What is this disease?
Herpetic stomatitis is a pathological process that develops in the mucous membrane lining the oral cavity. The causative agent of this disease is herpes simplex virus type 1. In children under the age of five, this virus is detected in 60% of all cases. By adolescence, it is detected in the vast majority of people. Herpes stomatitis in children develops during the baby’s first contact with the virus. This occurs most often before the age of three.
The high incidence is explained by:
- low level of production of own antibodies;
- immaturity of cellular immunity;
- the fact that the baby does not receive antibodies from mother's milk;
- high reactivity of the child's body.
If the baby is bottle-fed, he may get sick in the first months of life. Viral infection often goes into a latent state. It persists in the nerve ganglia.
"Epstein's Pearls"
In 65-85% of babies after birth, several yellow-white tubercles with a diameter of 1-3 mm are found along the palatine suture. They are called palatal cysts or “Epstein's pearls.”
They are formed from residual fragments of the epithelial lining, which is destroyed under the influence of enzymes during fetal development. Epstein Pearls are filled with keratin.
Palatal cysts do not require treatment and do not cause discomfort to the child. They atrophy on their own in the first months of life.
Causes
The cause of the development of the pathology is the herpes simplex virus type 1. It belongs to DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae viral family. The pathogen multiplies rapidly in the epithelial cells of the oral mucosa. Then it enters nearby lymph nodes (submandibular) and continues to reproduce in them. Then it enters the blood and migrates to the parenchymal organs (spleen, liver, kidneys). There it multiplies and enters the bloodstream again. As a result, it again appears in large quantities in the epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes. They are massively defeated. It is localized in the oropharynx, oral cavity, nose, lips, and nearby skin. Stomatitis and herpes of the skin and mucous membranes develop when the infection generalizes simultaneously.
Children become infected with it as follows:
- through contact and everyday life (using shared utensils, toys, through kissing);
- airborne (coughing, sneezing);
- from a sick mother to the fetus through the placenta or during childbirth.
A baby can become infected from sick adults, children, and carriers.
The following factors contribute to the development of the disease:
- previously suffered inflammatory processes;
- previous antibiotic therapy;
- deficiency of microelements and vitamins in the body;
- mechanical damage to the skin and mucous membranes;
- insufficient fluid intake;
- poor oral hygiene.
In children, the virus is especially easily transmitted through contact. The infectious process quickly spreads to healthy areas.
Classification
According to the flow, acute, chronic, and wave-like variants of the pathology are distinguished. The following degrees of severity of the pathological process are distinguished:
- Mild - it is typically characterized by a slight increase in body temperature, moderate inflammation of the mucous membrane in the mouth, and enlargement of regional lymph nodes. Rashes form on the mucous membrane and skin.
- Medium – high temperature rises. Severe weakness and sudden deterioration in health. The baby begins to vomit and the pain in the mouth increases. Significant rashes appear in the mouth and the skin around it.
- Severe - a severe headache is added to the pathological process. High temperature rises, severe muscle pain. Not only regional but also distant lymph nodes enlarge. The rashes are located not only in the oral cavity, but on the skin next to it. They appear on the mucous membrane of the eye, on the eyelids, and on other parts of the face.
The severity of the pathology depends on the viral load (the amount of virus in the body) and the general reactivity of the body.
Features of the oral cavity
The mucous membrane of a healthy child's mouth is bright pink due to the large number of blood vessels. As she grows older, her shade fades.
The epithelial layer is distinguished by tenderness and vulnerability, as well as some dryness due to the not very active work of the salivary glands (up to 3-4 months).
The baby's mouth is ideally suited for sucking. A wide tongue, a fold on the gums formed by the mucous membrane, pads on the inside of the lips, a “suction cup” on the upper lip - all this provides a tight grip on the bottle or nipple and facilitates the process of obtaining food.
What features or problems can be detected by looking into a baby’s mouth? Main options:
- white bumps on the palate;
- abnormal appearance or position of the tongue;
- white plaque on the inside of the mouth.
Clinical manifestations
Stomatitis in children is characterized by a gradual onset of the disease. Clinical signs of the disease do not appear immediately after infection. The incubation period is typical for this pathology; it lasts from two days to three weeks.
Symptoms of herpetic stomatitis in children appear starting from the prodromal period.
Each period has its own clinic:
- Latent – lasts up to two weeks. The child's sleep is disturbed and he refuses to eat. The baby becomes restless and whiny. He has increased salivation, possible nausea and vomiting. The lymph nodes are enlarged and painful on palpation.
- The height of the disease - at this time rashes appear on the skin and mucous membranes. They are located on the soft, hard palate, gums, cheeks, lips and tongue. They are group or single, up to three millimeters in size. They are thin-walled bubbles filled with a clear liquid. Their formation lasts up to four days. The vesicles quickly open, then erosions and painful aphthae form. They are shallow ulcers covered with a white coating. The mucous membrane in the mouth is swollen and bleeding. The child develops a high temperature of up to 40 degrees. A runny nose, cough, and conjunctivitis occur.
- Fading - aphthae, erosions gradually heal and epithelialize. These formations heal without scarring. Often there is a wavy course of the disease. The periods of appearance of rashes alternate with rises in temperature.
