Bitterness in the mouth may indicate problems with the digestive system. Severe or persistent bitterness in the mouth is a reason to consult a doctor.
From time to time you may experience an unpleasant bitter taste in your mouth. As a rule, this is due to a sudden release of bile into the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, some bile may enter the esophagus and cause a bitter sensation in the mouth.
. Often a bitter taste in the mouth is felt in the morning, since bile can enter the stomach during sleep (especially if you sleep on your left side and dinner included fatty foods).
Bile is a secretion produced by the liver and is necessary for digesting food. The bile duct carries bile from the liver to the gallbladder, which acts as a storage reservoir. During the active digestive phase, bile from the gallbladder enters the duodenum. Some substances have choleretic properties, that is, they increase the production of bile. Eating foods with choleretic properties (for example, pine nuts) can provoke a sharp increase in the flow of bile into the intestines and, as a result, the appearance of bitterness in the mouth. Some medications have the same effect - both medical preparations and traditional medicine (St. John's wort, sea buckthorn oil, etc.).
However, bitterness in the mouth should not be ignored
. Its appearance indicates that not everything is in order with the digestive system. For example, a bitter taste may appear after eating fatty (heavy) foods. Fatty foods stimulate bile secretion. Normally, the secreted bile should not enter the stomach and esophagus, but should be released exactly as much as is necessary for the digestive process in the intestines. The appearance of bitterness indicates that this is not the case. And we need to figure out what caused this. If bitterness in the mouth occurs frequently or persists for a long time, then it is better not to delay a visit to the doctor.
Symptoms
Bitterness in the mouth can manifest itself in different ways, for example:
- after overeating and eating certain foods - indicates the reflux of bile into the esophagus and diseases of the bile ducts,
- aftertaste after taking medications means a disruption of the normal microflora, a negative effect on the liver and the destruction of beneficial bacteria,
- after sports training - speaks of liver pathologies.
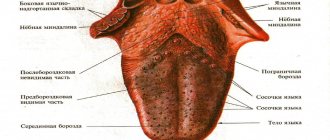
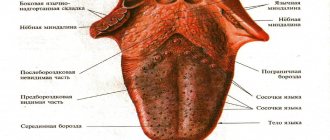
Bitterness can occur at different times of the day, after physical activity and during the abuse of bad habits. Often the symptom is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, dizziness, heaviness in the side and abdominal pain, white coating on the tongue and a feeling of bloating, heartburn and belching, dry mouth. At the appointment, you need to inform the doctor in detail about each sign.
Help before diagnosis
Even if a diagnosis has not yet been made, several measures can be taken to alleviate the condition:
- Adjust your diet, remove fatty and fried foods, eat more often and in small portions.
- Stop smoking or reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke.
- Limit alcohol consumption.
- Drink more water.
Monitor the quality of oral hygiene. You should brush your teeth twice a day, as well as use mouthwash and floss. If you have problems with your teeth, you need to visit a dentist.
Photo: goffkein/freepik.com
Important! You should not try to use folk remedies or treat yourself - this can be dangerous. If a bitter taste in your mouth appears regularly, you should consult a doctor and get recommendations for treatment.
Which doctor treats bitterness in the mouth?
First of all, bitterness in the mouth is considered as a symptom of gastroenterological disorders, so when the first signs appear, you need to make an appointment with a gastroenterologist.
To make an appointment with a doctor, choose any method:
- call the clinic +7 (495) 103-99-55,
- order a call back,
- leave a request for an appointment using a convenient form on the website:
Often people do not pay attention to bitterness in the mouth, explaining the occurrence of the symptom with overeating, an uncomfortable position in bed and some other reasons.
IMPORTANT! Rarely does anyone think that bitterness in the mouth is a signal indicating the development of serious pathology of the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
If you have been experiencing this symptom for a long time, do not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication - make an appointment with a specialist at the Kuntsevo Treatment and Rehabilitation Center! An experienced gastroenterologist will collect anamnesis, complaints, conduct an objective examination, and refer you for laboratory and instrumental diagnostics to understand the cause of the pathology.
SIGN UP
1.General information
Modern medicine knows a monstrous, incalculable number of clearly defined and described symptoms, i.e. objective signs of a particular disease. At the same time, with the accumulation of statistical data and research results, as well as with the development of the theoretical paradigm, the number of symptoms classified as pathognomonic (this term implies an unambiguous sign that is always observed in a given disease and is not found in any other diseases) is rapidly and steadily decreasing. The tendency to blur the informativeness of diagnostic signs is to some extent promoted by both pathomorphosis (changes in the typical clinical picture of diseases over the years and decades), and the tendency of modern man to self-medicate, which often “blurs” or distorts the symptoms.
