance of a green coating on the mucous membrane of the tongue often frightens parents, especially if it is found in a newborn or infant.
The most common cause of this phenomenon is candidiasis - a fungal infection of the oral cavity that occurs due to imperfect immune defense in the body of a 1-year-old baby or while taking strong antibacterial drugs.
This plaque has varying color intensities and can spread to other parts of the oral cavity, found on the cheeks, palate and lips. After removing it, you can see the red surface of the tongue with small blisters or ulcers, which cause discomfort to the child.
You should start treating green plaque only after consulting a doctor. Therapeutic measures will consist of taking special drugs with antifungal action and local antiseptics to treat thrush and prevent bacterial complications.
Read also: How bite affects posture and spinal health
Main types of raid
Before you figure out why your tongue is orange, you need to know exactly what types of plaque there are.
Localization differs as follows:
- completely covers the tongue;
- localized at the edges;
- located at the root;
- concentrated in the center;
- accumulates at the tip;
- located under the tongue;
- has one-sided localization.
The type of plaque can be thick, dry, or greasy. Depending on the time of occurrence, such a disorder can be present constantly, it can only occur in the evening, in the morning, it occurs after coloring products or taking certain medications.
By the nature of the plaque, one can accurately judge the presence of certain diseases. In order not to trigger the development of a dangerous pathology, it is imperative to accurately assess the general condition of the surface of the tongue every morning before brushing your teeth.
Brown coating on the tongue
A brown tongue in a child is not such a rare occurrence. There can be many reasons for this:
- Severe diseases of the digestive system , accompanied by inflammatory changes, stagnation of bile in the bile ducts, and disruption of the digestive processes.
- Constant dehydration of the child's body due to high ambient temperatures or insufficient fluid intake.
- Insufficient intake of B
- Taking certain medications : antibiotics, antiseptic solutions, concentrated herbal decoctions.
It is very difficult to establish the exact root cause of the appearance of such a dark plaque. This can only be done by an experienced doctor, who, after additional examinations, will be able to prescribe the optimal treatment.
Dark
Dark spots on the tongue often occur when eating food that contains dark pigments that color the plaque on the surface of the mucous membranes. Such spots do not pose any danger to the child and disappear after hygiene procedures. But there are a number of conditions that manifest as dark spots in the mouth and which can have very serious consequences.
Black
Black spots on the tongue in children most often appear during a long course of antibiotic therapy as a result of the active proliferation of microorganisms and fungi. Blackening of the tongue develops gradually and can last up to 2-3 weeks. The main treatment for this condition is to restore normal microflora in the child’s intestines and oral cavity. For this purpose, eubiotic drugs are prescribed (for example, Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin).
It is extremely rare that black spots on the tongue appear as a result of deep degenerative processes accompanied by necrosis of areas of the mucous membrane. This condition is very dangerous and requires emergency medical attention. The treatment of such spots is often surgical.
Blue
Blue spots in a child's mouth are a rare occurrence. They may appear in the following situations:
- The presence of severe heart failure due to heart disease and defects. Spots on the tongue appear due to stagnation of blood in the venous bed and are accompanied by blue discoloration of the lips and limbs. Their treatment consists of eliminating cardiac pathology and normalizing blood microcirculation in the vessels.
- With the growth of a benign vascular tumor - hemangiomas. This blue spot is most often single. Treatment is only possible through surgery.
Black coating on the tongue
The presence of a black coating on a child’s tongue looks quite scary, and there may be several reasons for this phenomenon:
Bacterial sore throat is often accompanied by the appearance of dark plaques on the mucous membranes, even black. In this case, the child will have signs of inflammation in the tonsils: red throat, high fever, pain when swallowing, weakness.
Hidden forms of diabetes mellitus, which lead to persistent disruption of the acid-base balance in the body. Excess acid or acidosis will cause darkening of the tongue.
Taking some antibiotics causes the growth of pathogenic microflora in the mouth, which causes the mucous membranes to become permanently stained black.
Treatment of such plaque will consist of eliminating the causes that caused its appearance. After a sore throat is treated, medications are stopped, or diabetes is identified and compensated for, this symptom will most likely go away on its own.
How is plaque formed?
Epithelial cells on the surface of the tongue are constantly exposed to fairly aggressive factors: acidic foods, temperature changes, bacteria. That is why their lifespan is not long and after they are exfoliated, young cells appear. If the processes of changing cellular layers are excessively active, then the upper layers do not have time to peel off and remain on the surface of the mucosa in the form of plaque.
Another factor in the formation of plaque can be microorganisms. Children often do not pay enough attention to oral hygiene, as a result of which microscopic particles of food can remain between the lingual papillae, which become a place for active reproduction of bacteria. Taking antibacterial drugs often provokes the growth of pathogenic microflora in the mouth (fungi), some varieties of which are quite brightly colored.
Blue coating on the tongue
A blue tongue is a sign of blood stagnation.
Very often, various diseases of the cardiovascular (congenital heart defects, arrhythmias, heart failure) and nervous system (hemorrhages, cysts, epilepsy) lead to the fact that blood flows through the tissues more slowly than it should - cyanosis or cyanosis appears on the limbs, lips and language. Therefore, if you notice such a symptom in your child, you should urgently contact your doctor for advice.
Read also: Now the beauty and health of your child is completely in your hands
Bald
Normally, the lingual surface is covered with a large number of small taste buds, which give it a velvety appearance. If such papillae die or atrophy for any reason, “bald” spots appear. They are pink in color, irregular in shape and do not spread to the mucous membranes of the cheeks, lips or gums.
Reasons that can cause the appearance of such pink “bald” spots:
- Inflammatory diseases (glossitis, stomatitis).
- Tongue injuries.
- Burns from heat or chemicals.
“Bald” spots do not cause any inconvenience to children, but may slightly change the taste sensations. It is impossible to cure such formations, since the taste buds cannot be restored.
If you find that your one-year-old or older child’s tongue has become spotted, you should not panic and try to treat it yourself. Also, the appearance of spots on the tongue should not be ignored, as they may indicate the presence of serious diseases. It is necessary to consult a doctor who will find out the exact cause of such changes and, if necessary, select appropriate treatment for the child.
Prevention
In order to prevent the appearance of plaque on a child’s tongue, there are a number of preventive measures that many experts focus on:
- The room in which the child lives should always be clean, well ventilated and humidified.
- You should not prescribe antibiotics to your child yourself. The use of such medications must be strictly justified.
- It is necessary to closely monitor the baby's health. If the slightest symptoms appear that indicate a possible disease from the internal organs, you should urgently seek medical help.
- Limit your child's consumption of sweets containing synthetic coloring pigments: sweet carbonated drinks, candies, chewing gum. This will not only prevent the appearance of active staining of the tongue, but will also preserve the health of delicate children's teeth.
If plaque does appear on the tongue, there is no need to try to remove or treat it yourself. Consult your doctor about the possible causes of this phenomenon and the necessary treatment for it.
Posted in For parents by biglamed
When should you consult a doctor?
Important! Experts recommend not to delay visiting a pediatrician if you have one or more accompanying symptoms that cause discomfort to your baby and negatively affect his mood and general condition.
You should not put off going to the pediatrician in cases where :
- the plaque lasts for five days;
- it is not possible to remove deposits with a brush or bandage;
- the child refuses milk, is capricious and cries for no reason;
- formations appear on the gums and inside of the cheeks.