The illness usually lasts up to two weeks. In children under one year of age, generalization of the process is possible. The development of sepsis, damage to all internal organs and meninges is likely.
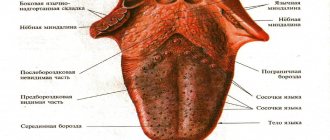
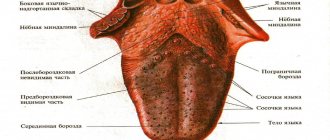
Language
Normally, the tongue is located along the midline of the jaw. If there is a constant deviation (recession) to the right or left, parents should show the child to a neurologist. This symptom may indicate damage to the caudal group of nerves of the skull. An additional sign is a drooping soft palate.
Another reason to seek help is that the language is too broad. This symptom is observed with hypothyroidism (decreased functional activity of the thyroid gland) and some genetic syndromes.
The listed phenomena are rare, unlike a short hyoid frenulum. This minimal anomaly in the structure of the maxillofacial apparatus can be determined visually; in addition, when screaming, the tip of the baby’s tongue rises. A short frenulum is not dangerous, but it can make sucking difficult and, in the future, complicate the pronunciation of sounds. In infancy, it is easily cut with a scalpel in an outpatient setting without suturing and virtually no blood.
Diagnostics
A patient suspected of having this disease is examined by a dentist. He asks the child’s parents about how the disease progressed. The diagnosis is established on the basis of the characteristic clinical picture of stomatitis, revealed during examination, anamnesis and characteristic complaints. Upon examination, typical mucosal lesions are revealed.
To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory testing of scrapings of the oral mucosa, the contents of ulcers, the patient’s saliva and blood is used.
The following are used for research:
- cytopolymerase chain reaction;
- immunofluorescence method;
- serological blood tests (RSC, ELISA, immunoglobulin M test);
- HSV test for the detection of immunodot G-specific glycoprotein.
These methods are used only for severe infections, as they are quite expensive.
Treatment
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis in children with mild and moderate forms is carried out on an outpatient basis. In severe cases and the development of complications, the baby is hospitalized. Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a pediatric dentist or periodontist.
Children are prescribed bed rest and a diet with pureed, non-irritating food. He is given separate hygiene items and dishes. Plenty of warm fluids are recommended.
The following drugs are prescribed:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nise, Paracetamol, Nurofen) are used to relieve temperature and inflammatory reactions.
- Antihistamines (Clemastine, Loratadine) are used to relieve swelling of the mucous membranes.
- Antiviral drugs (Famciclovir, Acyclovir, Zovirax) are used at the beginning of treatment or in severe cases.
- Immunomodulators (Lysozyme, Gamma globulin, Thymogen) are used to enhance immunity.
During treatment, vitamin-mineral complexes and fish oil are used in monthly courses.
Local drugs that act directly on the mucous membrane are widely used.
For local treatment of herpetic stomatitis the following are used:
- antiseptics (Hexoral, Miramistin) - they are used to rinse the mouth every four hours for two weeks;
- ointments and gels with anesthetics (Kamistad, Lidochlor gel) are used for pain relief, they are lubricated with mucous membranes three times a day for up to two weeks;
- antiviral agents (Ganciclovir, Acicovir) - destroy the viral cell, gums are treated with these ointments five times a day, two weeks;
- proteolytic enzymes (Trepsin, Chymotrypsin) are used to cleanse the necrotic surfaces of ulcers; they are washed with these solutions twice a day.
- rinsing with decoctions of medicinal herbs (calendula, chamomile, sage) is carried out after each meal for up to two weeks;
- epithelializing ointments (Solcoseryl, Methyluracil) are used to enhance the healing of erosions and ulcers, used in the recovery stage, used up to four times a day for ten days.
Physiotherapy is applied locally. Irradiation of affected mucous membranes with ultraviolet and infrared rays is used.
Therapy methods
Treatment of candidiasis begins with treatment of the oral cavity. The first procedure is performed by a specialist at the appointment. Antiseptic agents are used to remove plaque. The doctor may then apply an antifungal agent.
The parent should closely monitor the dentist’s actions, since in the future they will have to treat the oral cavity themselves at home. The necessary medications will be prescribed by a specialist. Local antifungal agents are dangerous in case of overdose, especially for children, so you must strictly follow your doctor’s recommendations.
In advanced cases, medications are prescribed in the form of solutions, drops or tablets. There are few drugs available to treat candidiasis in children. Replacing them with adult counterparts is also dangerous. The dosage must be strictly observed.
A mandatory addition to the main therapy is maintaining good hygiene, good sleep, proper nutrition and taking measures to strengthen the immune system (eating healthy foods, taking pharmaceutical vitamins if necessary, walking, etc.).
Prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at preventing infection. This presents certain difficulties, since the vast majority of the population is infected with it. It is better if the child gets sick from it at an older age.
For this it is recommended:
- avoid contact with infected people;
- will provide personal utensils and personal hygiene products for the child;
- Kissing people with herpetic rashes is prohibited;
- strengthening the baby's immune system.
It is recommended that the child be provided with adequate nutrition and regularly given vitamin and mineral complexes.