There are almost universal symptoms that accompany most known diseases - for example, headache or “general malaise”, i.e. decrease in subjective well-being. Based on these complaints alone, it is impossible not only to make an accurate diagnosis, but even to suggest the field to which it will relate (neurology, endocrinology, virology, and many others). Other symptoms seem to more clearly indicate the most likely source of the problem, but upon closer examination it turns out that not everything is so simple here either. Such “understandable” but sometimes very misleading symptoms include, in particular, bitterness in the mouth.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Treatment methods
Basically, the treatment of bitterness in the mouth comes down to taking medications. The specialist selects complex therapy based on the results of tests and instrumental examinations. The gastroenterologist identifies one of three problems:
- Liver disorders. Means are prescribed to stabilize the operation of the “filter”,
- Digestive tract dysfunction. Drugs that affect the digestive system normalize the work
- Uncontrolled bile production. Eliminated by drugs that affect the level of secretion, for example, anticholinergics.
Diagnostic methods
Only a doctor can determine the cause of the symptoms described above. To make an accurate diagnosis and develop a therapeutic regimen, the doctor may prescribe the following procedures:
- examination of the skin and tongue, palpation of the abdomen;
- blood test for liver tests - ALT, AST, bilirubin;
- FGDS is a diagnostic procedure during which an endoscopist evaluates the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, identifies foci of inflammation, and takes tissue for histological examination;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs - liver, pancreas, gallbladder and spleen;
- blood test for hormones;
- coprogram and general clinical blood test.
Why do we need to treat bitterness in the mouth?
Since an unpleasant taste in the mouth is a symptom of some pathology, a comprehensive examination is needed, without which it is impossible to establish a diagnosis. Our clinic has the latest equipment for ultrasound diagnostics of the liver and gallbladder, gastroscopy, etc., which help identify the pathological process in a short time. Our own laboratory allows you to get test results within a few hours. It is the quick examination process that attracts many Moscow residents to our clinic, as well as experienced, qualified staff ready to help every patient.
2. Reasons
Even a non-specialist in the vast majority of cases associates a bitter taste in the mouth with a pathological state of the digestive system, more precisely, the liver and/or biliary tract. Indeed, the biochemical and physiological evolution of higher mammals has led to a strange paradox. As you know, bile produced by the liver is absolutely necessary for the digestion of food, be it the simplest food or exquisite delicacies. But at the same time, bile itself has a sharp unpleasant odor and an unbearably bitter taste, so normally it goes directly into the intestines (starting from the duodenum) and does not come into contact with the taste buds of the oral cavity. However, in a number of abnormal or clearly pathological conditions and processes, bile stagnates, is thrown into the stomach and esophagus, its taste is felt in the mouth - in a word, that same bitterness appears. In some cases, this may be associated with the consumption of too fatty foods or simply with banal overeating (the bitterness disappears as the body copes with the overload), in others it serves as one of the diagnostically significant signs of a serious gastroenterological disease. Thus, the most likely groups of causes of bitterness in the mouth are:
- diseases and any congestion in the biliary (bile) system, i.e. all kinds of dyskinesias, anomalies or pathologies of the bile ducts, cholelithiasis, pathology of the gallbladder, etc.;
- liver diseases: hepatitis, oncopathology, cirrhosis, etc.;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract with reflux syndrome (reflux into the esophagus): gastritis, gastroduodenitis, cancer of the pancreas and other gastrointestinal organs.
However, the above reasons, with all their diversity and, indeed, the greatest probability, do not exhaust the list of possible sources of bitterness in the mouth. You should also add to it:
- allergic reactions (in particular to dental materials);
- chemical intoxication, incl. taking certain groups of medications with hepatotropic side effects;
- inflammatory processes (especially with a purulent component) in the oral cavity;
- the presence of worms;
- endocrine disorders;
- infections;
- dysbacteriosis;
- hormonal changes associated with gestation (pregnancy) or menopause;
- deficiency or imbalance of a number of microelements necessary for the body (B vitamins, zinc, etc.);
- smoking (the more cigarettes smoked per day, the more stable and intense the bitter taste in the mouth and lips), as well as withdrawal symptoms when quitting smoking, which can be controlled with a special diet and vitamin therapy;
- alcohol consumption;
- abnormal mental states (depression, chronic stress, etc.).
Visit our Gastroenterology page
Foods that may cause a bitter taste in your mouth
A good place to start is to take stock of what you've recently eaten. Some foods cause a bitter aftertaste:
- Pine nuts;
- Fatty meats;
- Strong coffee or tea;
- St. John's wort decoction;
- Pasta;
- Sea buckthorn oil;
- Alcohol.
Typically, a bitter taste occurs immediately after eating or after several hours. Bitterness in the mouth can also be caused by taking certain medications - antibiotics, antiallergic drugs, blood pressure medications, and others.
What to do
- It is necessary to avoid “bitter” foods or not eat them before bed.
- Diversify the menu with fruits, especially citrus fruits.
- Add buckwheat porridge to the list of dishes.
- If the bitterness is caused by taking pills, it disappears a few days after the end of treatment.
Prevention
To avoid discomfort, it is recommended, first of all, to make adjustments to your own diet and diet. So, it is better to give up sweets, baked goods, fatty and fried foods, alcohol, as well as products containing large amounts of dyes, preservatives and other synthetic additives. The daily menu should be filled with fiber, cereals, lean fish, meat, vegetable broths - such a diet will restore the “affected” functions of the gastrointestinal tract as soon as possible.
Since a bitter taste in the mouth often “haunts” smokers and those who abuse alcohol, giving up bad habits is also on the list of mandatory preventive measures. The daily fluid intake (pure water, natural juices, fresh compotes, fruit drinks) should be 2–2.5 liters. This will ensure healthy functioning of the digestive tract and have a positive effect on metabolism in general.
To combat nausea and bitterness, patients are prescribed a diet, symptomatic drug treatment, and, if indicated, surgery.
Timely treatment of chronic and acute diseases (primarily infectious lesions of the oral cavity, upper respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract) will also prevent the occurrence of discomfort. Due to the fact that nausea and bitterness in the mouth can have not only physiological (overeating, pregnancy, intoxication), but also pathological causes (diseases of the liver and other digestive organs, dental problems), if discomfort persists for a long time, you should seek help from a doctor , be examined and undergo appropriate treatment.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To reduce discomfort during diagnostic procedures, it is necessary to reconsider the diet: switch to frequent small meals, eliminate fatty foods and alcohol. Careful oral hygiene with the help of toothpastes, dental floss, and irrigators is important. Doctors advise stopping smoking or reducing the number of cigarettes smoked per day as much as possible.
If you have a strong bitter taste, you should regularly rinse your mouth with boiled water and lemon juice; at work, you can eat a mint candy or a slice of lemon. The feeling of bitterness helps to reduce the rational drinking regime with consumption of at least 1.5 water per day. If the symptom is accompanied by severe abdominal pain, repeated vomiting or other dyspeptic disorders, you should immediately visit a doctor.
Conservative therapy
Therapeutic measures are selected taking into account the cause of bitterness in the mouth. An important component of therapy is a special diet that improves digestion processes, and physiotherapy techniques are also actively used. The main direction is drug etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy. Most often used:
- Choleretic agents
. Prescribed drugs that improve the colloidal properties of bile (choleretics) and stimulate its excretion through the bile ducts (cholekinetics). Medicines are recommended for cholecystitis and cholangitis to normalize digestive function. - Antispasmodics
. The products relax the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, relieve pain in the abdomen, which often occurs simultaneously with a bitter taste. Analgesics from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are indicated for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. - Enzymes
. Combined preparations of pancreatic enzymes and bile acids stimulate digestion, due to which the bitterness in the mouth disappears. For hepatitis and infectious liver lesions, they must be combined with hepatoprotectors. - Antihelminthic drugs.
Recommended for helminthiasis that affects the bile ducts and liver tissue - opisthorchiasis, echinococcosis. To eliminate giardiasis, specific antiparasitic medications are effective. - Antiviral agents
. When treating hepatitis caused by viruses B or C, separate protocols are used that involve the use of inhibitors of the assembly and formation of viral particles. Pegylated interferons are also prescribed.
Clinical symptoms
Impaired sense of taste is associated with a large number of diseases. Depending on the type of pathological process occurring, the patient may experience many associated symptoms:
- state of lethargy and weakness;
- a grayish or whitish coating forms on the tongue;
- pain and discomfort affect the area of the right hypochondrium or the iliac region;
- frequent belching with the smell of consumed food, air;
- feeling of stale breath, feeling of heaviness on the side;
- change in the standard color of the skin and whites of the eyes to yellowish shades;
- slowdown of metabolic processes with hair loss;
- constipation, diarrhea and other intestinal disorders.
If the source of the unpleasant taste is the formation of stones in the cavity of the gallbladder, then the clinical picture is complemented by painful sensations due to their movement.